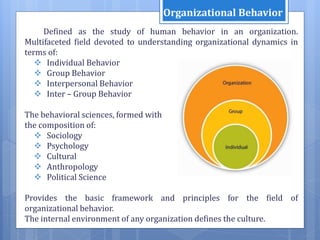
This document discusses 13 trends in organizational behavior. It summarizes each trend in 1-2 sentences. The trends include changes in diversity and inclusion in organizations, the consideration of ethical ideology and justice, more efficient use of time and money, evolving views of group behavior and power dynamics, greater understanding of cultural learning, breaking gender stereotypes, and moving beyond constraints to recognize employees' pro-social nature.