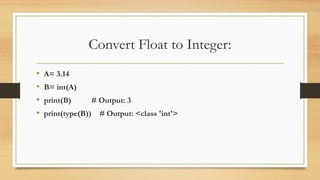
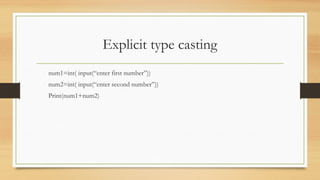
Type conversion in Python involves converting a variable from one data type to another, utilizing built-in functions for both implicit and explicit conversions. Implicit conversion happens automatically, while explicit conversion requires the programmer's intervention using functions like int(), float(), and str(). It is essential to note that data loss can occur during conversion and some conversions between incompatible types may result in errors.





![Convert List to Tuple:
• X= [1, 2, 3]
• Y = tuple(X)
• print(Y) # Output: (1, 2, 3)
• print(type(Y)) # Output: <class 'tuple'>](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/typesconversion-240910051315-4e733616/85/types-conversion-in-python-with-exa-pptx-7-320.jpg)