Embed presentation
Download to read offline



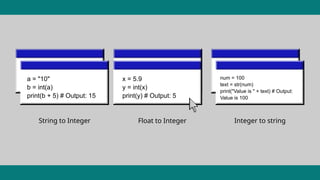


Type conversion in Python, also known as type casting, refers to the process of changing a variable's data type from one form to another. This is a fundamental operation in programming for data manipulation, ensuring compatibility between different data types in expressions, and controlling how data is represented. Python supports two main types of conversion: Implicit Type Conversion (Coercion): This occurs automatically when the Python interpreter converts one data type to another during an operation to prevent data loss or type errors. For example, when an integer is combined with a float in an arithmetic operation, the integer is implicitly converted to a float. Explicit Type Conversion (Type Casting): This involves manually converting a variable's data type using built-in functions like int(), float(), str(), list(), tuple(), set(), etc. This allows programmers to explicitly control the data type and is often used when a specific data type is required for a particular operation or function. Explicit conversion may lead to data loss if the target type cannot fully represent the original value (e.g., converting a float to an integer truncates the decimal part).





