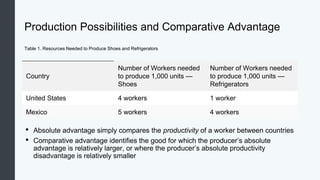
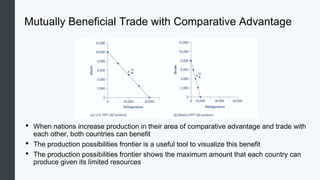
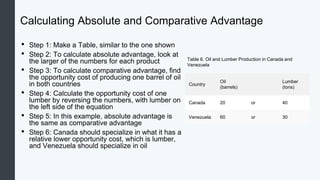
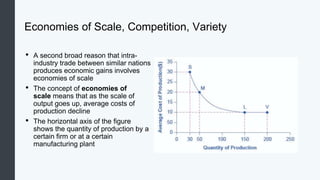
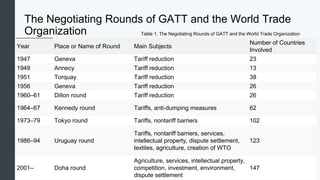
Globalization allows countries to specialize and trade based on comparative advantage. While barriers like tariffs aim to protect domestic industries, free trade overall benefits economies through gains from specialization and scale. Some costs of globalization include job losses, but most economists argue the gains outweigh the costs when balanced with appropriate domestic policies. Over the long term, organizations like GATT and WTO have significantly reduced trade barriers worldwide through negotiation rounds between member nations.