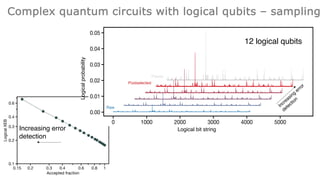
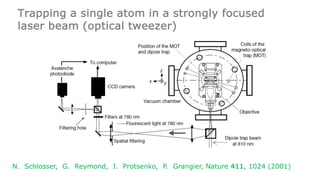
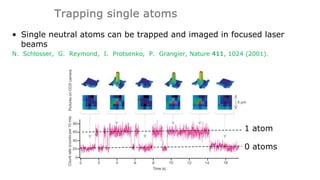
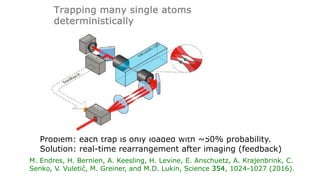
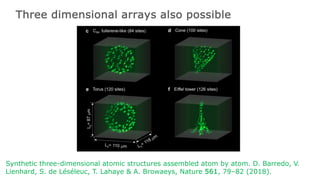
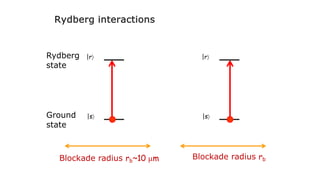
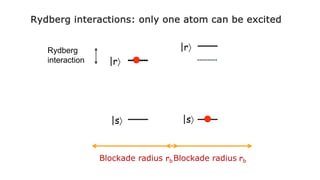
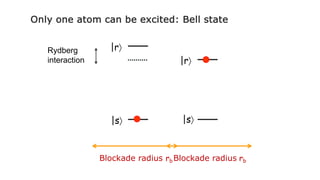
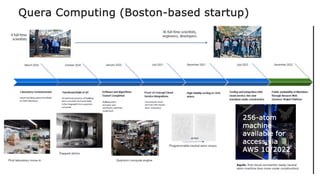
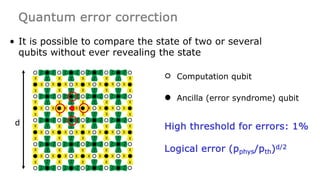
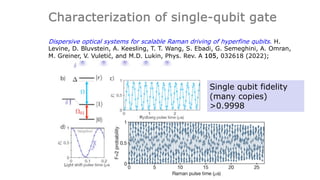
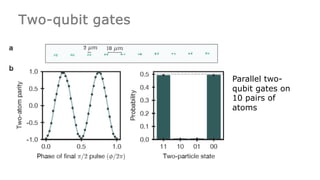
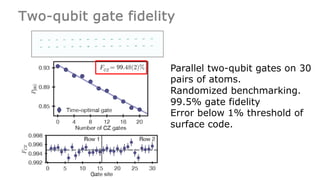
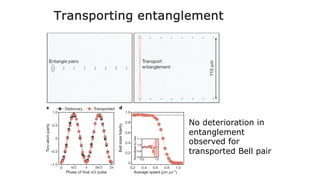
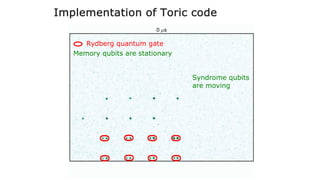
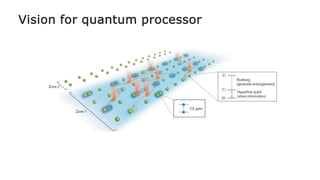
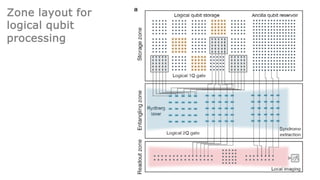
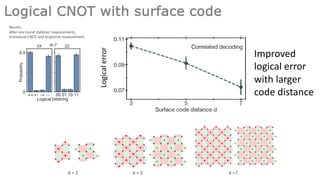
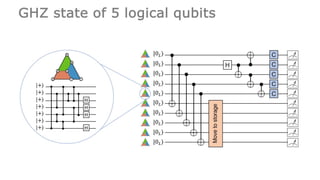
This document summarizes research on using neutral atoms for quantum computing. It describes how individual atoms can be deterministically trapped and arranged using optical tweezers and feedback. Quantum gates between atoms are performed using Rydberg interactions. High fidelity single and two-qubit gates have been achieved. Logical qubits are implemented using error correction codes like surface codes to protect against errors. Circuits with many logical qubits have been demonstrated, including GHZ states of 5 logical qubits and sampling circuits with 12 logical qubits. The goal is to scale up to thousands of physical qubits and hundreds of high-fidelity logical qubits for running quantum algorithms.














![Classically hard sampling circuits
with logical qubits: [[8,3,2]] hypercube
code
12 logical
qubits](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/vladanvuleticq2bsv2023presentation-231209231044-e57a9bc9/85/Towards-Error-Corrected-Quantum-Computing-with-Neutral-Atoms-33-320.jpg)