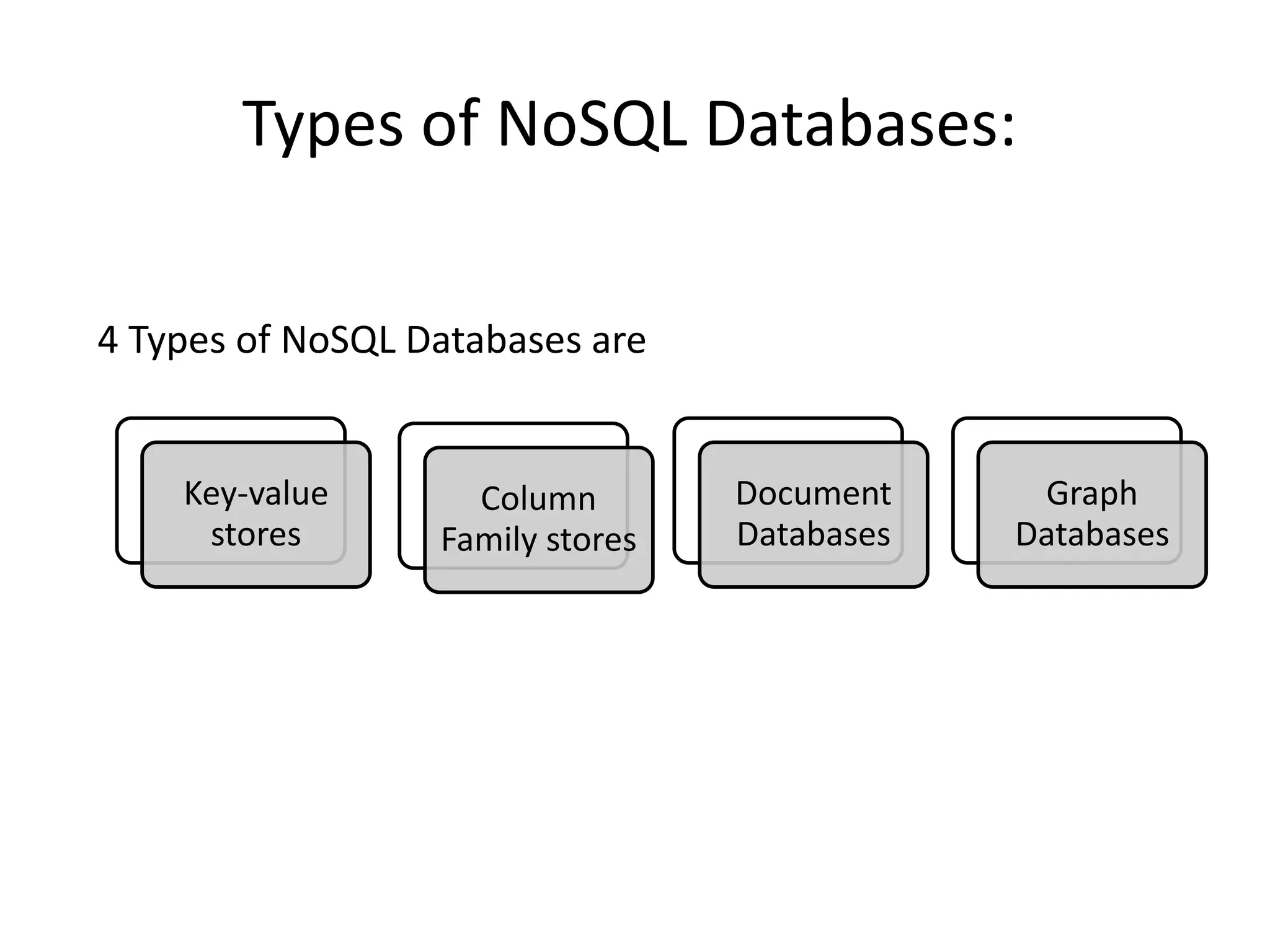
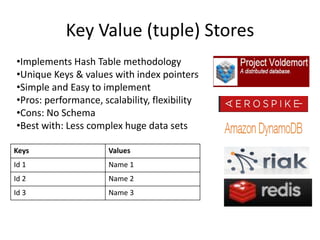
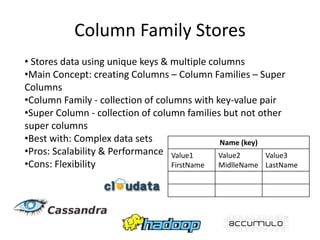
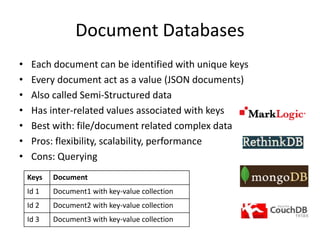
There are 4 main types of NoSQL databases: key-value stores, column family stores, document databases, and graph databases. Key-value stores store unique keys mapped to values, column family stores organize data into columns and column families, document databases store documents as values identified by unique keys, and graph databases represent data as nodes connected by edges to model relationships. Each type has different strengths for certain types of data based on structure, relationships, and querying needs.