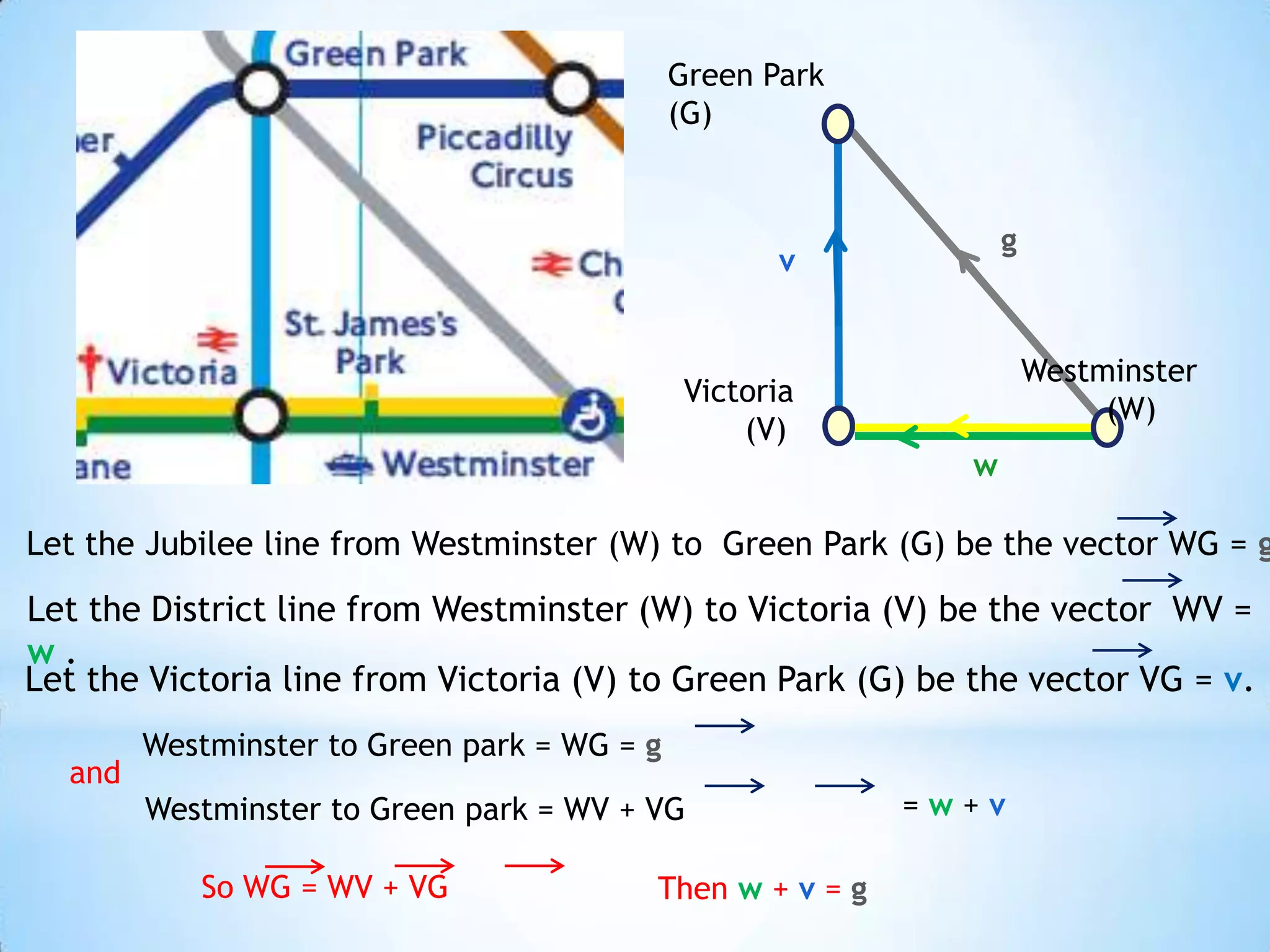
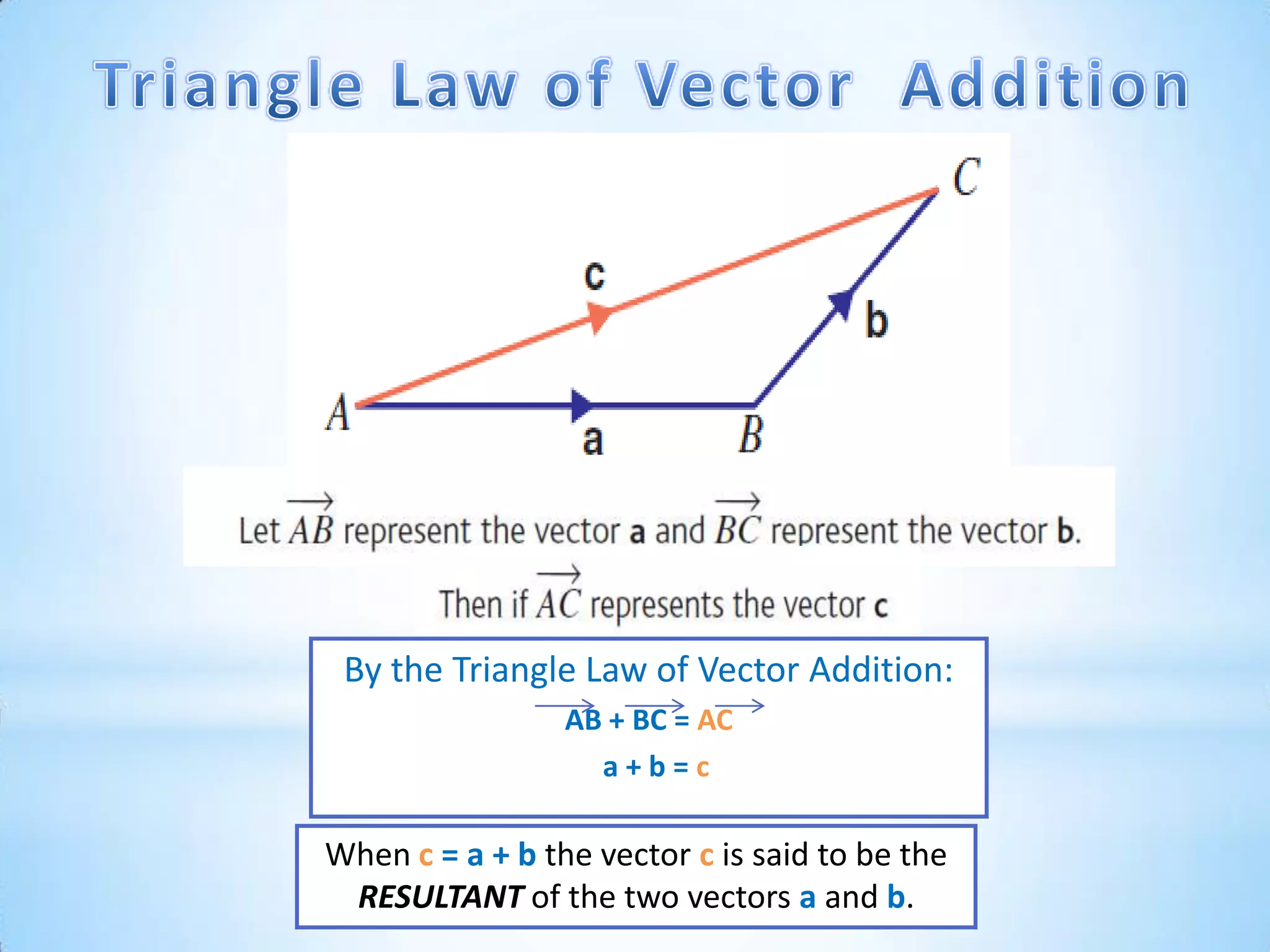
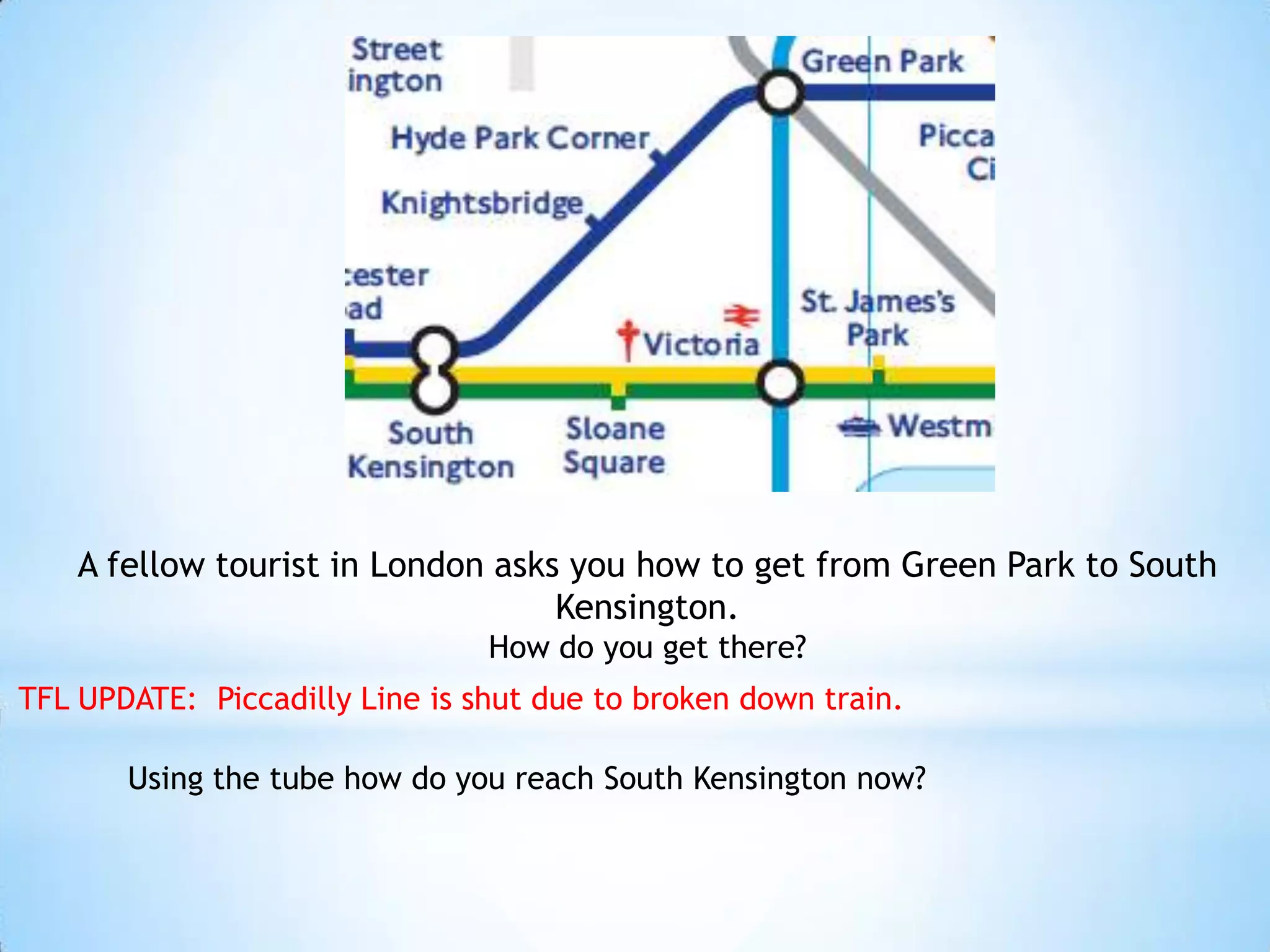
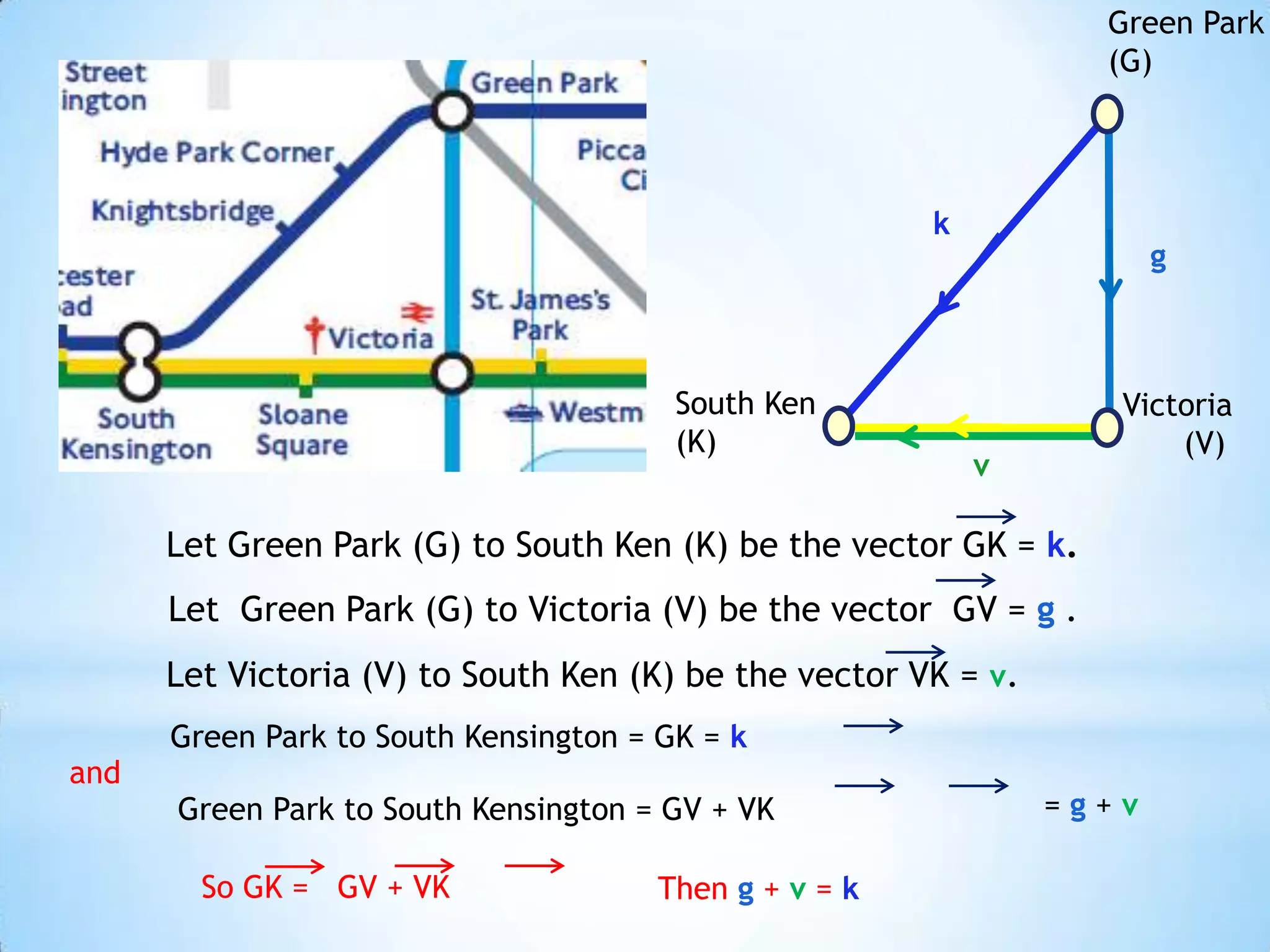
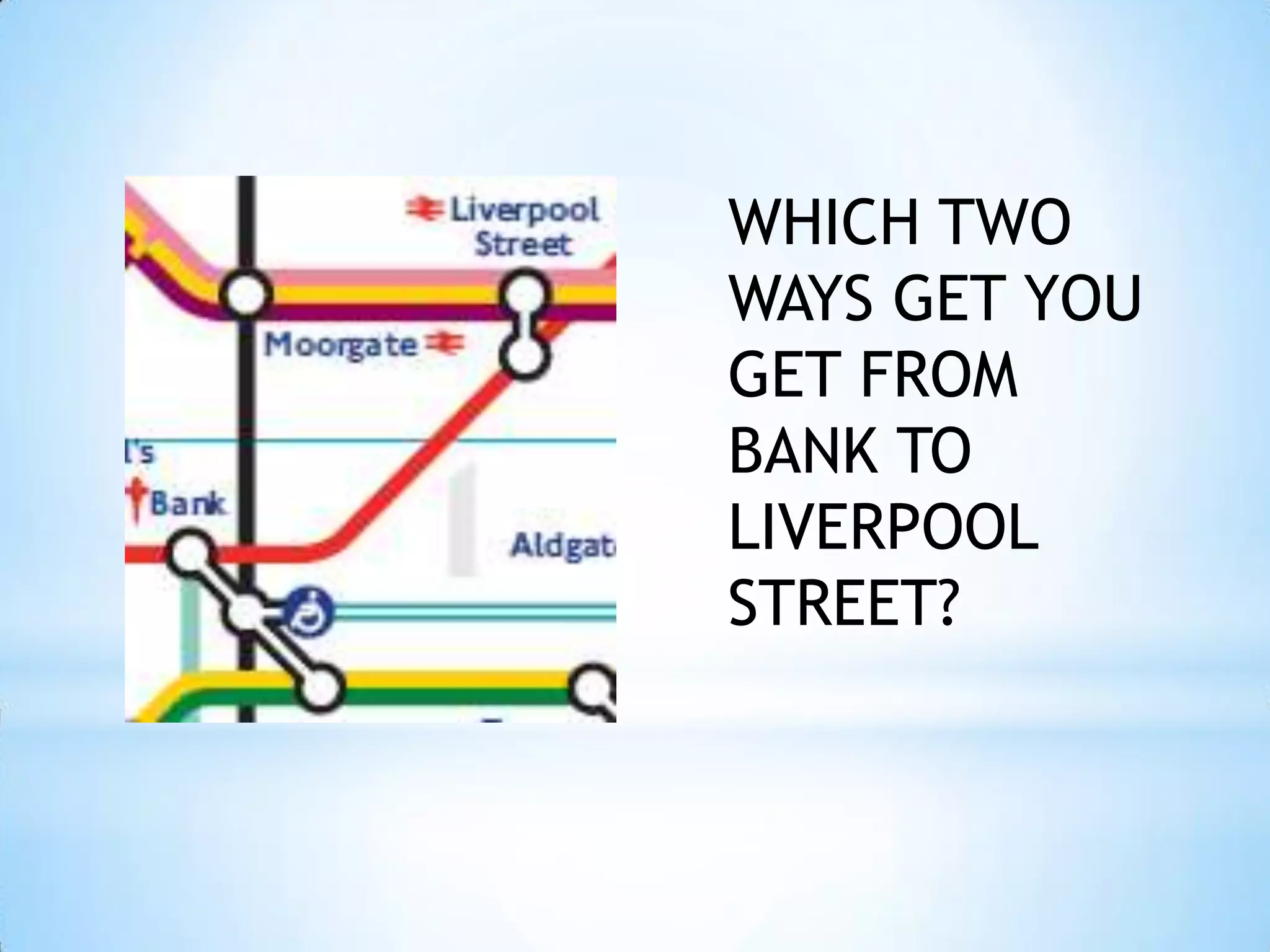
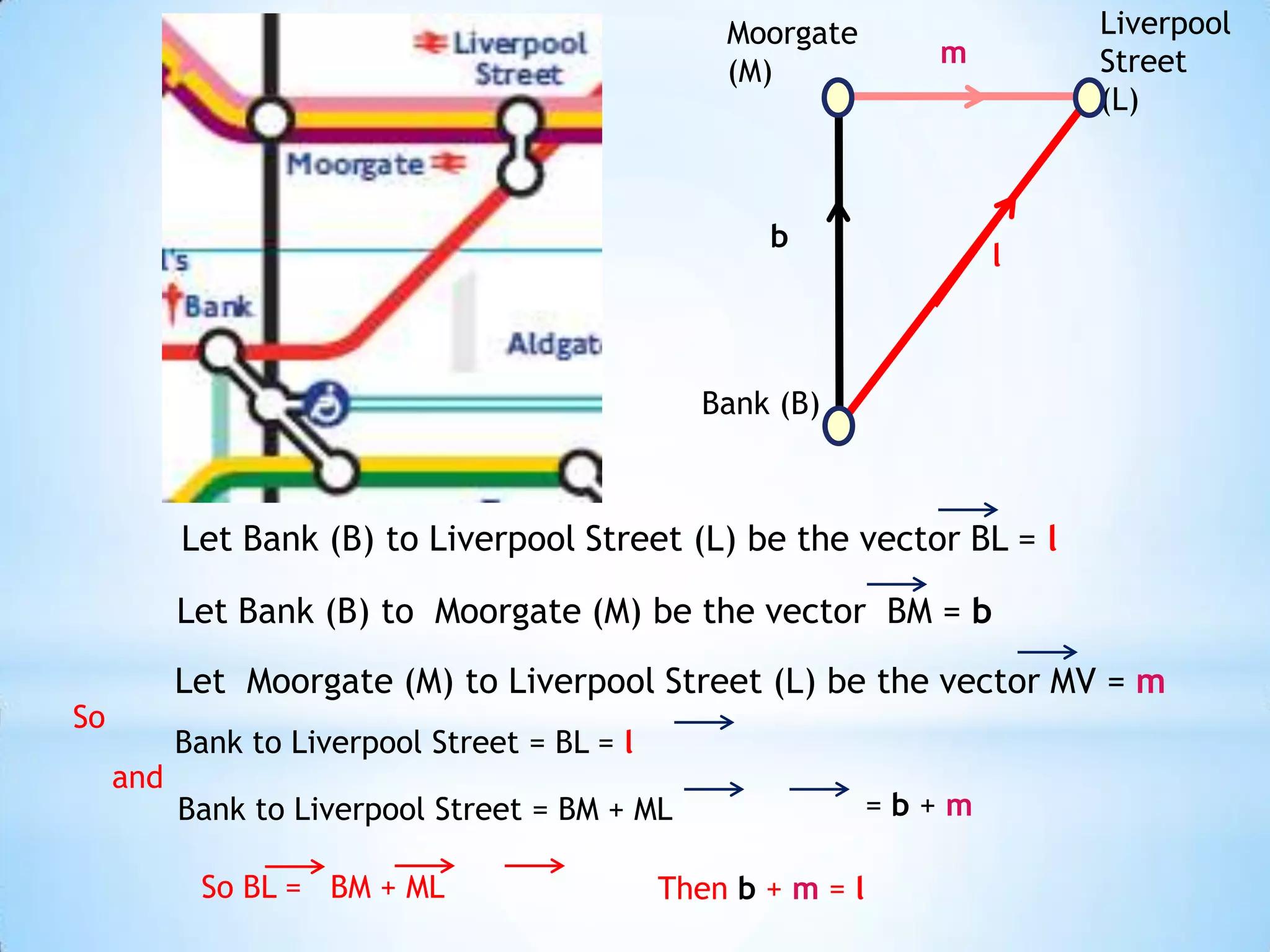
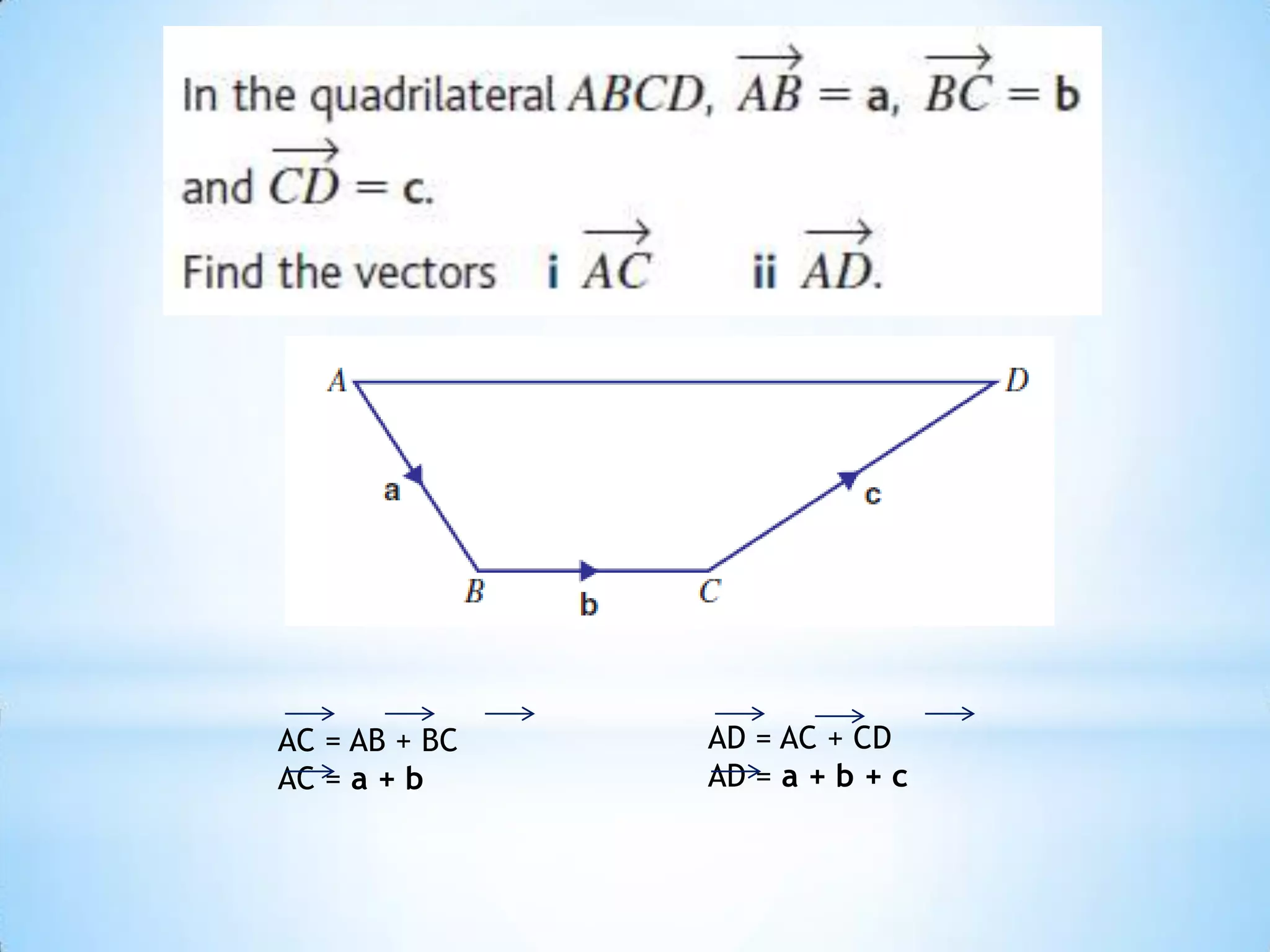
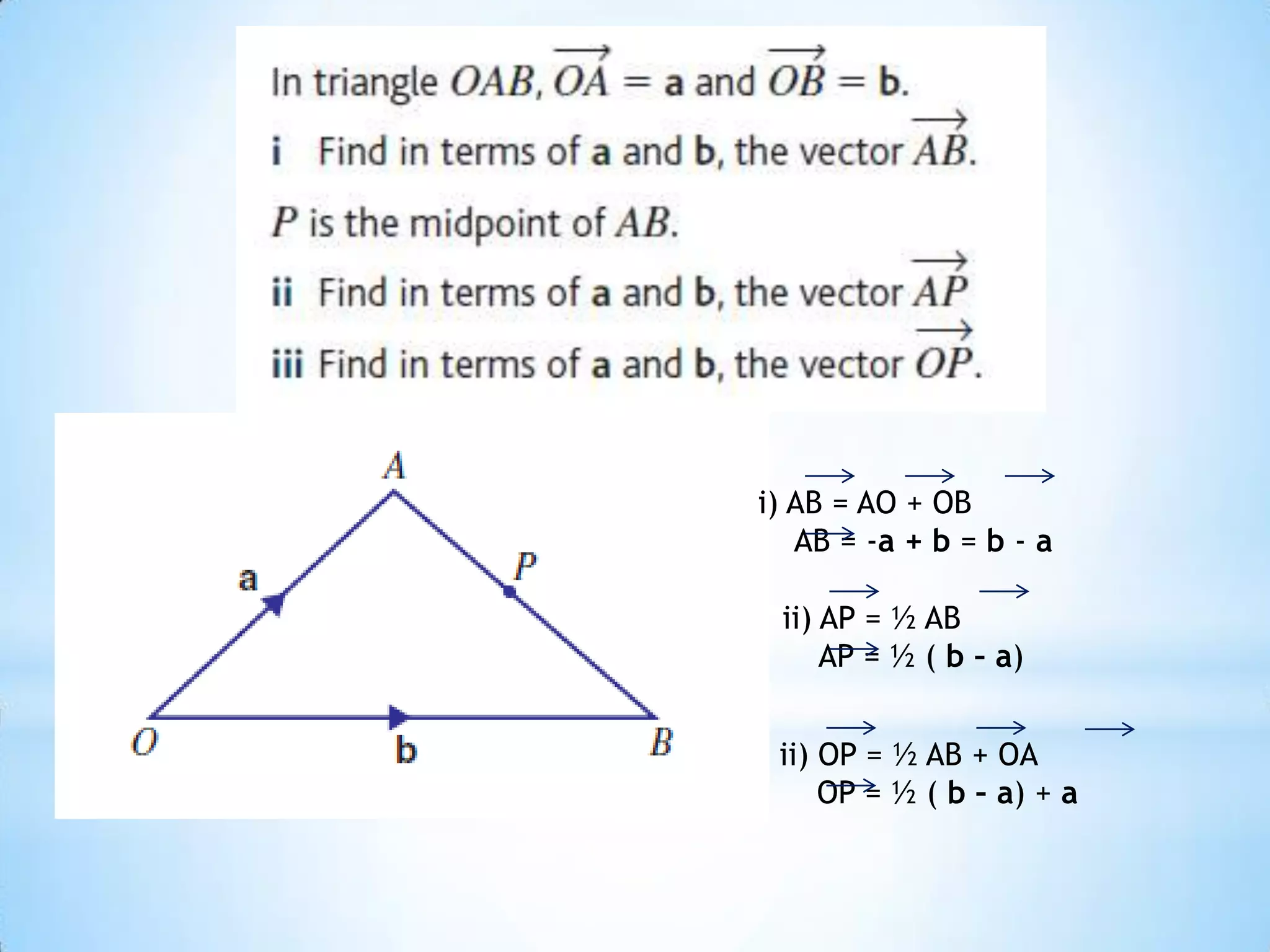
The document provides instructions for navigating the London Underground when certain lines are closed for maintenance. It explains how to get from Westminster to Green Park by taking the District Line from Westminster to Victoria and then the Victoria Line from Victoria to Green Park. Similarly, it explains how to get from Green Park to South Kensington by taking the Victoria Line from Green Park to Victoria and then the District Line from Victoria to South Kensington. Finally, it notes that there are two ways to get from Bank to Liverpool Street: taking the Central Line from Bank to Moorgate and then the Circle/Hammersmith & City lines from Moorgate to Liverpool Street, or taking the Northern Line directly from Bank to Liverpool Street.