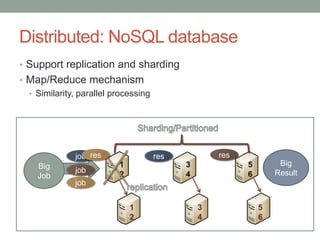
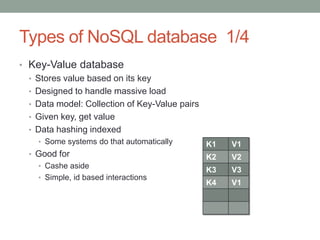
The document discusses limitations of relational databases for large, unstructured data and introduces NoSQL technology as an alternative. It describes four types of NoSQL databases - key-value, column-oriented, graph and document - and how they address issues like flexibility, distribution and scaling. Examples are given showing how NoSQL databases like Cassandra can process large amounts of data much faster than MySQL. The conclusion is that NoSQL databases are better suited than relational databases for big data and dynamic applications needing fast, distributed processing of unstructured information at low cost.





![Types of NoSQL database 4/4Document databaseStores data as documentMore complex Key-Value databaseData model: Collection of Key-Value, collections as JSON or XML types document{ “name” : “Lady Gaga”, “ssn” : “213445”, “hobbies” : [“Dressing up”, “Singing”], “albums” : [{“name” : “The fame” “release_year” : “2008”}, {“name” : “Born this away” “release_year” : “2011”}]}{ {….}}{ {….}}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/improvementofnosqltechnologyforrelationaldatabasesv2-110504100500-phpapp02/85/Improvement-of-no-sql-technology-for-relational-databases-v2-10-320.jpg)