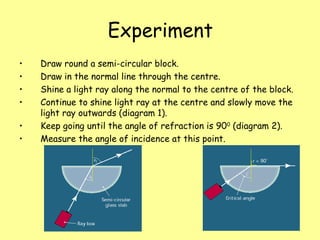
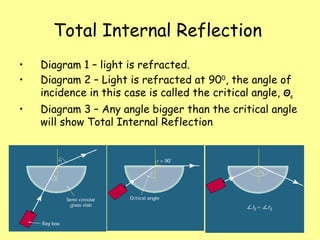
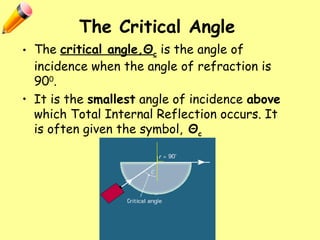
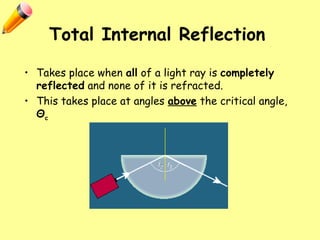
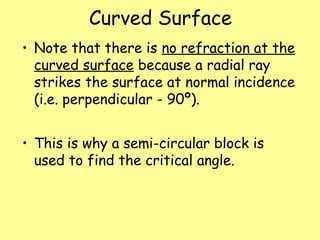
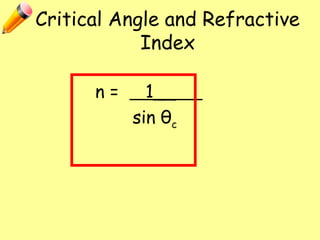
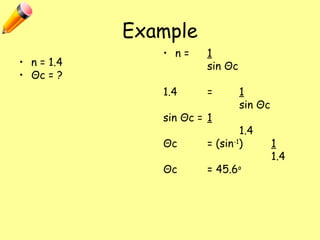
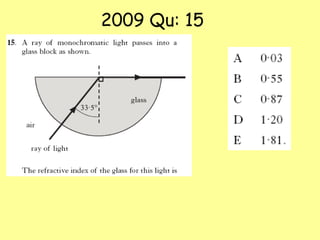
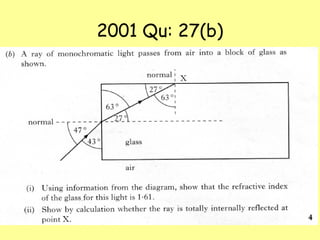
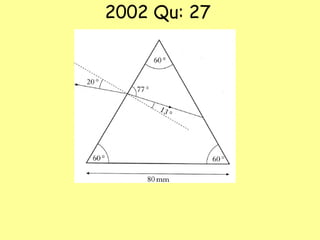
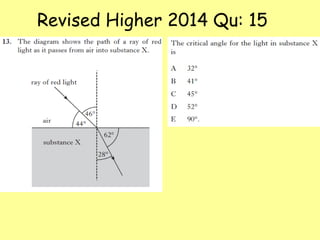
The document explains total internal reflection and the critical angle, emphasizing their relationship with refractive index and the conditions for total internal reflection to occur. It outlines an experimental procedure to find the critical angle, including diagrams and calculations. Furthermore, it highlights applications of total internal reflection in telecommunications, such as in optical fibers.