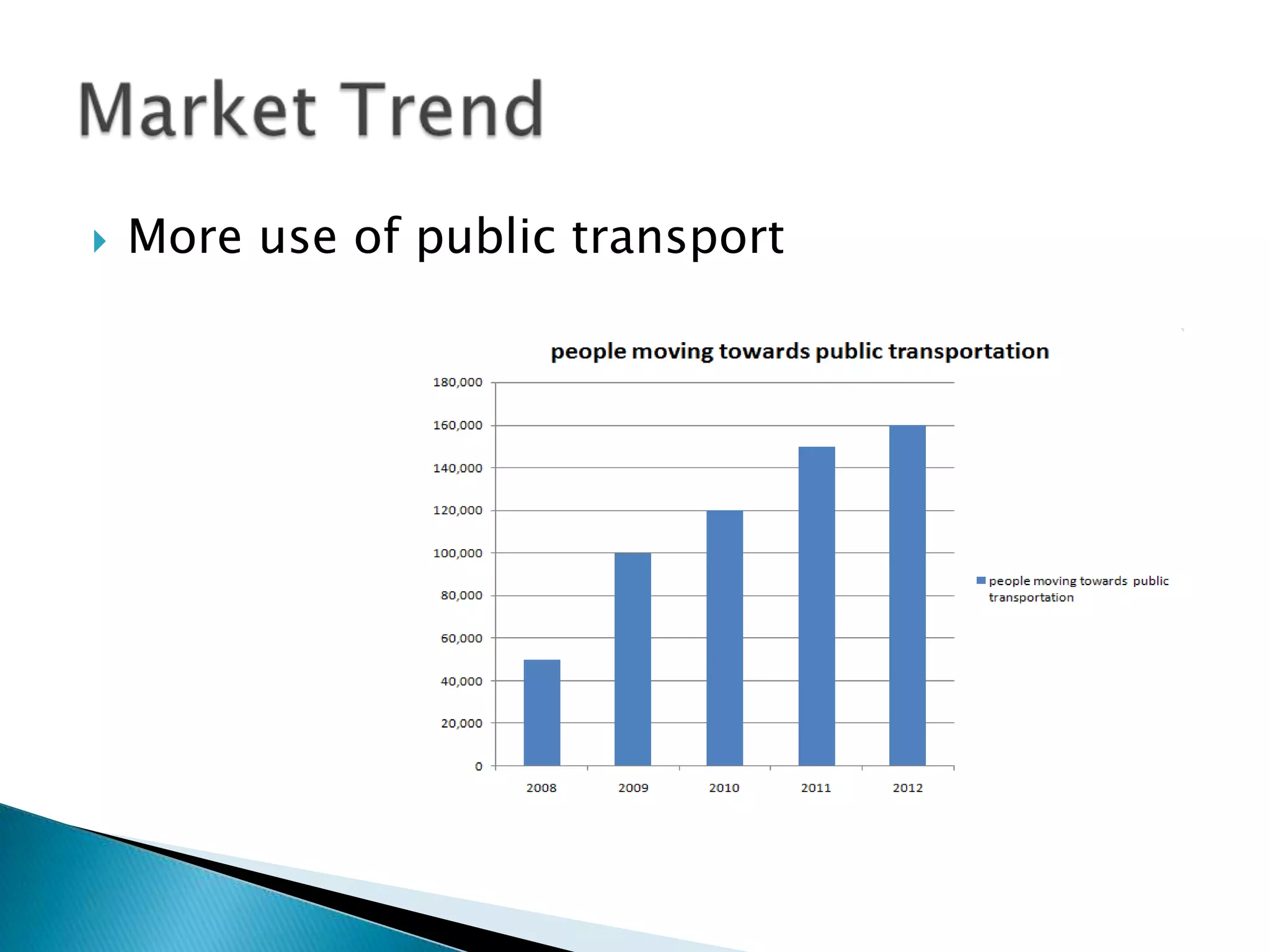
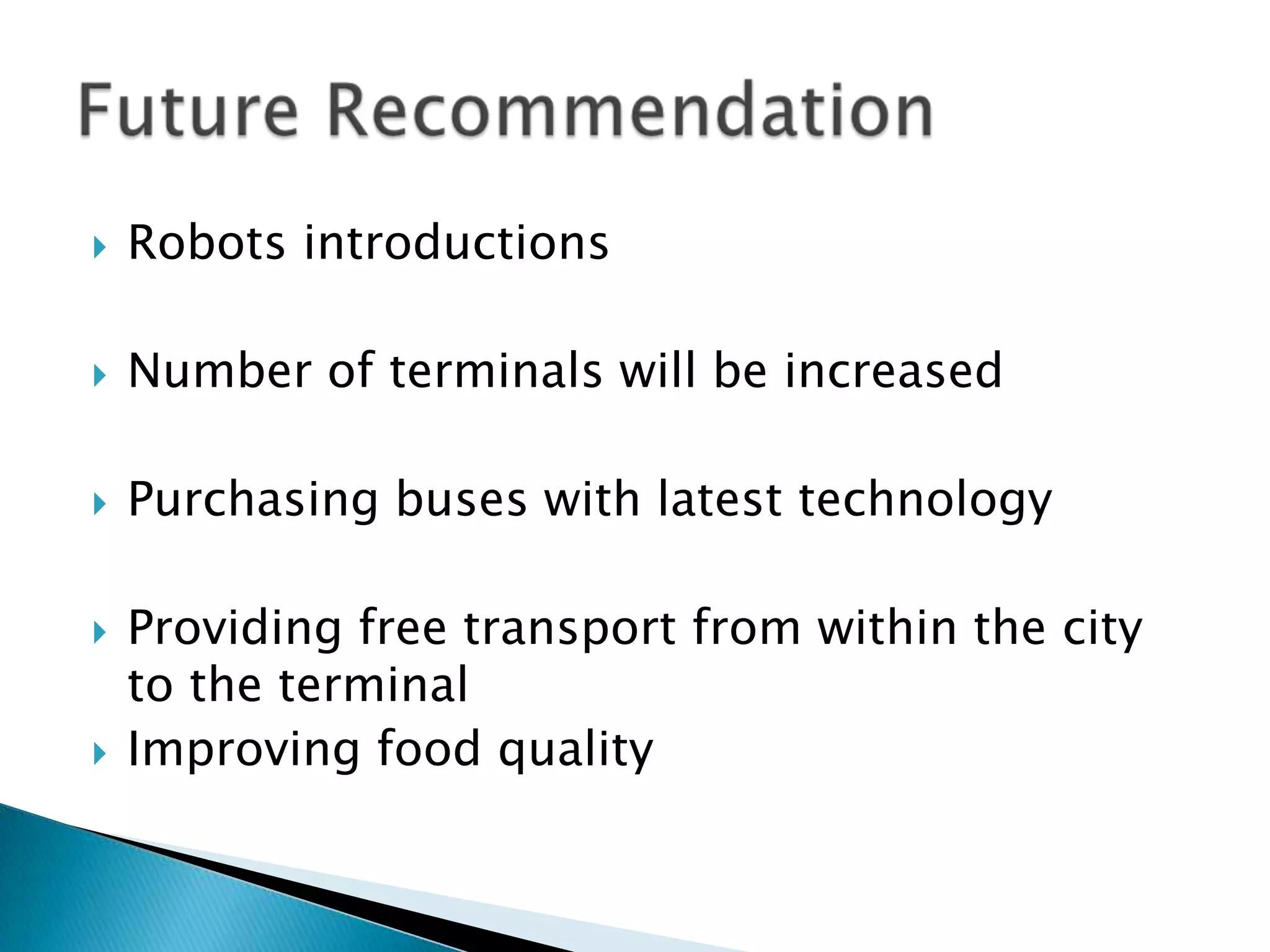
This document outlines a marketing plan for a transportation business with four group members. It includes sections on situation analysis, market need, objectives, SWOT analysis, target markets, marketing mix, financial forecast, strategies, positioning, and future recommendations. The marketing objectives are to gain market share, decrease customer acquisition costs and marketing costs. A Porter's Five Forces analysis is included. Target customers are business travelers and families. Future recommendations include introducing robots, expanding terminals, and improving technology and food quality.