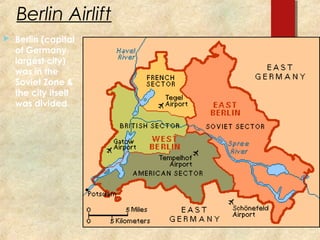
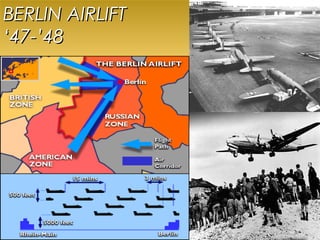
This document provides an overview of the Cold War between the United States and Soviet Union. It discusses the competing ideological systems and military alliances between the two superpowers. Key events that defined the Cold War included the Yalta Conference, the Berlin Airlift, the building of the Berlin Wall, the Cuban Missile Crisis, and the Vietnam War. Propaganda and threats of military force were tools both sides used to gain influence and spread their ideological systems during the Cold War standoff.