This presentation provides a comprehensive introduction to Python programming for undergraduate students. It covers the history of Python, key features, and applications across industries like AI/ML, data science, web development, and automation. Fundamental programming concepts such as keywords, identifiers, variables, data types, input/output, comments, and indentation are explained. The presentation also details operators, expressions, type conversion (explicit and implicit), string operations, and array handling using Python’s array module. Real-world use cases from companies like Google, YouTube, Instagram, Netflix, and NASA are included, making it ideal for B.Sc. (CS/IT), BCA, and engineering students.






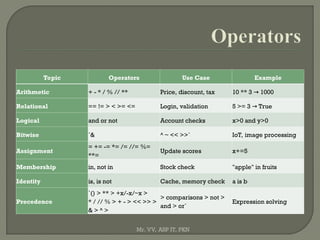
![Aspect Operators Expressions
Definition Symbols that perform operations on values. Code that evaluates to a single value.
Purpose
Perform arithmetic, logical, relational, or
assignment operations.
Compute or return a value.
Examples +, -, *, /, ==, and, or
2 + 3 * 4, x > 10 and y < 5, len("Hi") +
1
Returns Usually primitive values (int, float, bool). Always results in a single value.
Usage in
Python
a + b, x == y, not flag sum([1,2,3]) / len([1,2,3])
Mr. VV, ASP IT, PKN](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pythonprogrammingessentialsastudent-friendlyapproach-250727054032-f195befb/85/Python-Programming-Essentials-A-Student-Friendly-Approach-ppt-7-320.jpg)
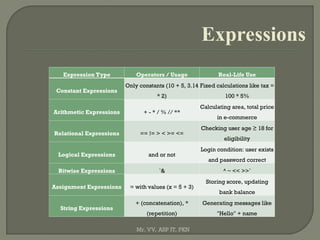

![Strings Methods Example
Concatenate + "Hello"+"World"
Repeat * "Hi!"*3 Hi!Hi!Hi!
→
Slice [start:end] "Python"[:3] Pyt
→
Case Conversion upper(), lower(), title(), capitalize() "hi".upper() HI
→
Strip & Replace strip(), replace() " hi ".strip() hi
→
Split & Join split(), join() "a,b".split(",") ['a','b']
→
Search find(), startswith(), endswith() "python".find("th") 2
→
f-String f"Name: {name}" Name: Alice
A string is a sequence of characters enclosed in single (' '), double (" "), or triple quotes (''' ''').
Immutable (cannot be changed after creation)
Indexed & Sliced (s[0], s[1:4])
Example:
s = "Python"
print(s.upper()) # 'PYTHON'
print(s[0:3]) # 'Pyt'
Mr. VV, ASP IT, PKN](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pythonprogrammingessentialsastudent-friendlyapproach-250727054032-f195befb/85/Python-Programming-Essentials-A-Student-Friendly-Approach-ppt-11-320.jpg)
![Array (array module) Methods Example
Create array('i',[10,20,30]) Integers only
Append & Insert append(), insert() [10,15,20,30]
Remove & Pop remove(), pop() [10,15,30,40]
Index & Slice index(), [1:3] index(30) 2
→
Reverse & Sort reverse(), sort() [40,30,15,10]
An array is a collection of items stored at contiguous memory locations.
In Python, we mostly use lists as arrays, but there is also a special array module for numeric
arrays.
Mr. VV, ASP IT, PKN](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pythonprogrammingessentialsastudent-friendlyapproach-250727054032-f195befb/85/Python-Programming-Essentials-A-Student-Friendly-Approach-ppt-12-320.jpg)