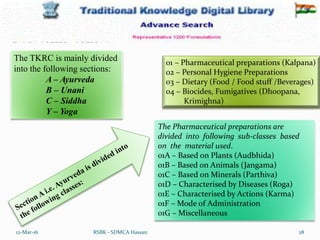
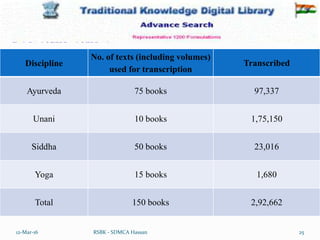
The document discusses the Traditional Knowledge Digital Library (TKDL) of India. It provides background on TKDL, describing how it was established in 2001 through collaboration between CSIR and AYUSH to prevent biopiracy and protect traditional knowledge. TKDL has digitized over 34 million pages of information from traditional medicine texts and translated it into multiple languages for access by international patent examiners. It aims to protect Indian traditional knowledge and prevent incorrect patents by providing a searchable database for prior art. The document outlines the development, contents, and importance of TKDL in preventing biopiracy of Indian traditional knowledge.






















![12-Mar-16 26
RSBK - SDMCA Hassan
AYURVEDA BOOKS:
1. Ayurveda Sara Sangraha – Shri Baidyanath Ayurveda Bhavan
Limited Calcutta, Edn.2003
2. Ayurveda Prakasha – Translated by Gulraj sarma Misra,
Chaukamba Bharati Academy, Varanasi, Edn.Reprint 1999
3. Ashtanga Hridaya – Commentary by Arunadatta edited by
Bhishagacharyan Harisastri paradakara Vaidya: Chaukamba
Orientalia, Varanasi; edn.8th, 1998. [Time Of Origin 5th century]
4. Ashtanga Sangraha – Commentary by Indu – Part-I : CCRAS;
Newdelhi [Time Of Origin 5th-10th Cent.]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/tkdl-240219105020-3e13fceb/85/Traditional-Knowledge-Digital-Library-TKDL-26-320.jpg)