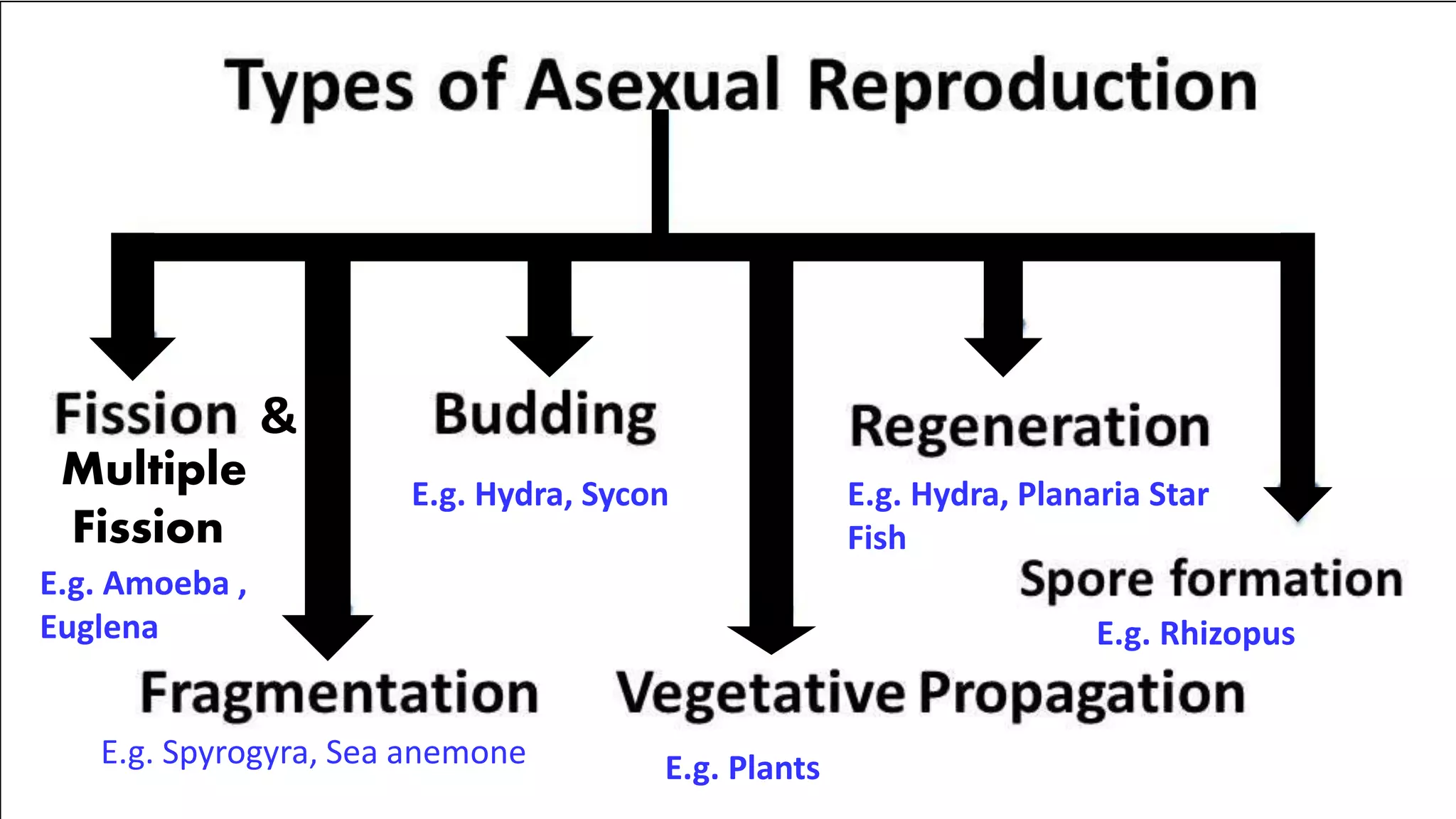
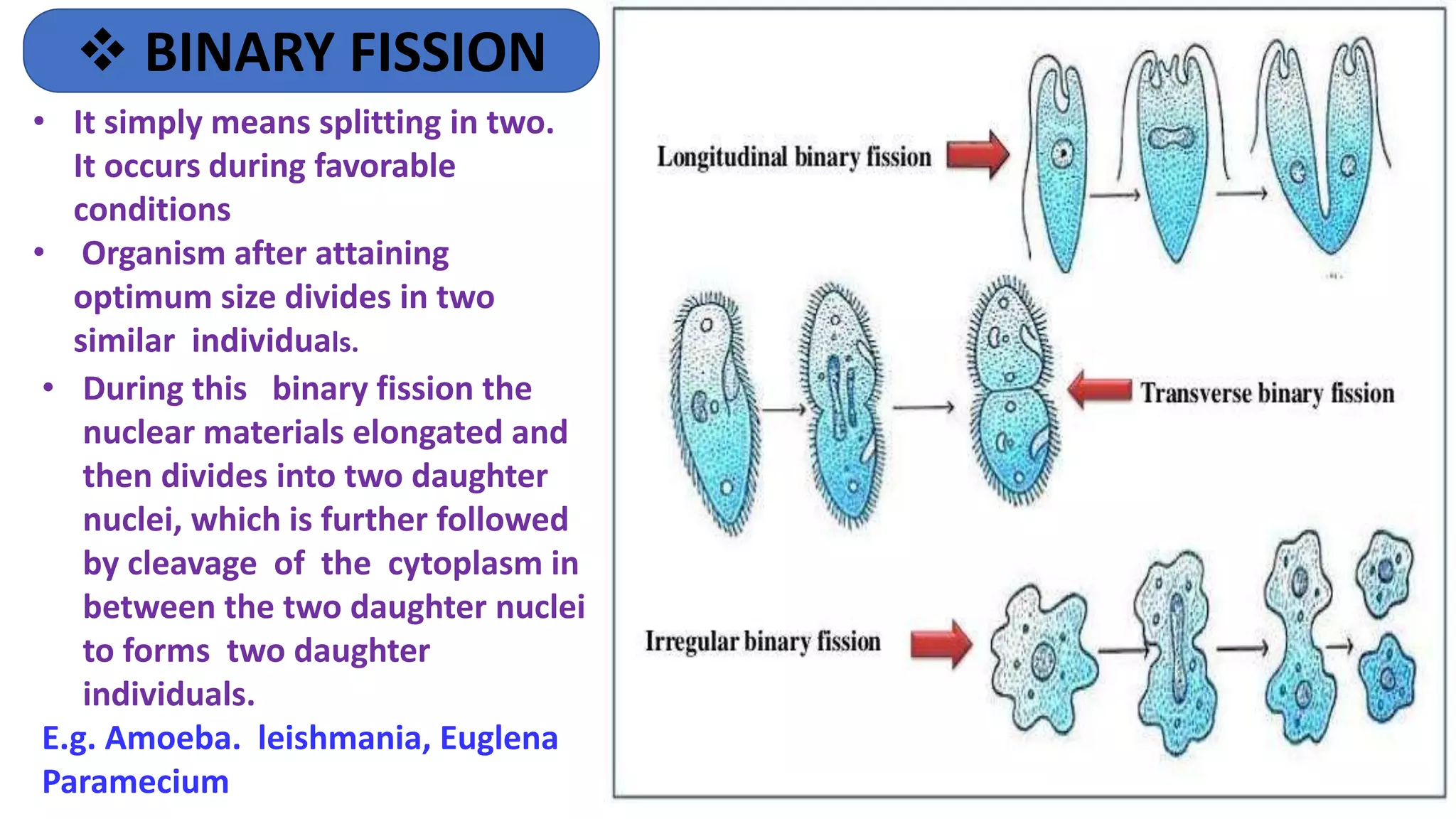
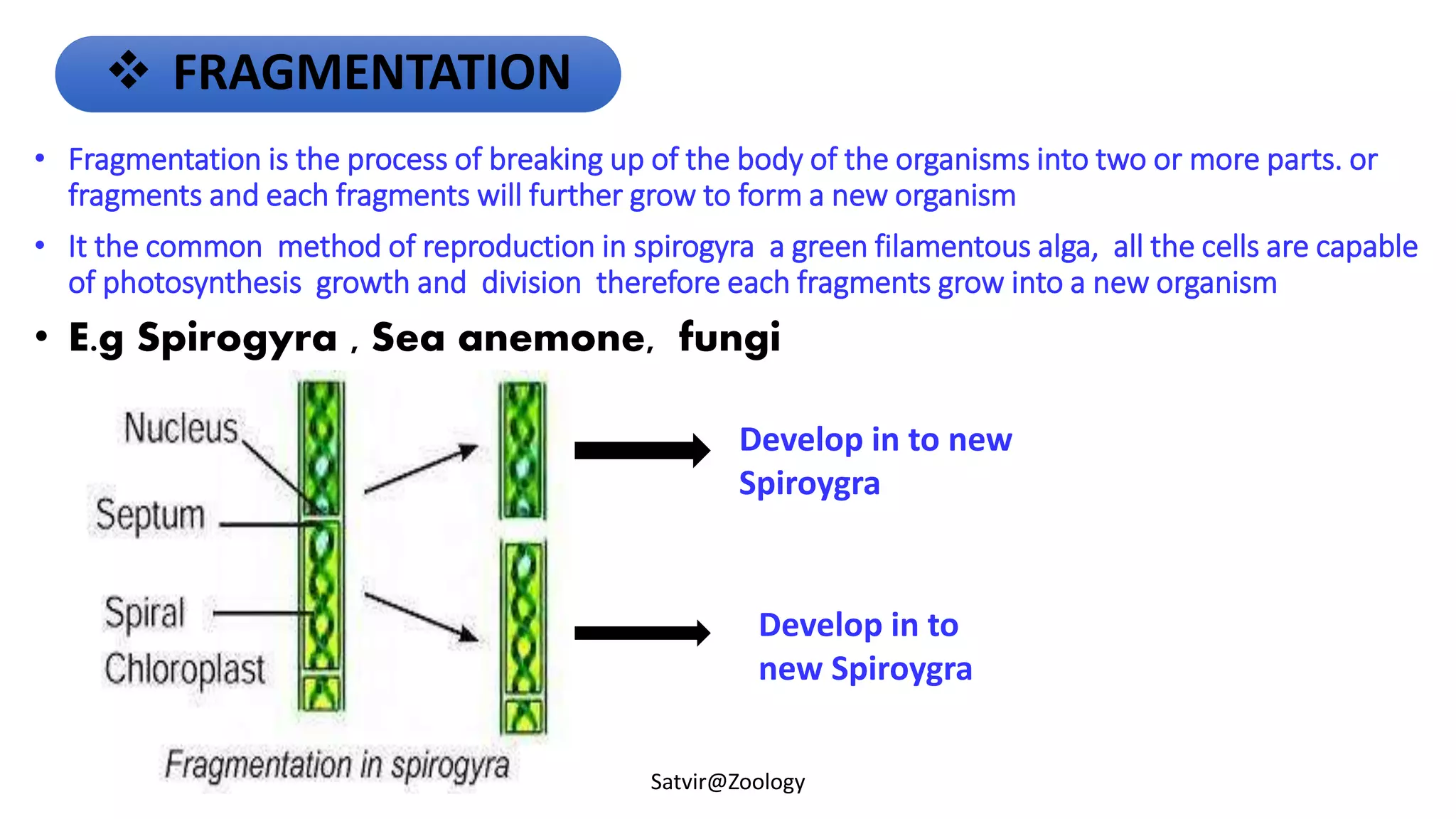
Mr. Satvir Singh Bhaglal discusses various types of asexual reproduction including binary fission, multiple fission, budding, fragmentation, regeneration, and sporulation. Examples are provided for each type. The key differences between binary fission and multiple fission are outlined. Advantages of asexual reproduction include not requiring mates and allowing for rapid reproduction. However, asexual reproduction lacks diversity and offspring are genetically identical, making them susceptible to the same diseases and unable to adapt as well to environmental changes.