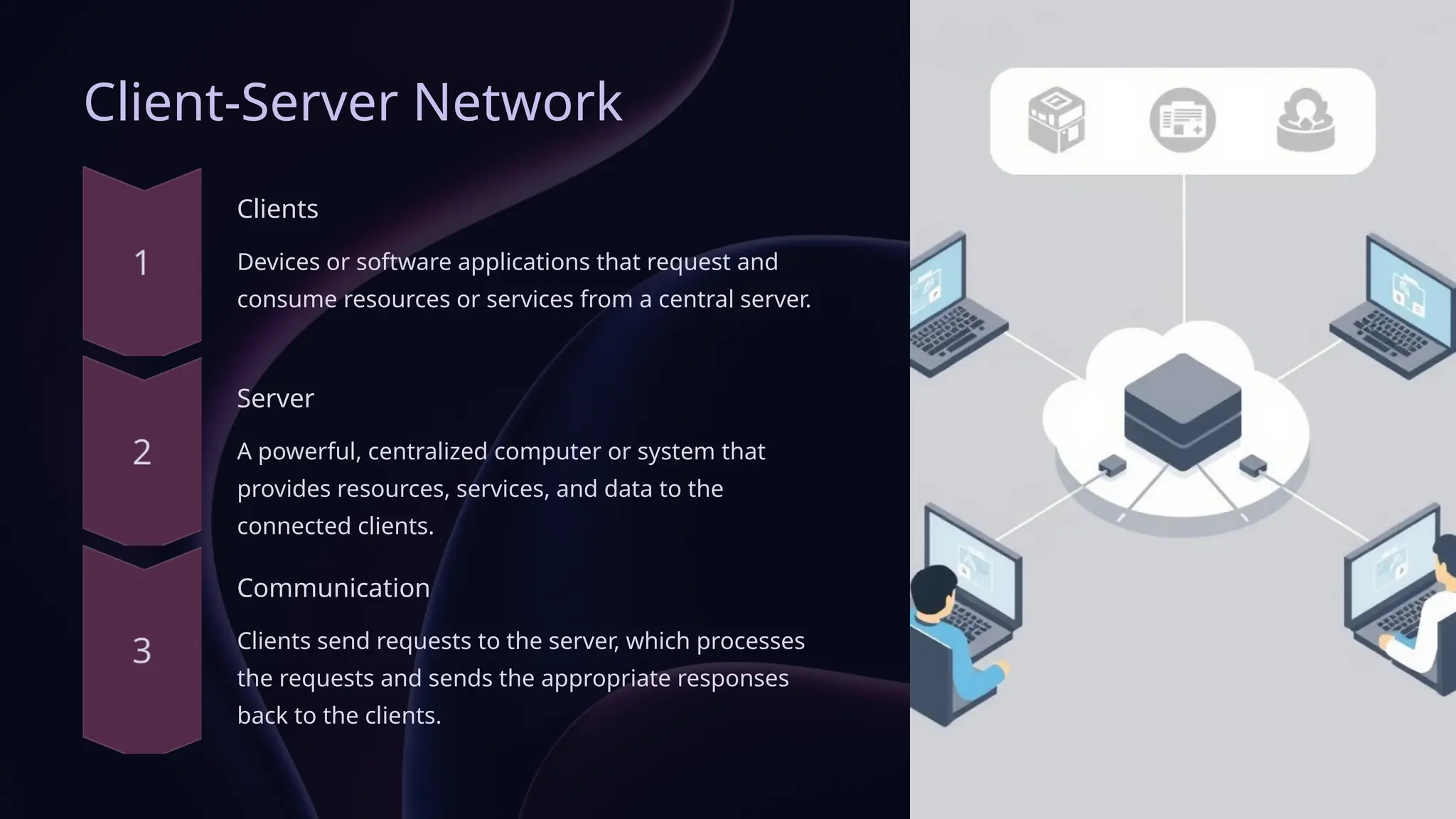
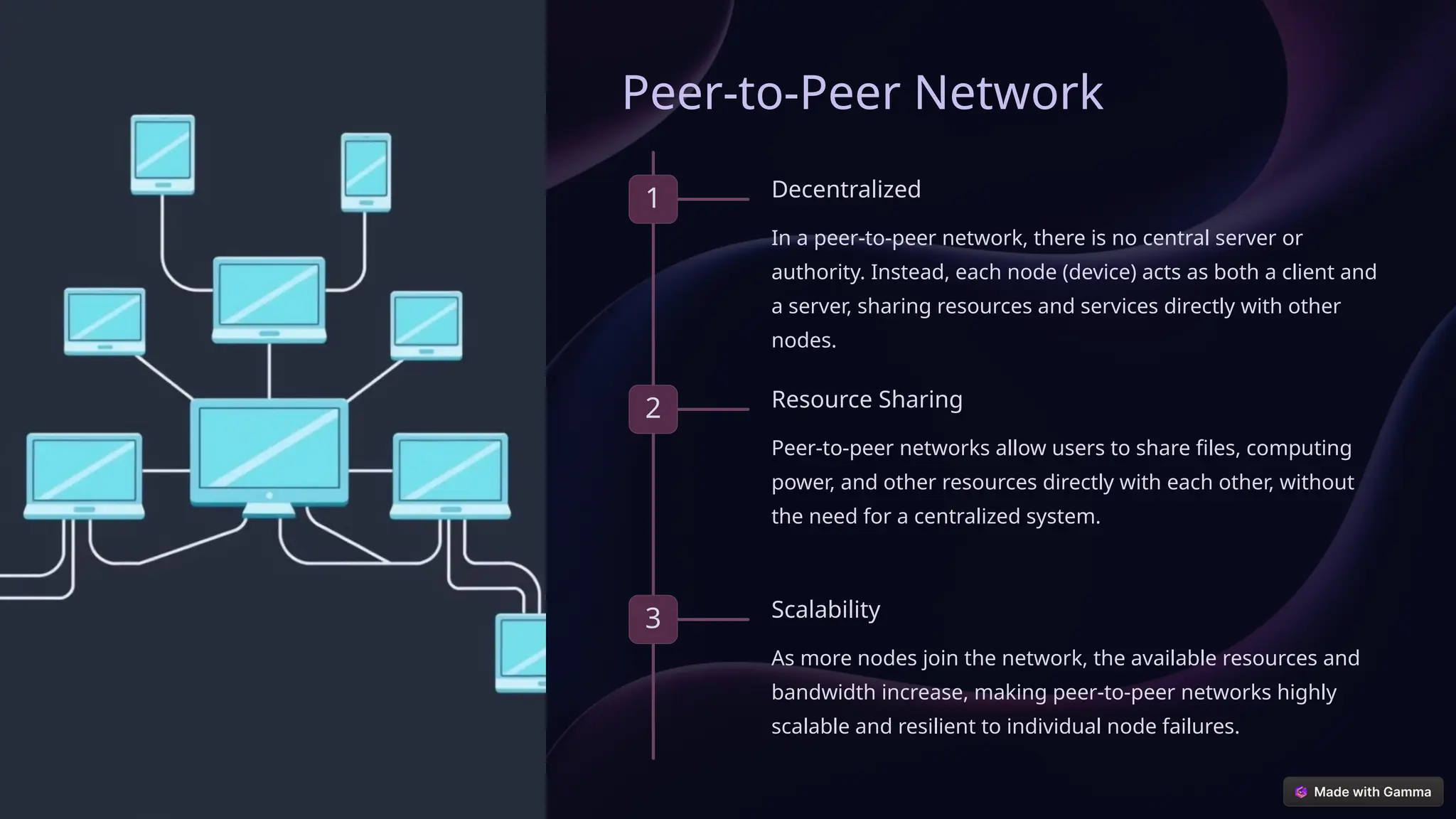
The document details various types of computer networks including Local Area Networks (LAN), Wide Area Networks (WAN), Metropolitan Area Networks (MAN), Personal Area Networks (PAN), Wireless LANs (WLAN), Virtual Private Networks (VPN), Client-Server, and Peer-to-Peer networks. Each type is designed for specific environments and needs, with distinct advantages and disadvantages related to speed, coverage, scalability, and security. Understanding these differences is essential for effective technology deployment and utilization in modern communication.