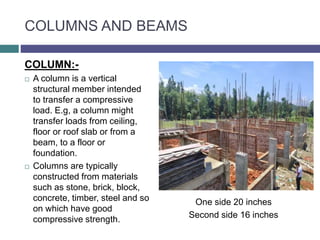
This document summarizes an internship presentation on the construction of a 63-bed hostel block at a government polytechnic college in Kashmir. It provides details on the project such as its cost, timeline, building specifications, and objectives of the internship. The methodology section explains the construction process from laying the raft foundation and shuttering to concreting, installing columns and beams, and completing the brickwork. Materials used included M20 grade concrete, OPC 43 grade cement, and a 1:1.5:3 mix design. The conclusion states that the interns gained basic construction knowledge and learned about site safety and communication.