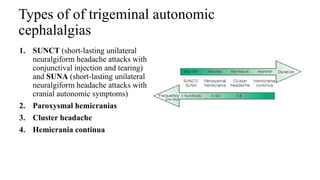
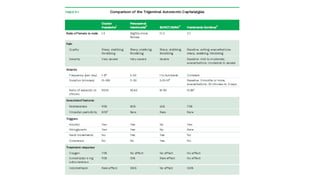
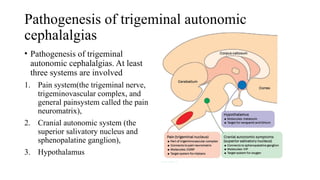
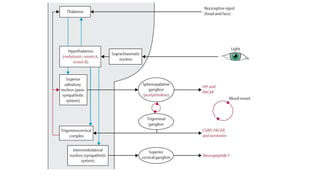
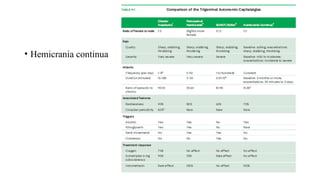
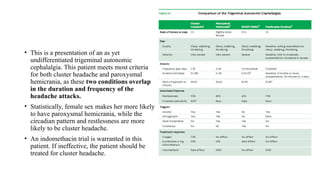
Trigeminal autonomic cephalalgias (TACs) are a group of uncommon headache disorders characterized by intense unilateral pain and associated cranial autonomic symptoms. The main types include cluster headaches, paroxysmal hemicrania, and SUNA/SUNCT, each with specific onset patterns and responses to treatment. Management strategies involve acute treatment with high-flow oxygen and triptans, as well as preventive medications such as indomethacin and verapamil.