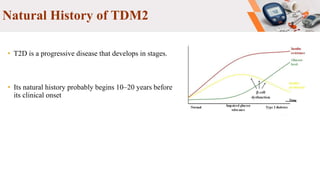
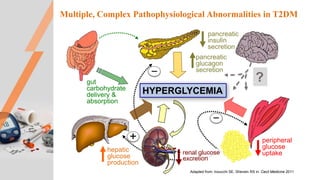
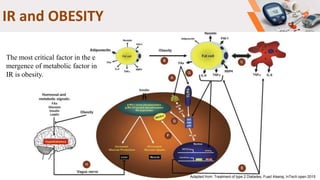
Type 2 diabetes pathogenesis involves multiple complex pathophysiological abnormalities that result in hyperglycemia. Key factors include insulin resistance caused by genetic and environmental factors like obesity, and beta cell dysfunction caused by glucotoxicity, lipotoxicity, and other stresses that impair insulin secretion and lead to loss of beta cell function and mass over time. Genetic factors also contribute significantly, as seen in familial risk and heritability studies, though identifying specific genes has been challenging due to the polygenic nature of type 2 diabetes.