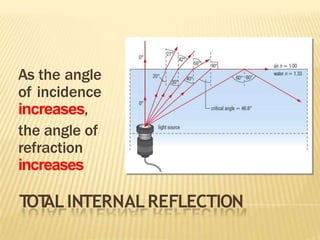
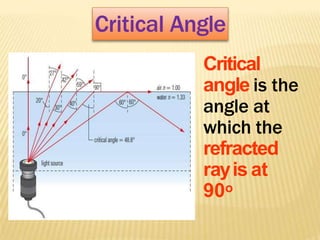
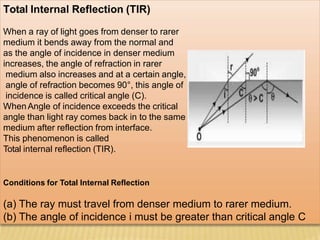
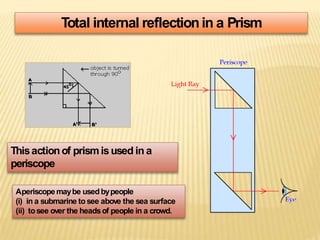
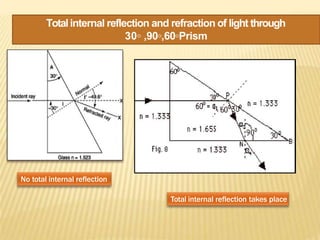
This document discusses total internal reflection and the critical angle. It explains that total internal reflection occurs when light travels from an optically denser medium to a less dense medium at an angle of incidence greater than the critical angle. At the critical angle, the refracted ray is at 90 degrees and any greater angle of incidence results in total internal reflection where the light ray is reflected back into the denser medium. Examples where total internal reflection is used include fiber optics, periscopes, and diamonds where multiple reflections inside the gem produce sparkling.