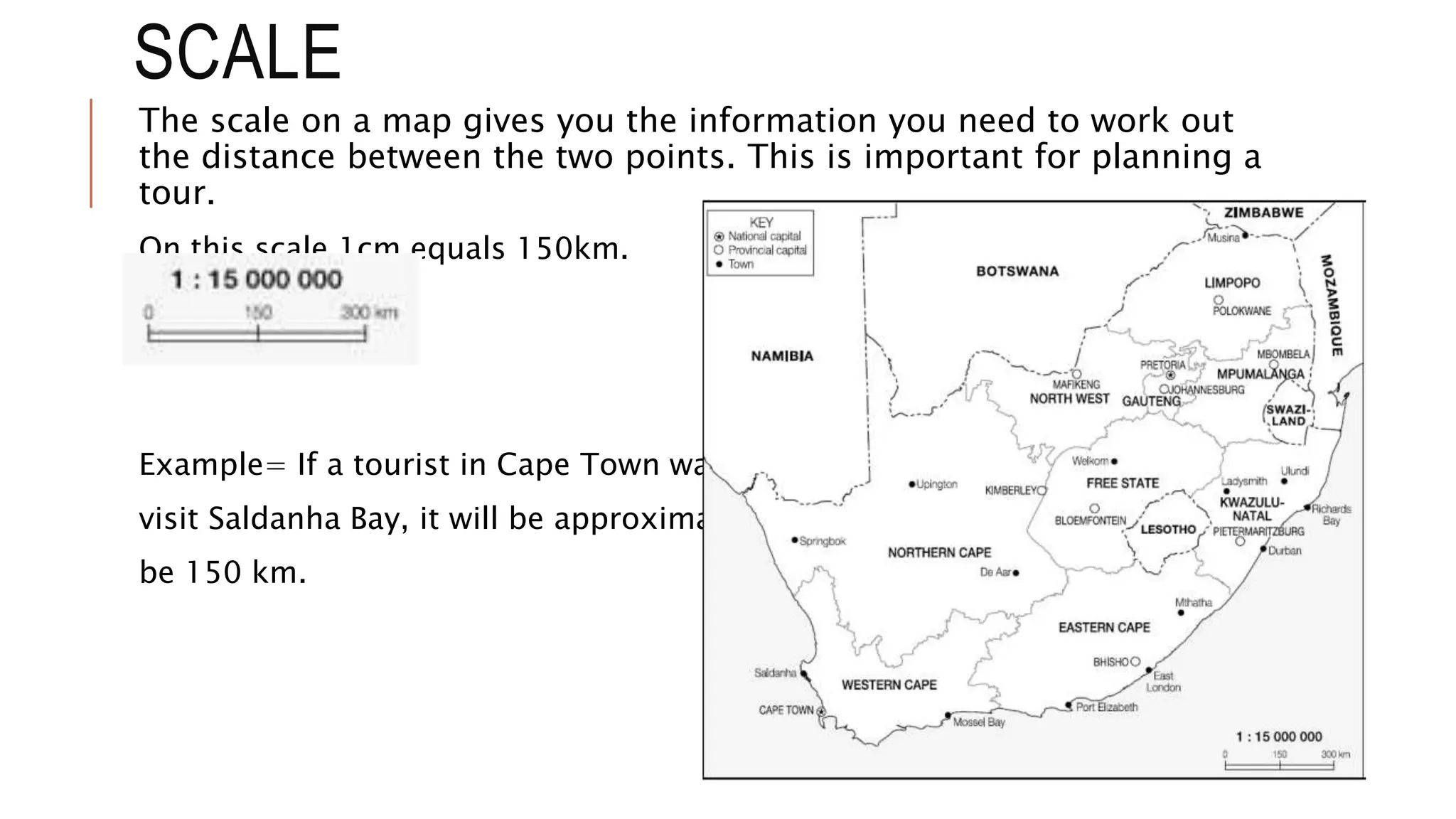
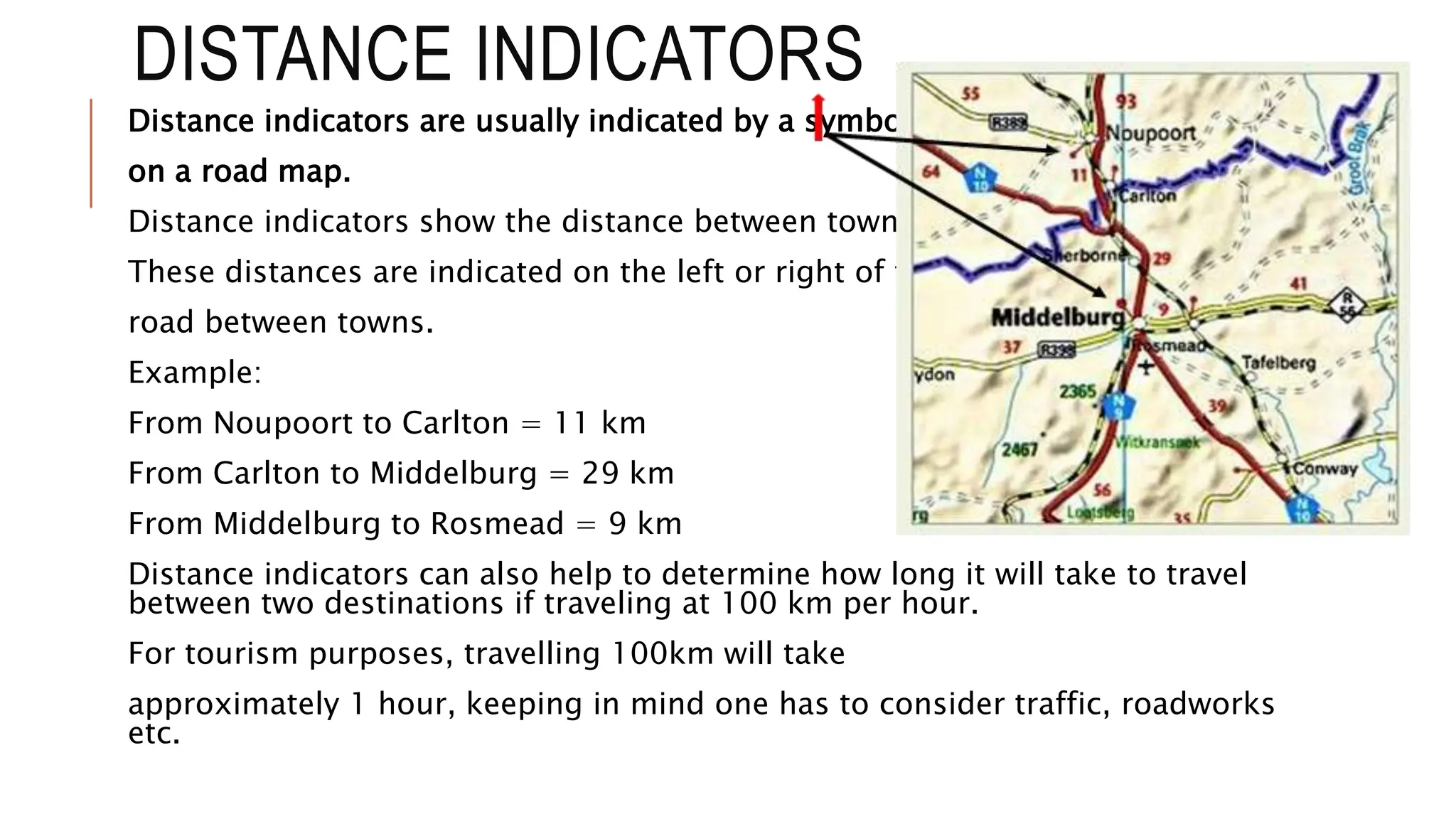
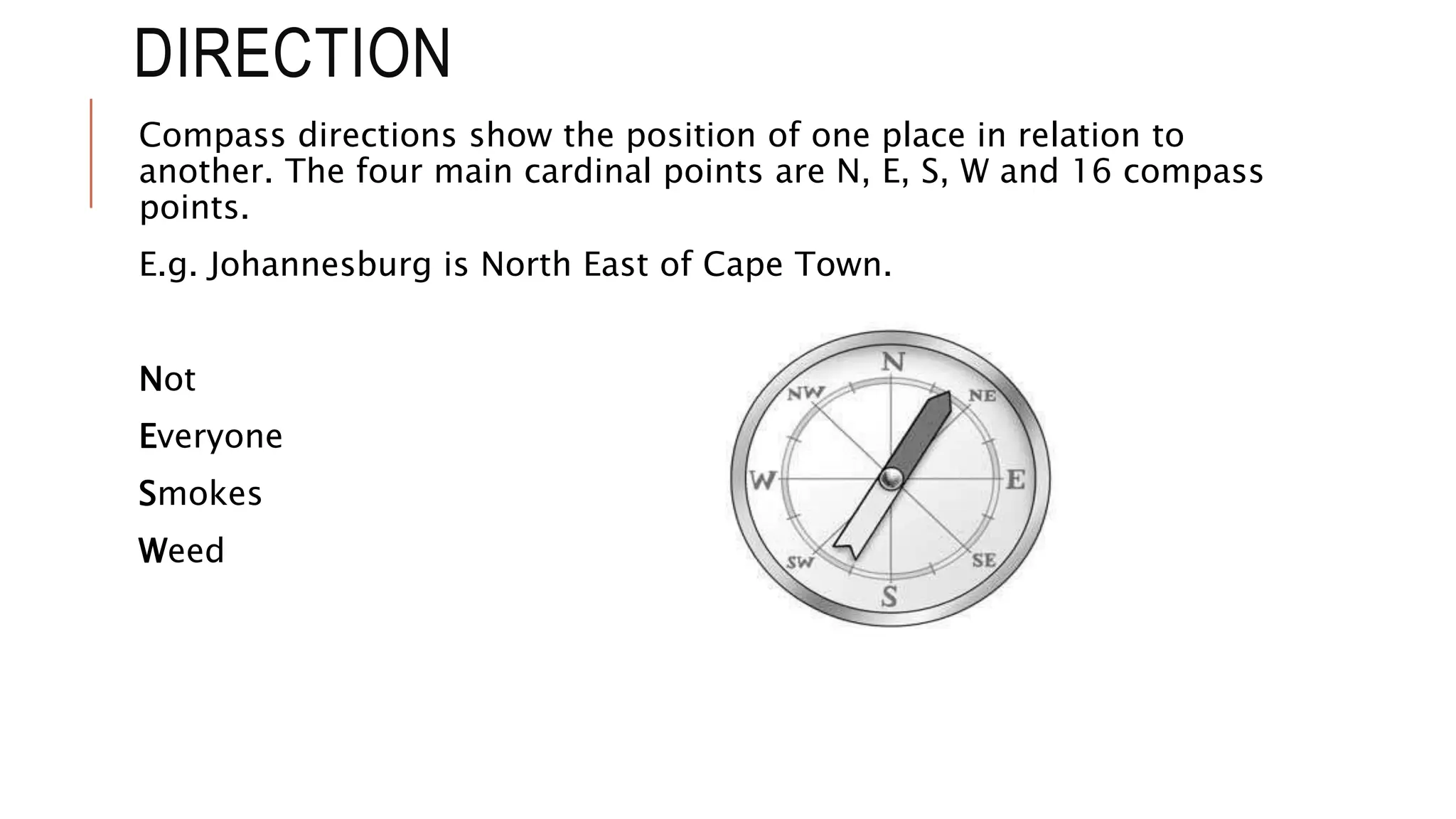
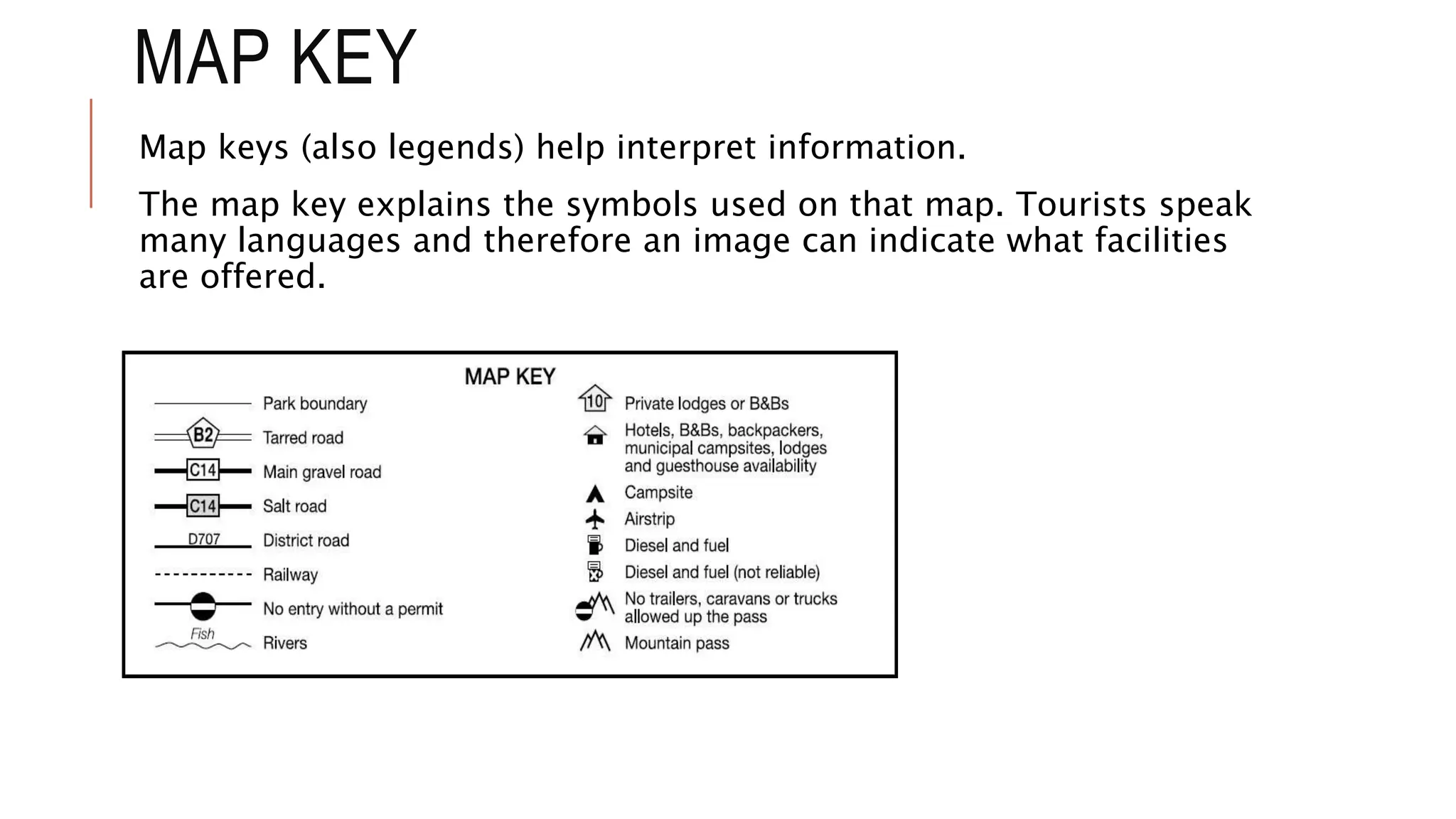
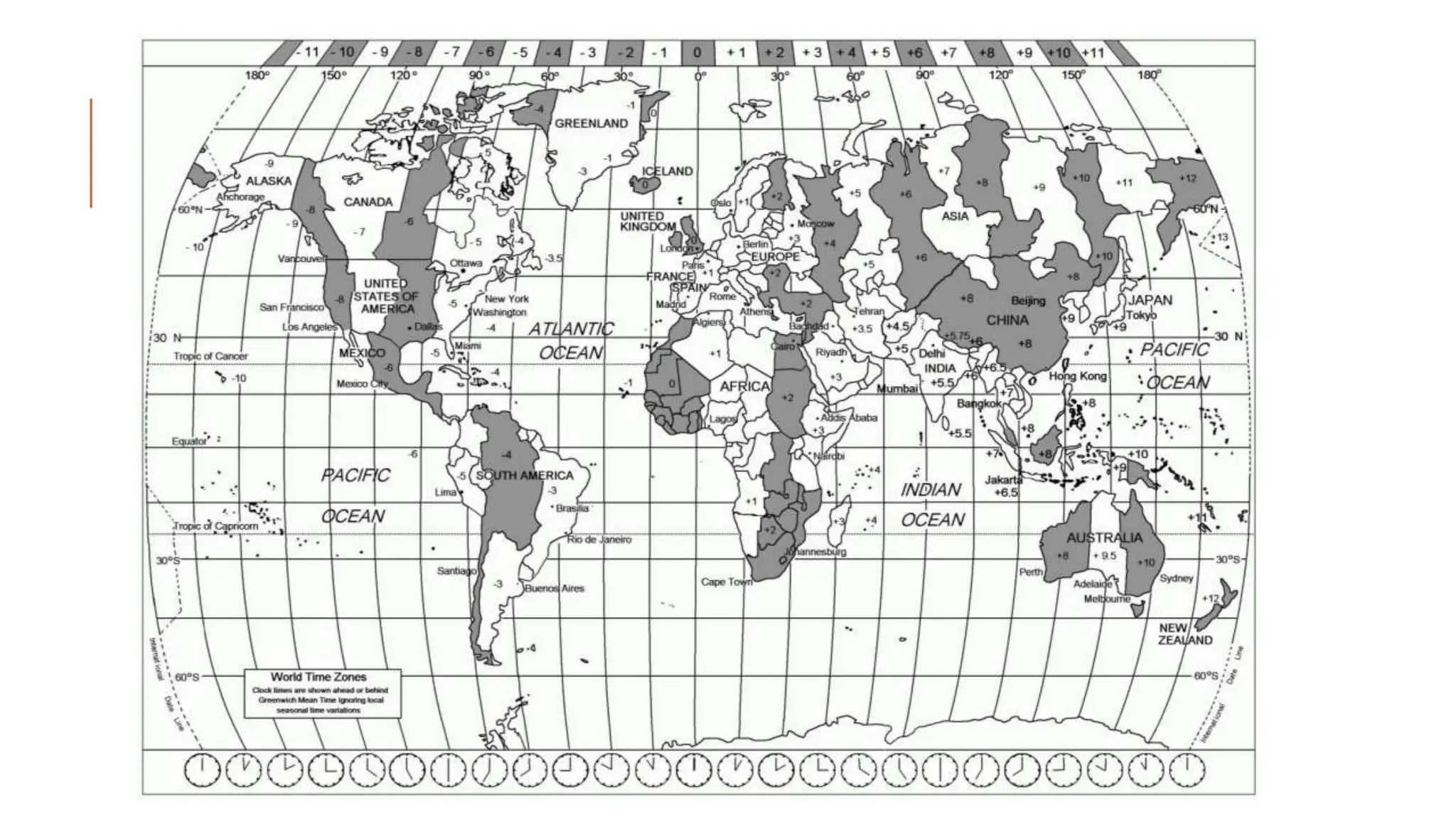
The document explains key map terminology and symbols essential for navigation, including scales, distance indicators, and compass directions, which help tourists plan their travels. It discusses various types of maps, such as road, street, political, physical, and electronic maps, highlighting their specific uses and features for tourists. Additionally, it covers the importance of time zones, the international date line, and the role of information communication technology in facilitating travel planning.