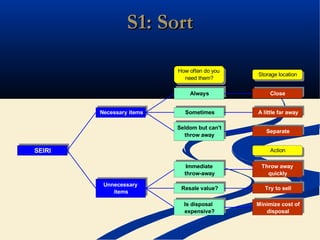
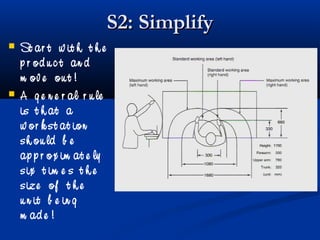
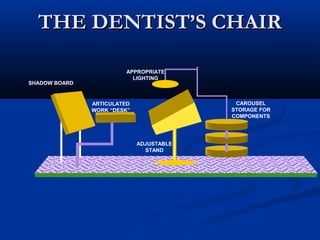
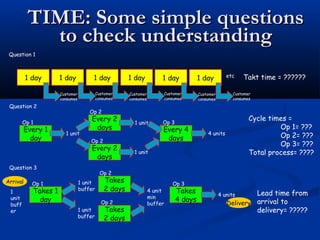
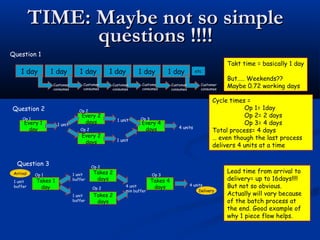
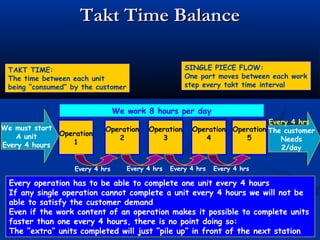
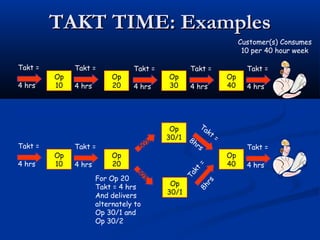
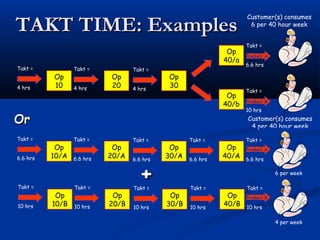
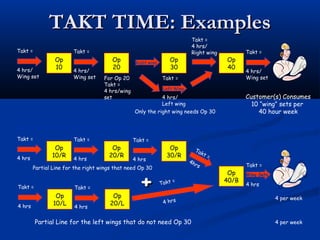
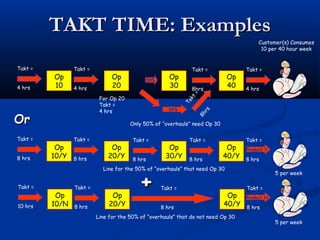
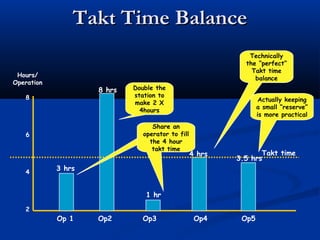
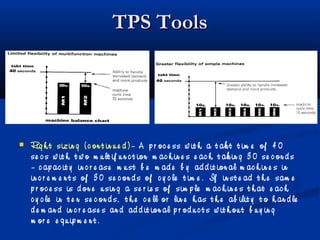
The document discusses various tools used in the Toyota Production System (TPS), including pull production, material replenishment systems (MRS), single-piece flow, takt time, and cycle time. It defines these terms and explains their importance in achieving lean production through techniques like balancing takt time across operations to reduce waste from batching and long lead times. Visual tools are emphasized for signaling needs and standardizing work processes in TPS.