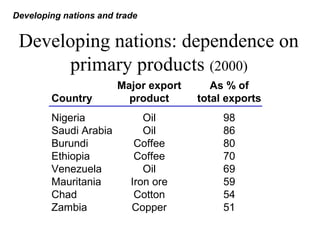
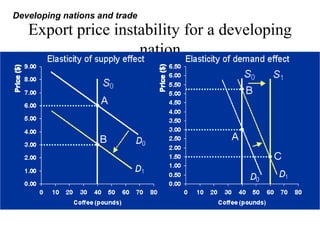
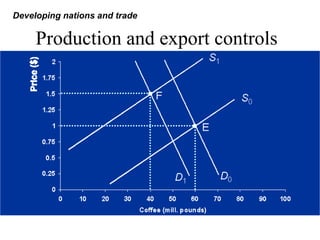
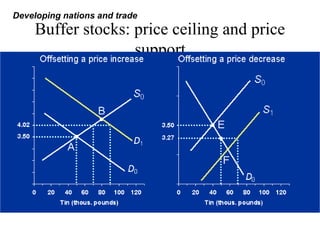
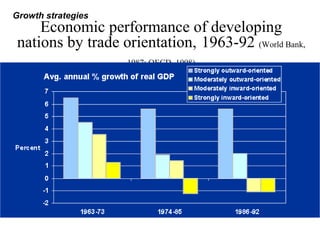
Developing nations face challenges in international trade including dependence on exports of primary goods, unstable export markets, and worsening terms of trade. They have attempted remedies like commodity agreements to stabilize prices, but these have had limited success. Developing nations have pursued both import substitution strategies, protecting domestic industries behind trade barriers, and export-led growth, focusing on manufactured exports. While both have benefits, import substitution risks inefficiency while export-led growth depends on demand in foreign markets. Case studies show mixed results for different countries' trade strategies.