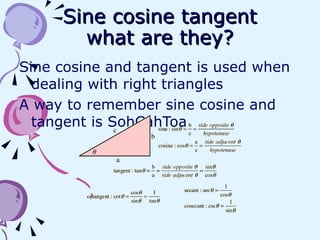
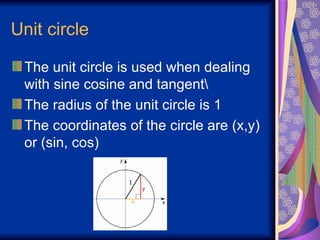
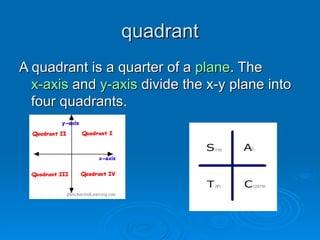
Trigonometry is the study of triangles and angles. It discusses topics like the unit circle, quadrants, trig functions of sine, cosine and tangent, angle measures in degrees and radians, and trig identities. The unit circle is used to find trig function values of angles, with a radius of 1 and coordinates of (x,y) or (sin,cos). A quadrant divides the x-y plane into four sections based on the x and y axes. Trig functions can also be used to convert between degree and radian angle measures using appropriate formulas.