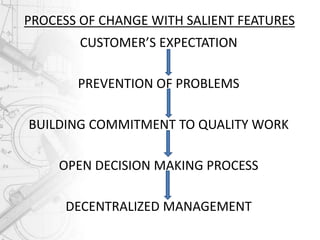
This document discusses Total Quality Management (TQM) in education. It defines TQM as managing the whole organization to achieve excellence. The goal of TQM is to "do the right things right the first time, every time." When applied to education, TQM emphasizes leadership, strategy, teamwork, and self-assessment to continually improve the education provided to students. The key principles of TQM in education include treating students as customers, continuous improvement of learning processes, and recognizing that failures are often due to systemic issues rather than individual blame.