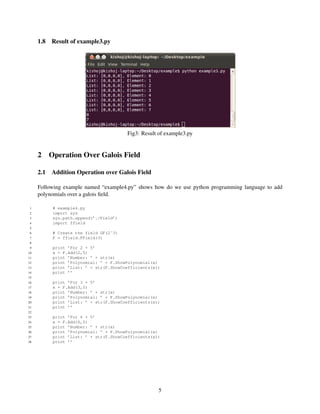
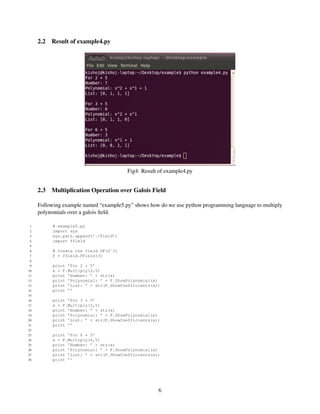
The document is a tutorial on programming with Python for Galois fields. It discusses how to import the FField class to work with Galois fields in Python, create a Galois field GF(2^3), represent elements as polynomials and coefficients, convert between representations, and perform addition and multiplication operations on elements in the field. Examples of Python code are provided to demonstrate working with Galois fields, obtaining polynomial and coefficient representations of elements, and using the FField class methods to operate on elements in the field.


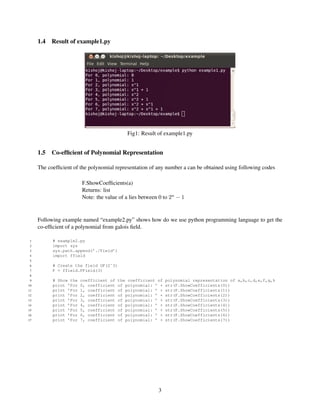
![1.6 Result of example2.py
Fig2: Result of example2.py
1.7 Conversion from co-efficient of polynomial to element
The coefficient(list) of the polynomial can be converted to the element(integer)
F.ConvertListToElement(list)
Returns: integer
Note: the value of a lies between 0 to 2n − 1
Following example named “example3.py” shows how do we use python programming language to convert
co-efficient of a polynomial to element over a galois field.
1 # example3.py
2 import sys
3 sys.path.append(’./Field’)
4 import ffield
5
6 # Create the field GF(2ˆ3)
7 F = ffield.FField(3)
8
9 # Converting list into the element
10 print "List: [0,0,0,0], Element: " + str(F.ConvertListToElement([0,0,0,0]))
11 print "List: [0,0,0,0], Element: " + str(F.ConvertListToElement([0,0,0,1]))
12 print "List: [0,0,0,0], Element: " + str(F.ConvertListToElement([0,0,1,0]))
13 print "List: [0,0,0,0], Element: " + str(F.ConvertListToElement([0,0,1,1]))
14 print "List: [0,0,0,0], Element: " + str(F.ConvertListToElement([0,1,0,0]))
15 print "List: [0,0,0,0], Element: " + str(F.ConvertListToElement([0,1,0,1]))
16 print "List: [0,0,0,0], Element: " + str(F.ConvertListToElement([0,1,1,0]))
17 print "List: [0,0,0,0], Element: " + str(F.ConvertListToElement([0,1,1,1]))
18
19 # Next method to convert
20 print F.ConvertListToElement(F.ShowCoefficients(0))
21 print F.ConvertListToElement(F.ShowCoefficients(7))
4](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/tutorial-120206002235-phpapp01/85/Galios-Python-Programming-4-320.jpg)