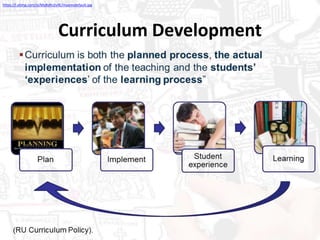
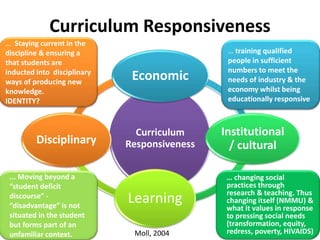
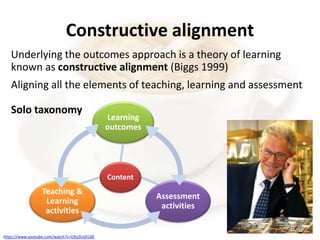
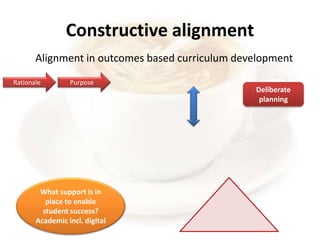
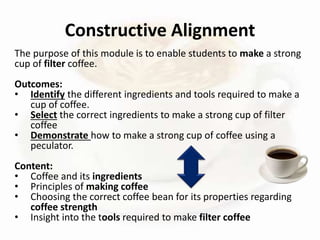
This document provides an overview of a presentation on transformative curriculum development. It discusses defining curriculum and transformation, and developing a shared understanding of these concepts. It also covers curriculum responsiveness, constructing transformative curricula, and the challenges of curriculum alignment. The purpose of higher education and dominant ideas shaping curriculum at NMMU are debated. Transformation is linked to addressing societal needs through curriculum content and activities. Constructive alignment between learning outcomes, teaching, and assessment is emphasized.