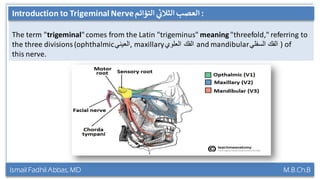
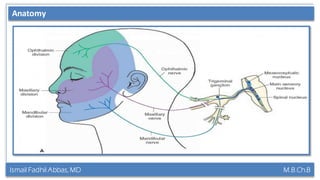
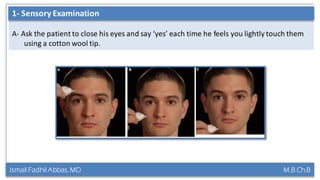
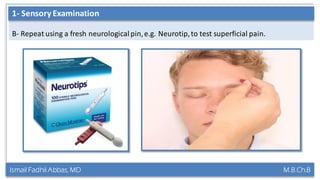
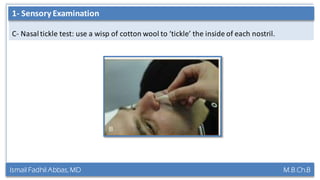
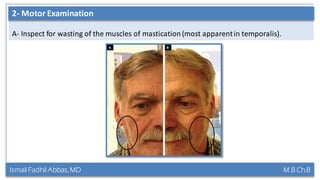
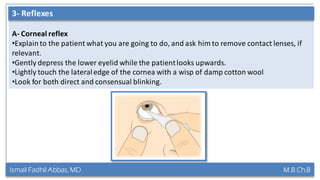
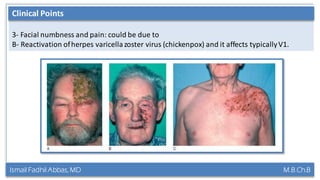
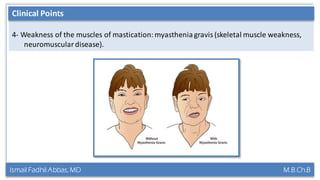
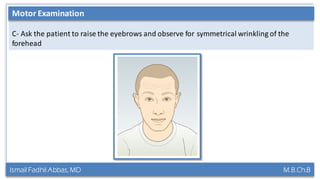
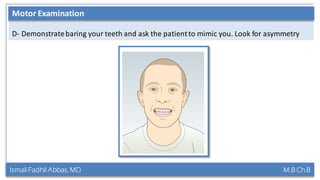
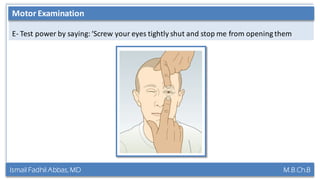
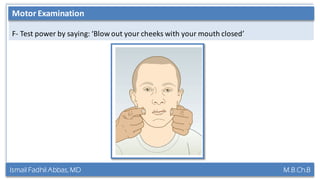
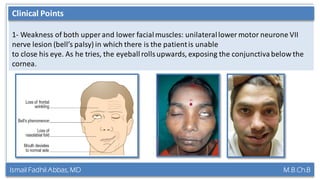
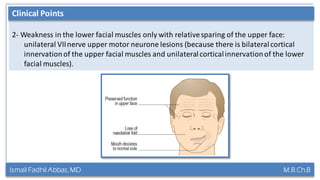
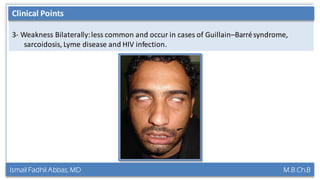
This document summarizes a lecture on the trigeminal and facial nerves. It discusses the anatomy and function of each nerve, how to examine them clinically, and what clinical findings may indicate specific conditions. The trigeminal nerve has three divisions innervating different parts of the face and controls sensation and muscle movement. The facial nerve controls facial muscle movement and secretions from salivary glands. Clinical tests of sensation, strength, and reflexes can localize lesions of these nerves.