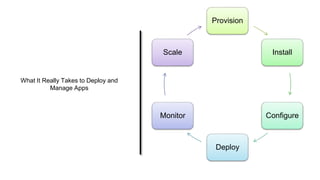
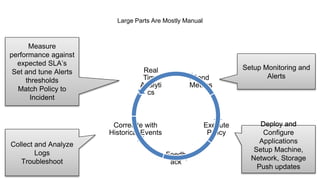
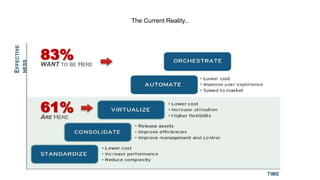
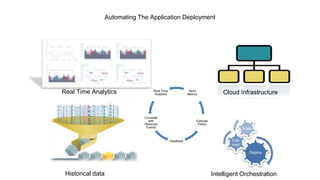
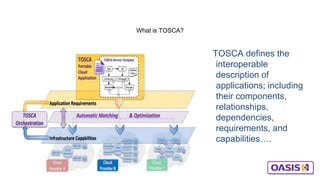
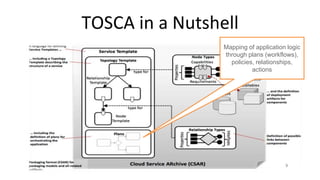
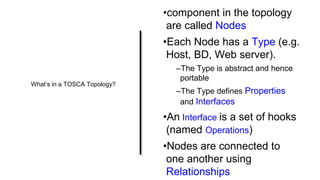
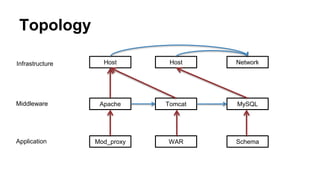
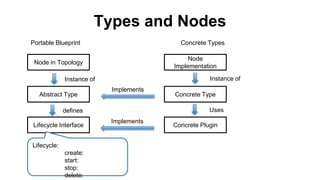
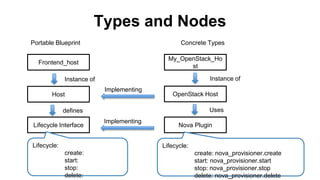
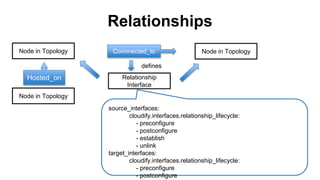
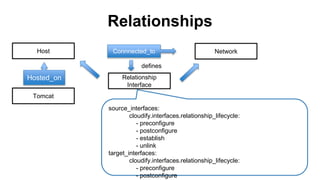
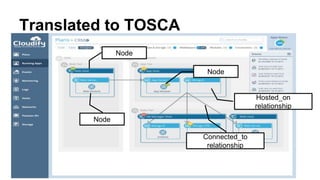
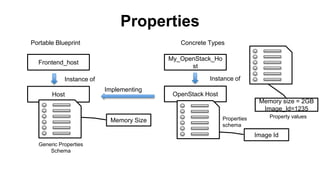
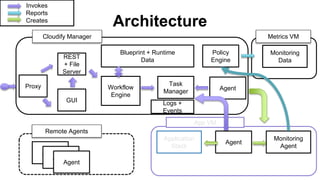
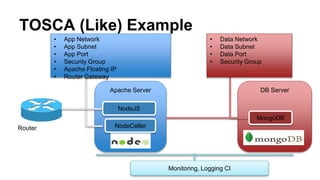
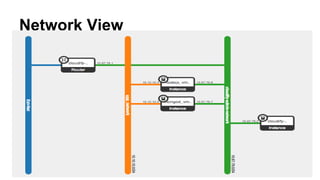
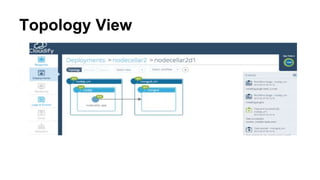
This document discusses application and network orchestration using TOSCA. It provides an overview of TOSCA, including its goals of enabling cross-cloud and cross-tool orchestration. It describes the key TOSCA building blocks such as topologies, workflows, policies, and how they are used to define application components, relationships, and orchestration logic in a portable way. Examples of defining a TOSCA topology and blueprint are also given.