The document discusses coordination in supply chains and the obstacles that can arise from a lack of coordination. Some key points:
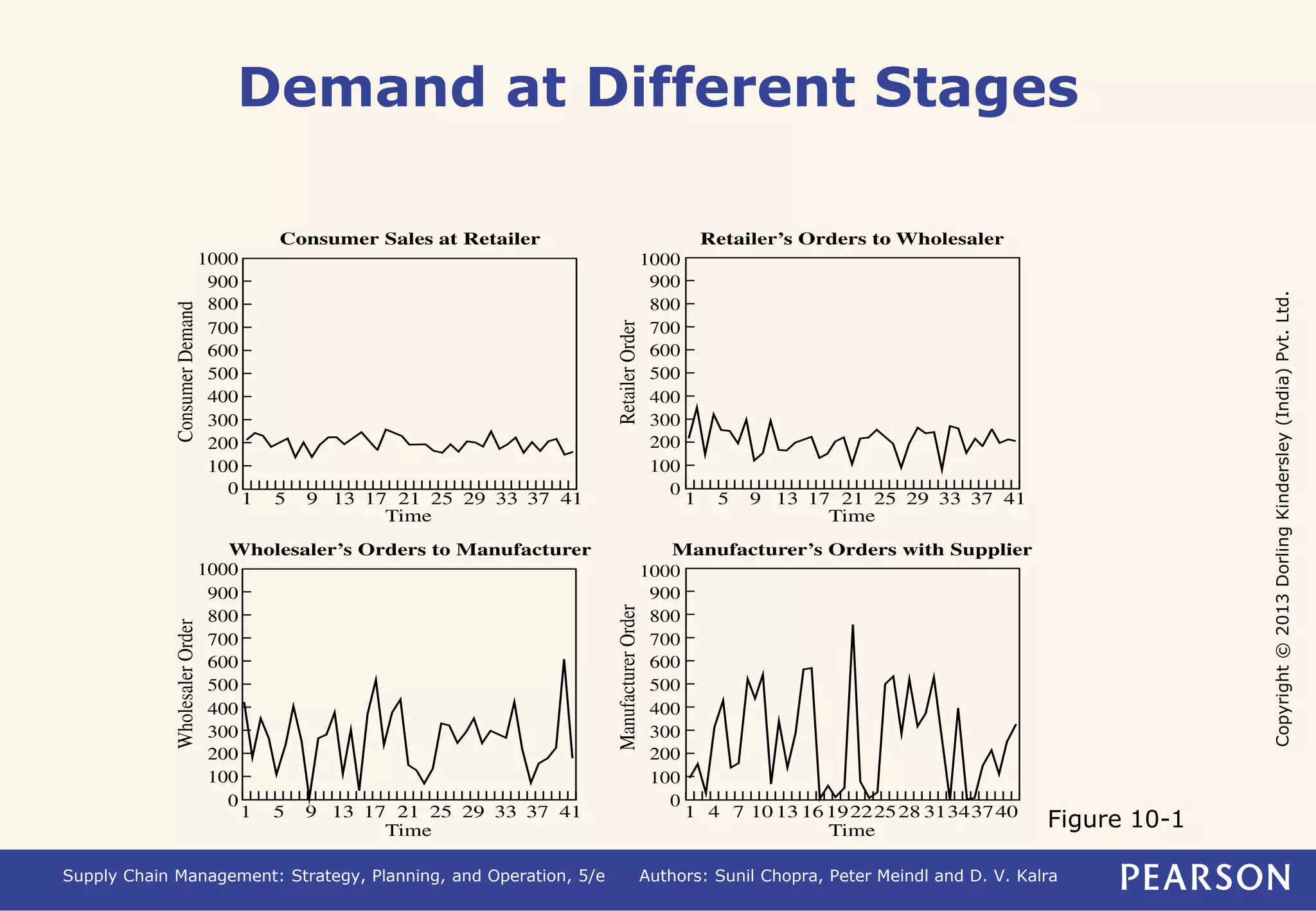
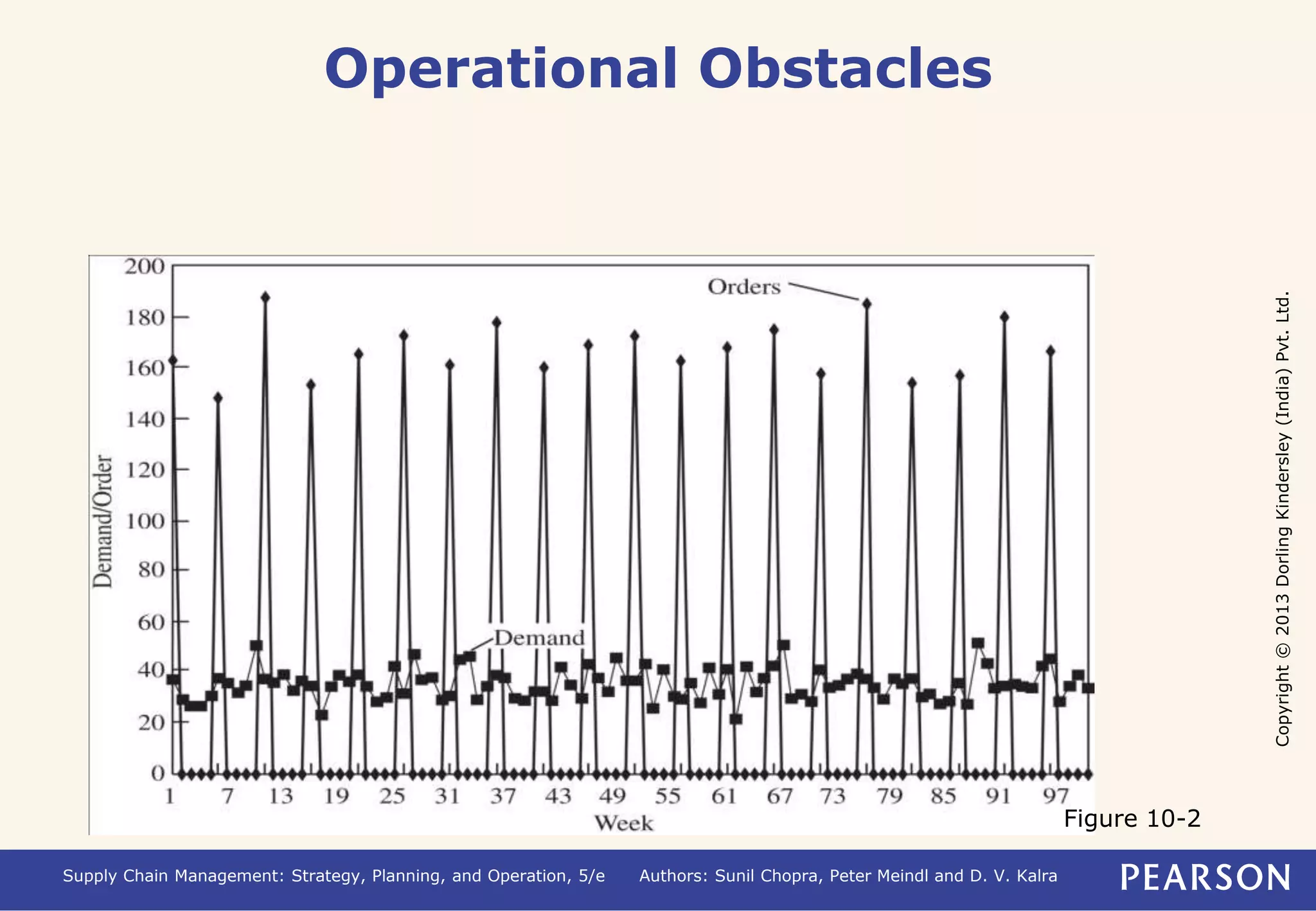
- A lack of coordination between supply chain stages can result in conflicting objectives and distorted information sharing, leading to the bullwhip effect where demand fluctuations increase up the supply chain.
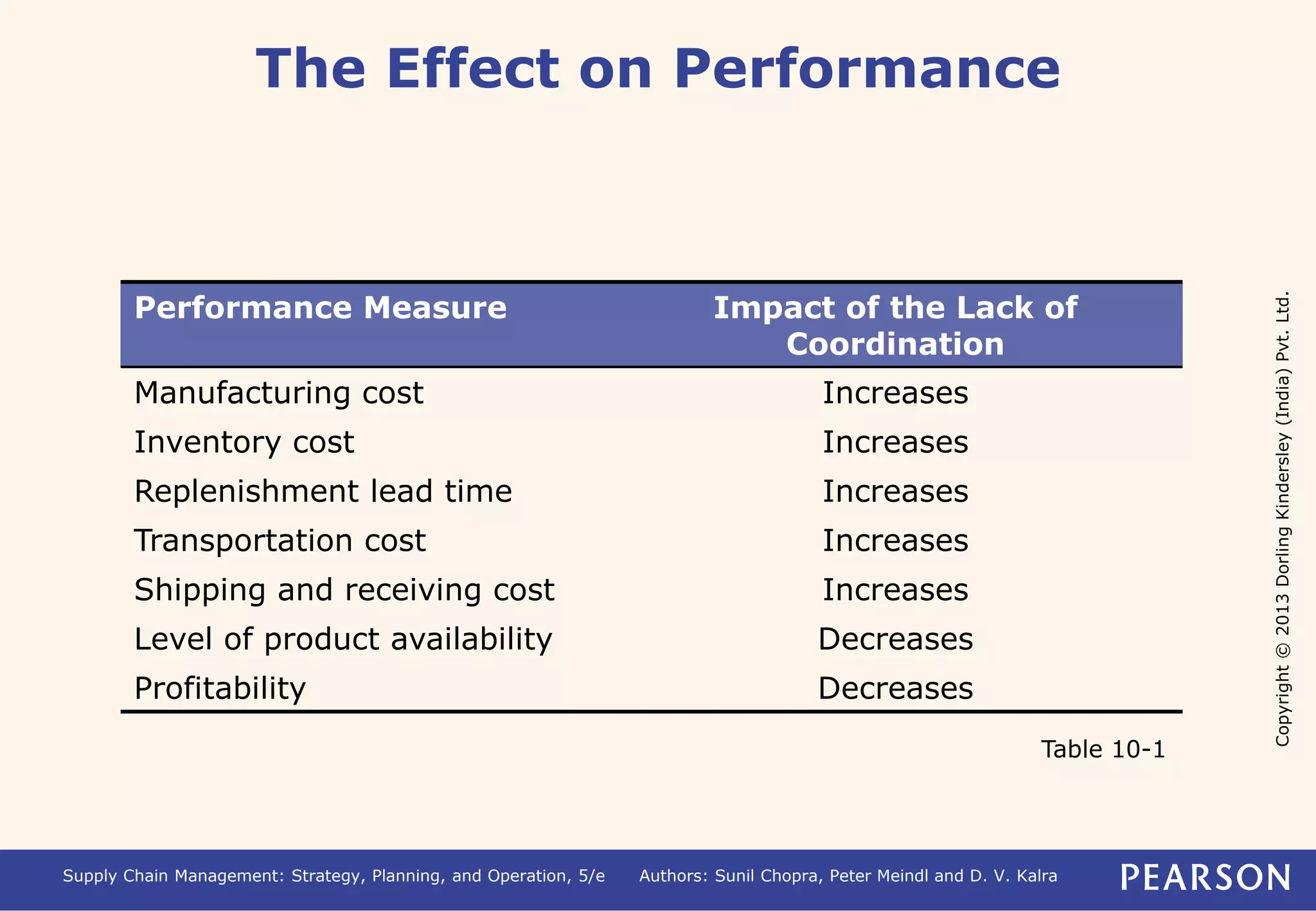
- The bullwhip effect distorts demand information and reduces total profits. It increases costs like inventory and manufacturing.
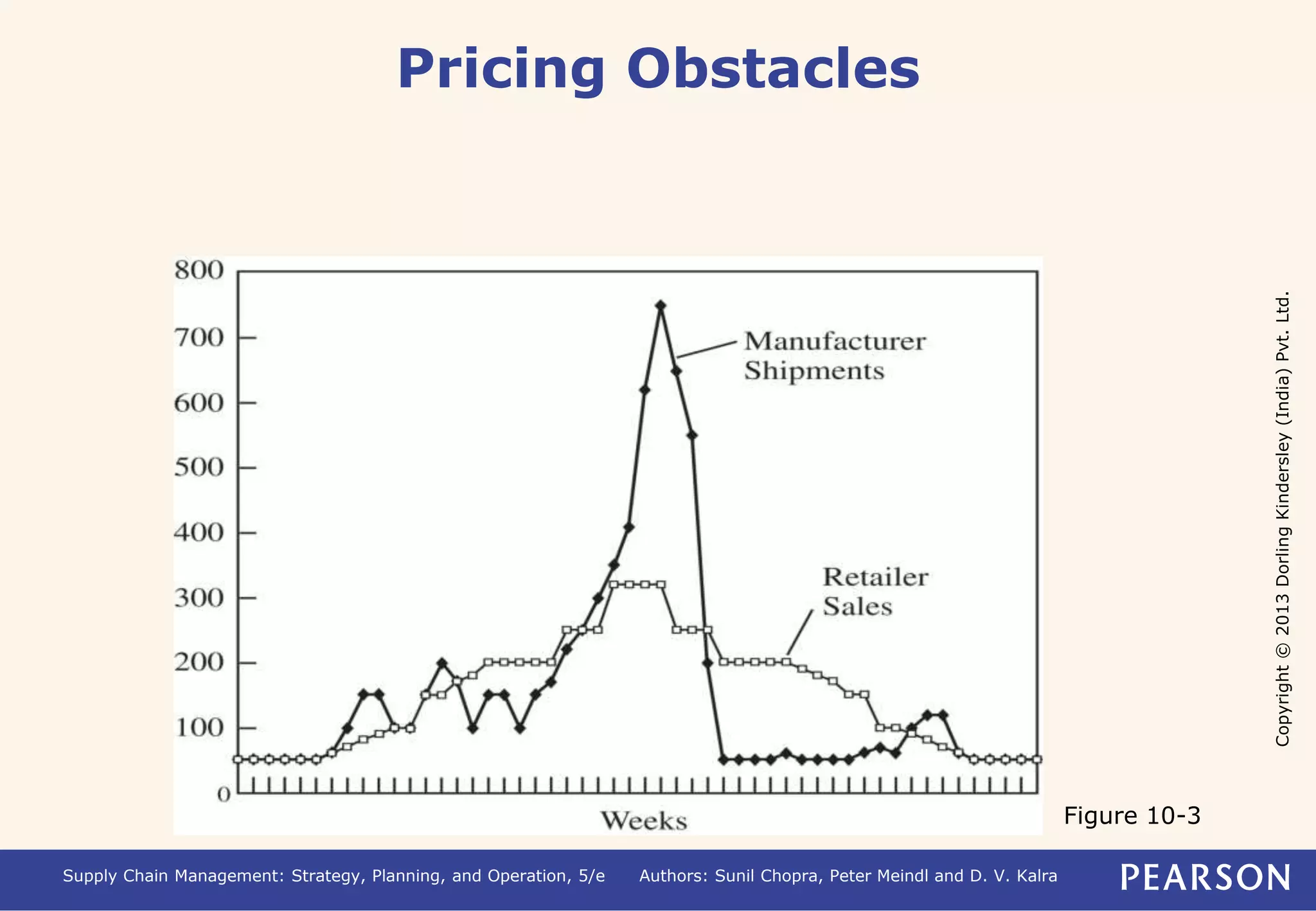
- Obstacles to coordination include misaligned incentives, lack of information sharing, operational inefficiencies, pricing issues, and behavioral problems between partners.
- Managers can improve coordination by aligning goals, improving information visibility, optimizing operations, stabilizing pricing, and building strategic partnerships