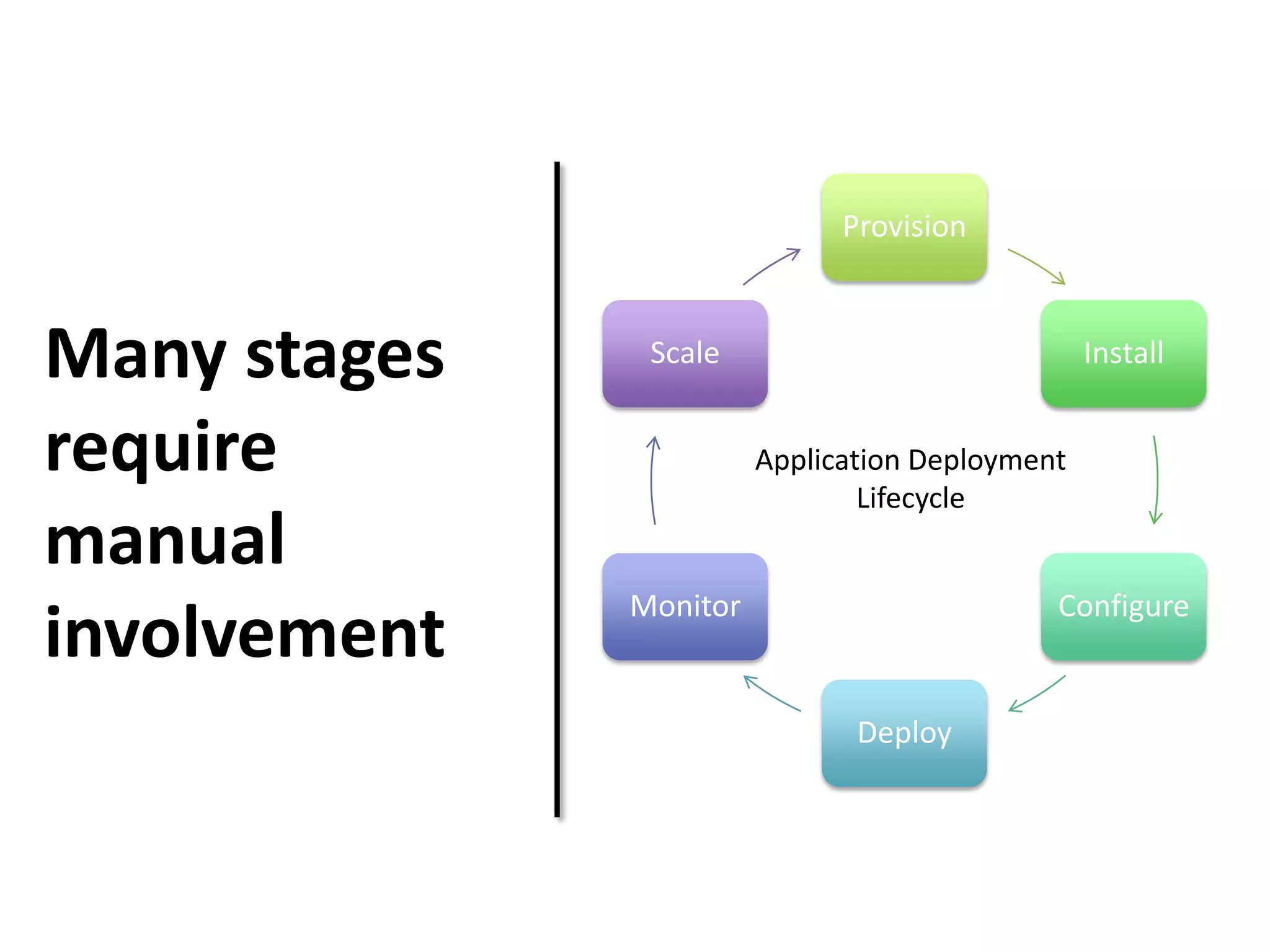
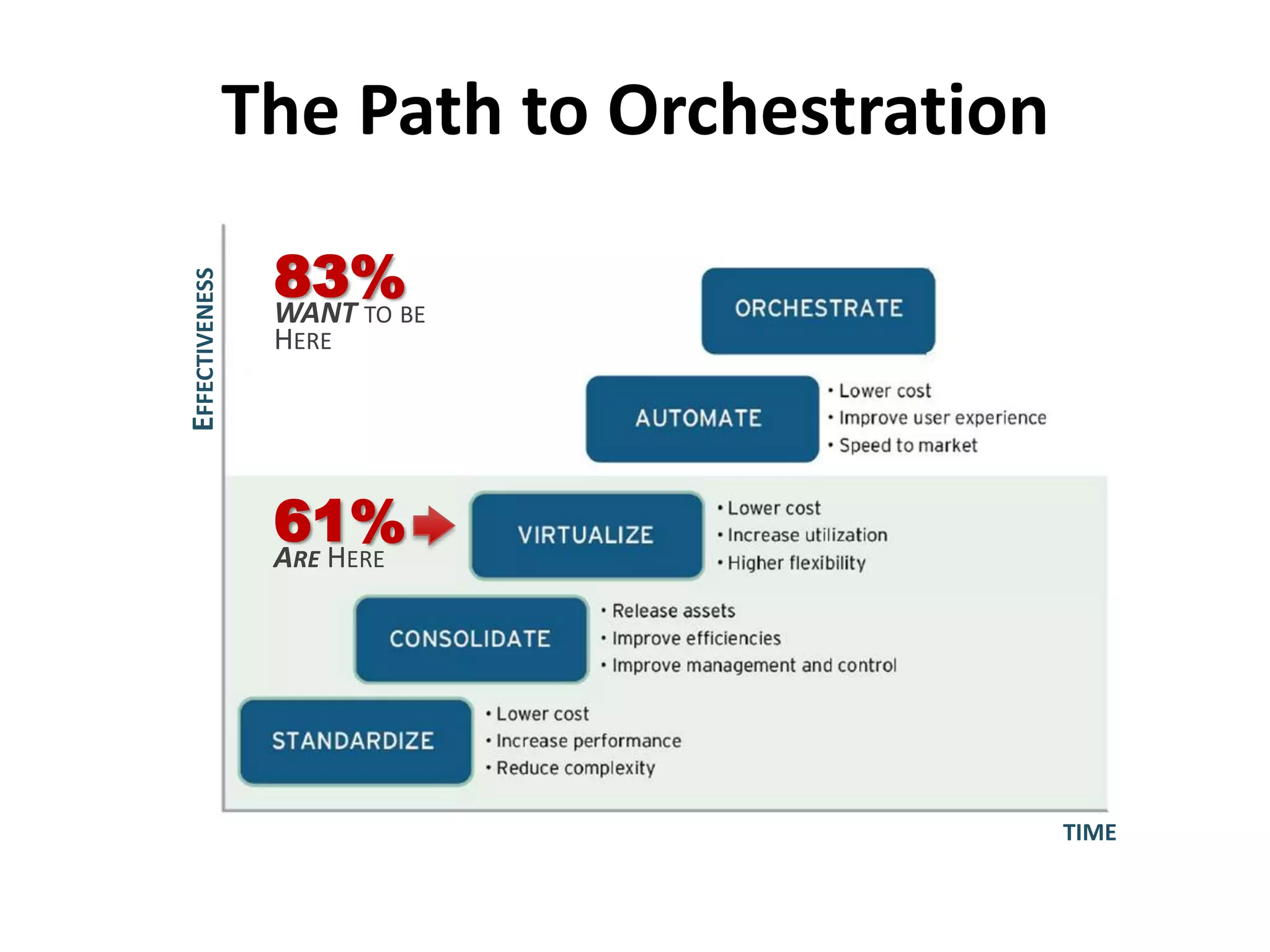
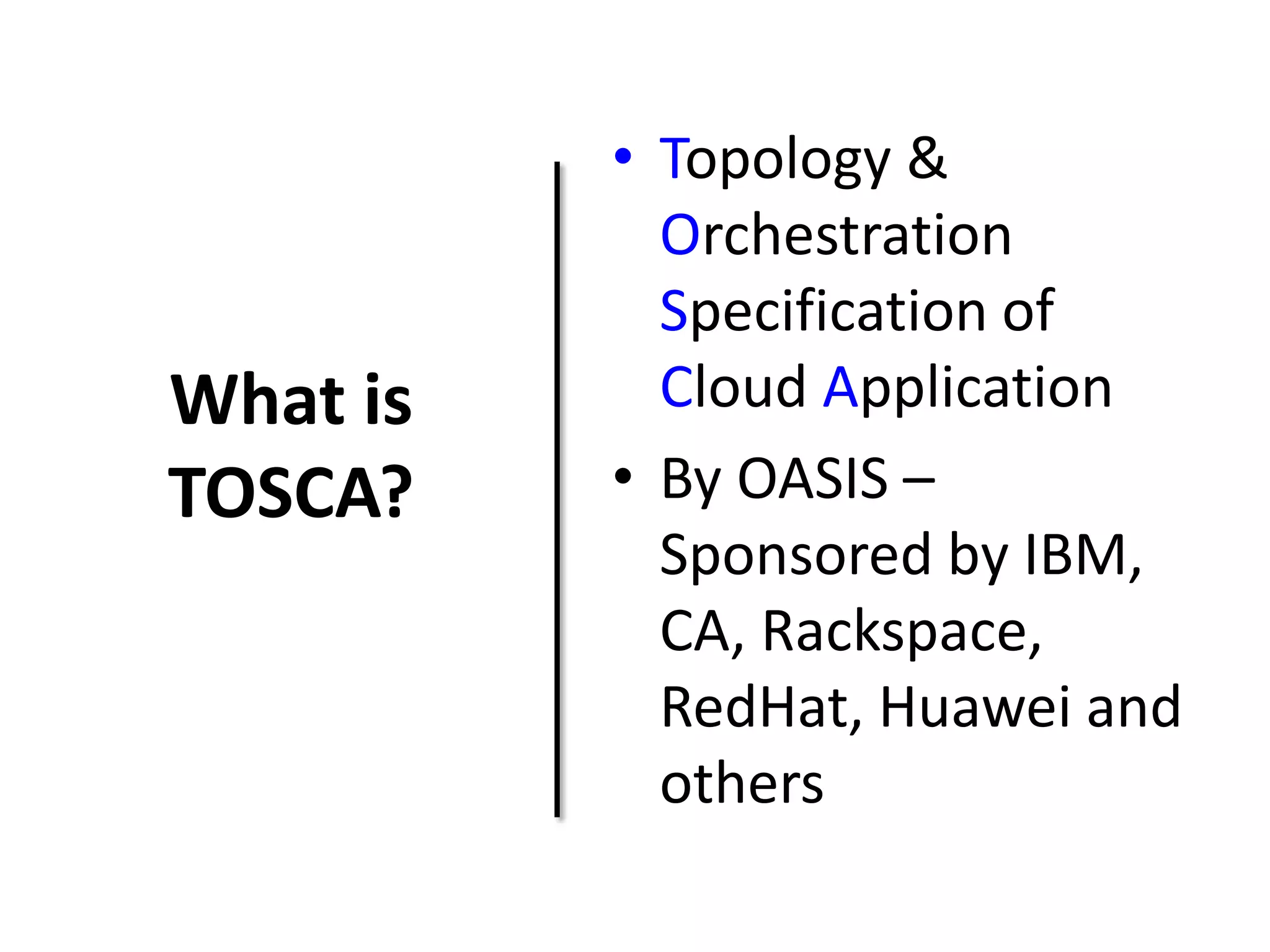
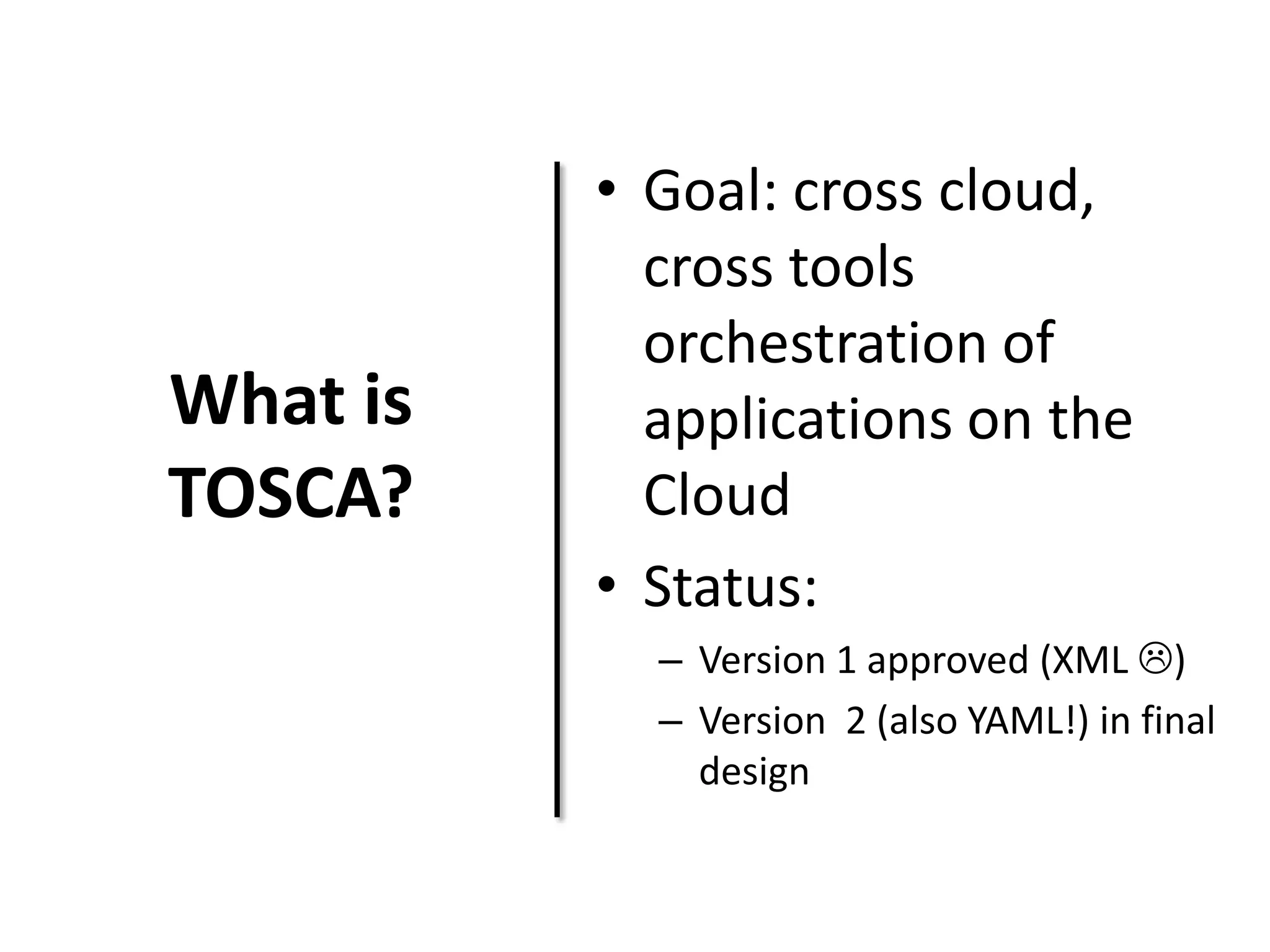
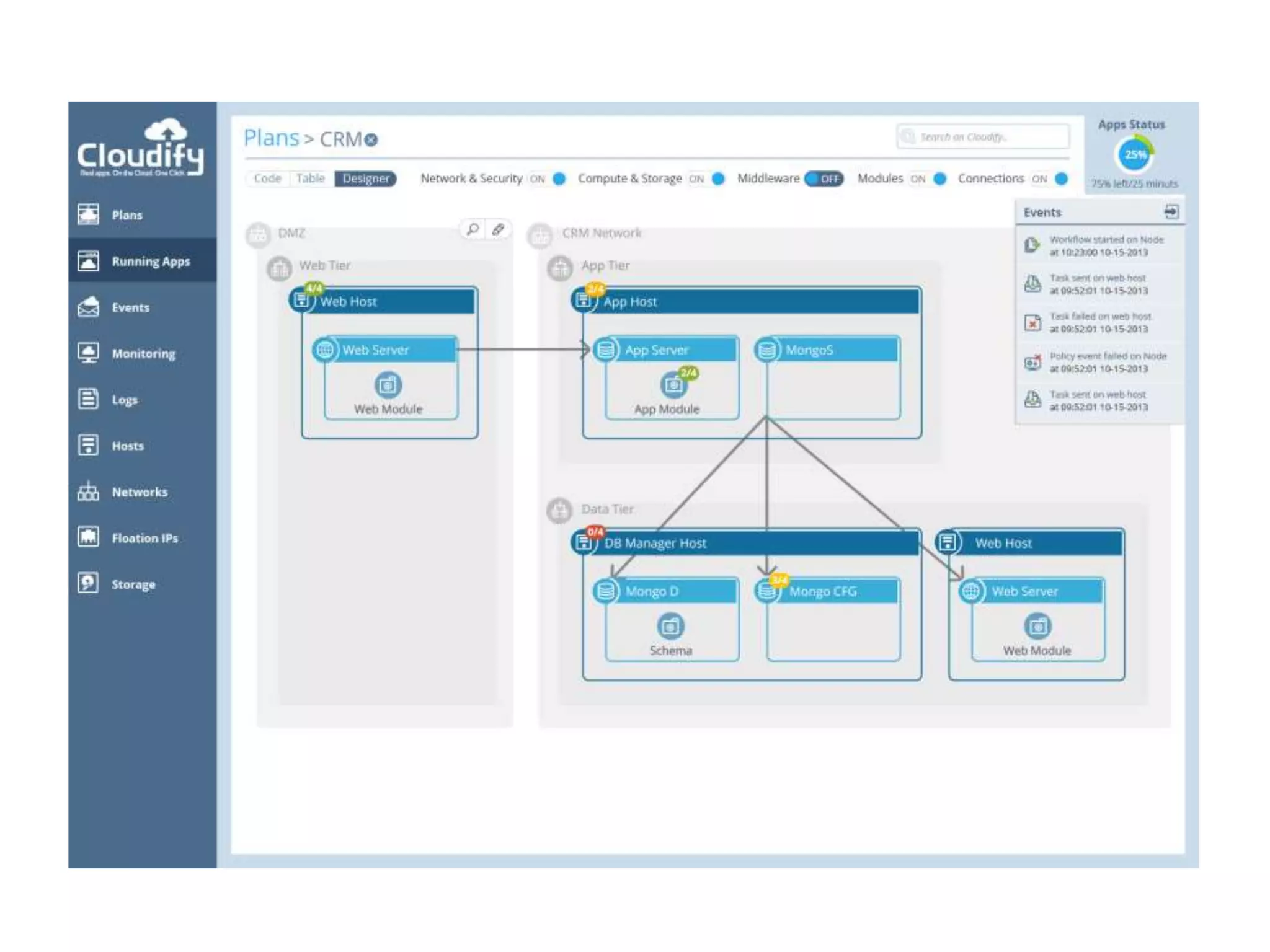
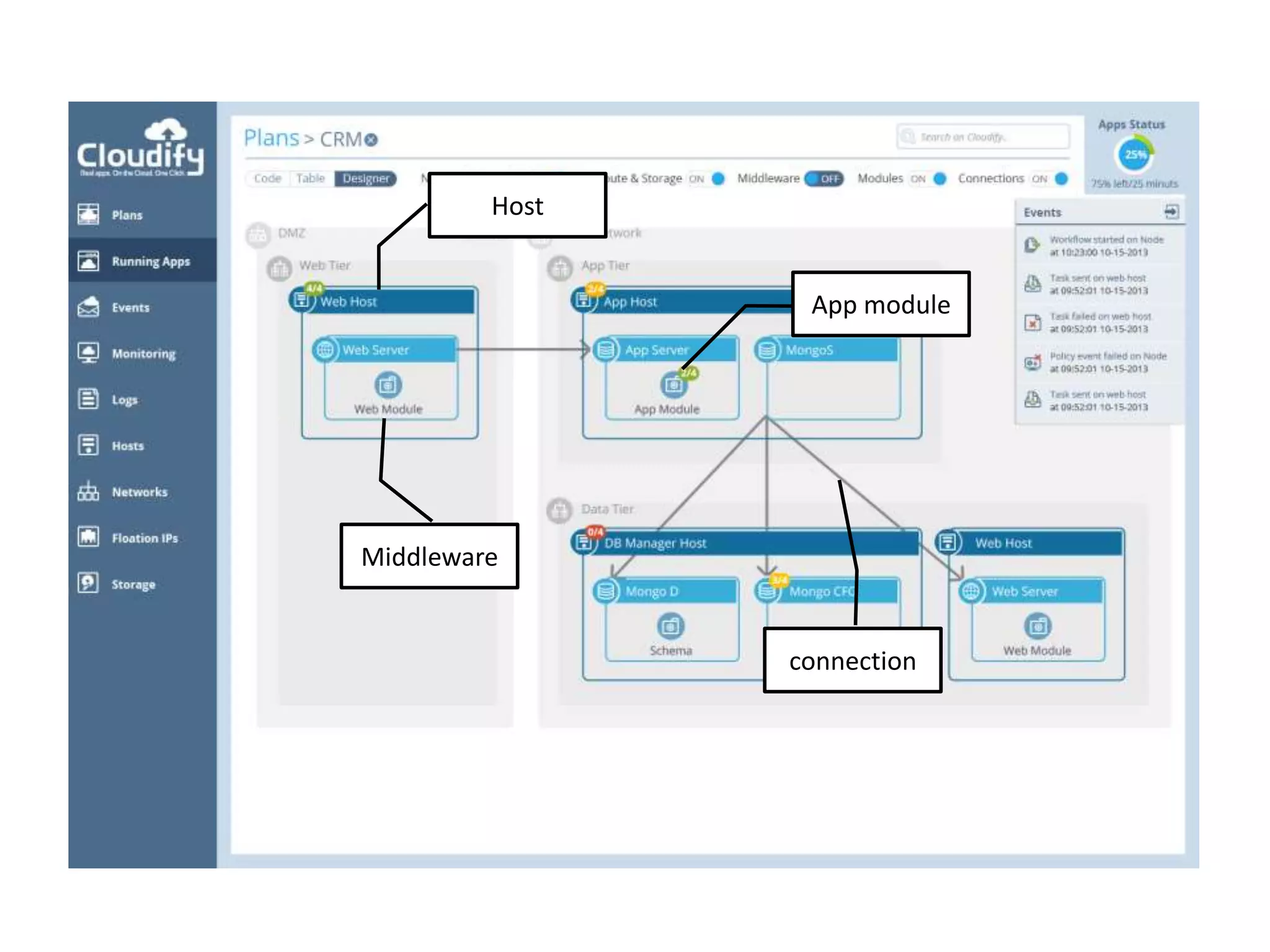
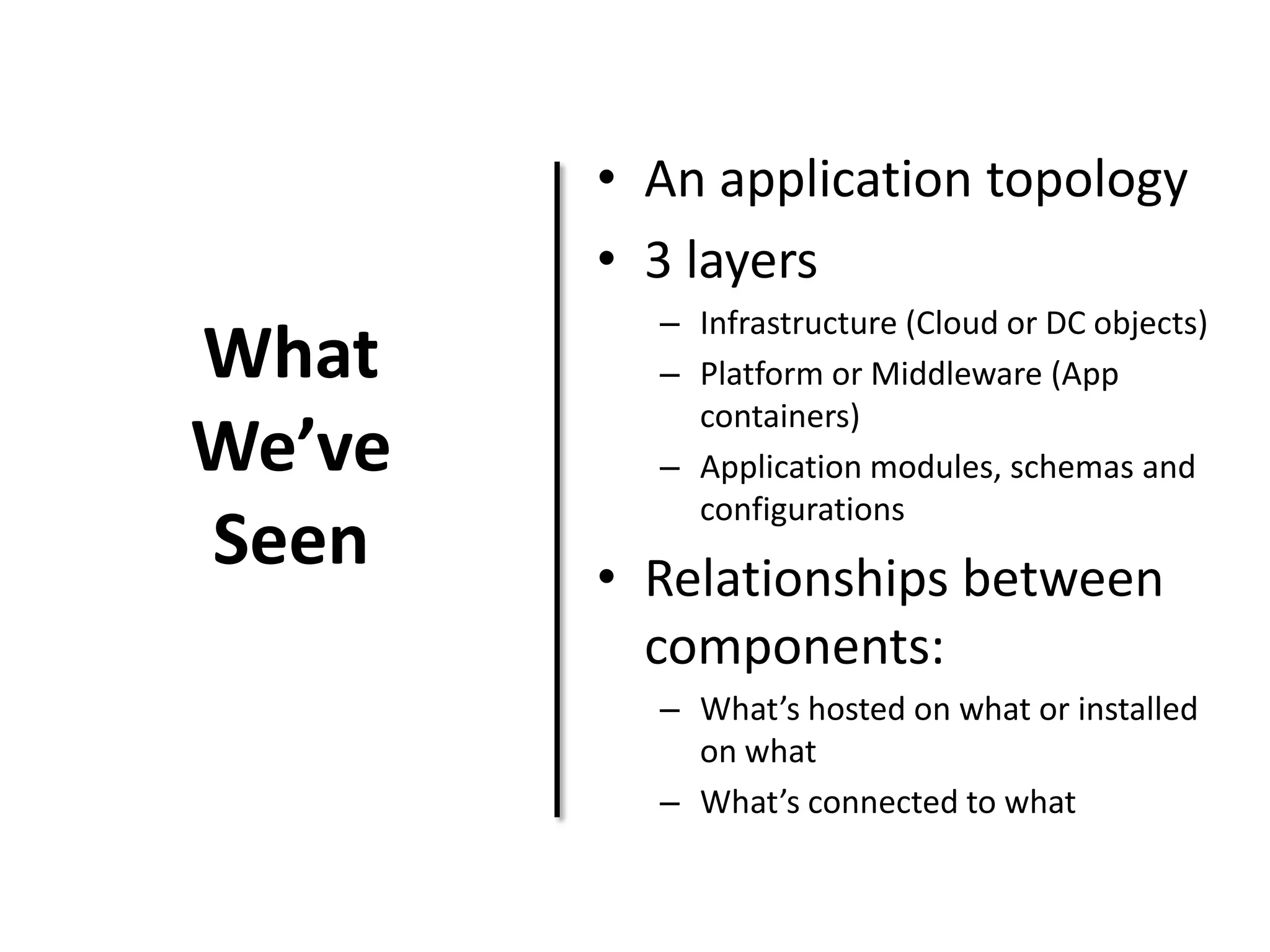
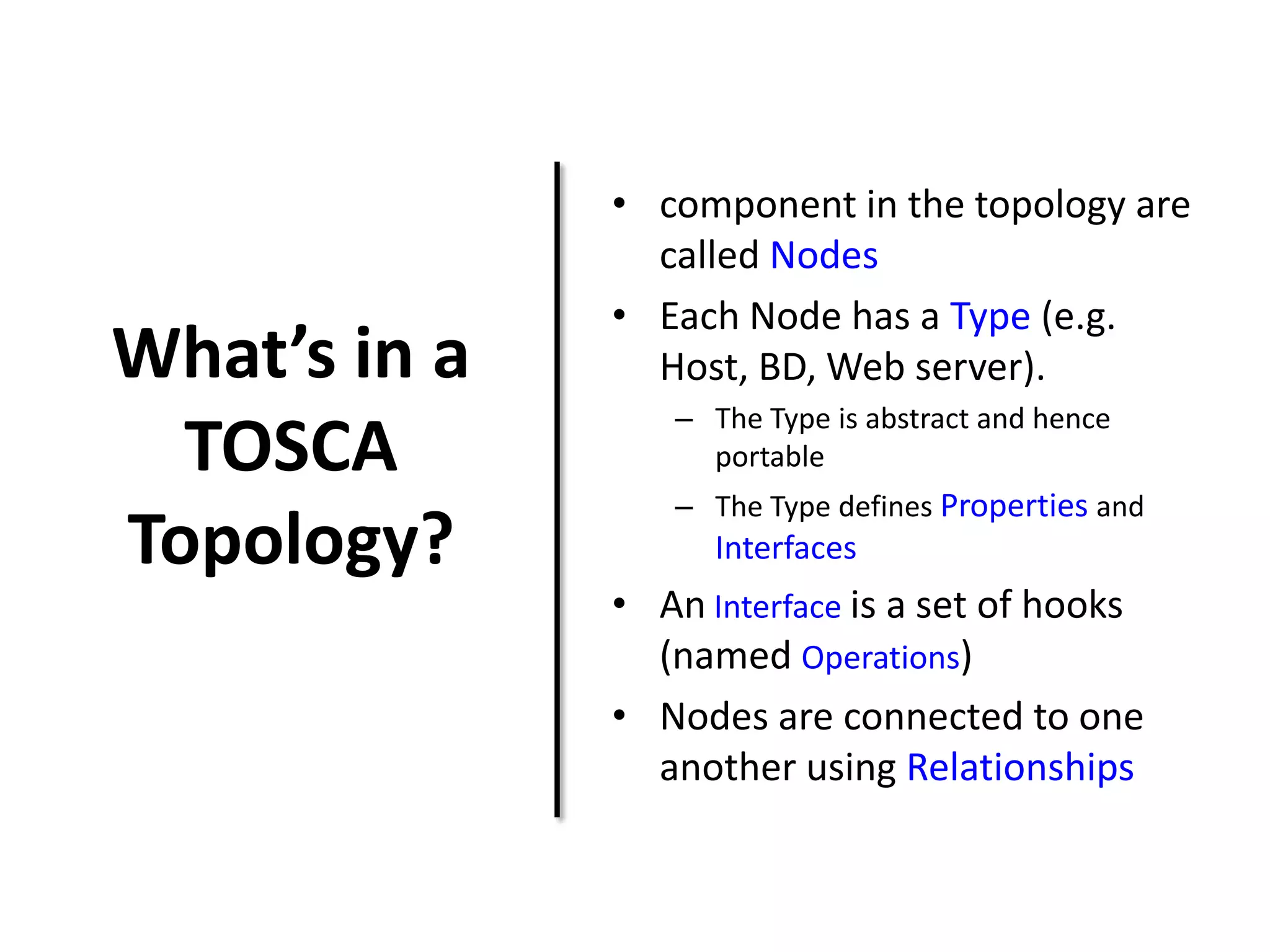
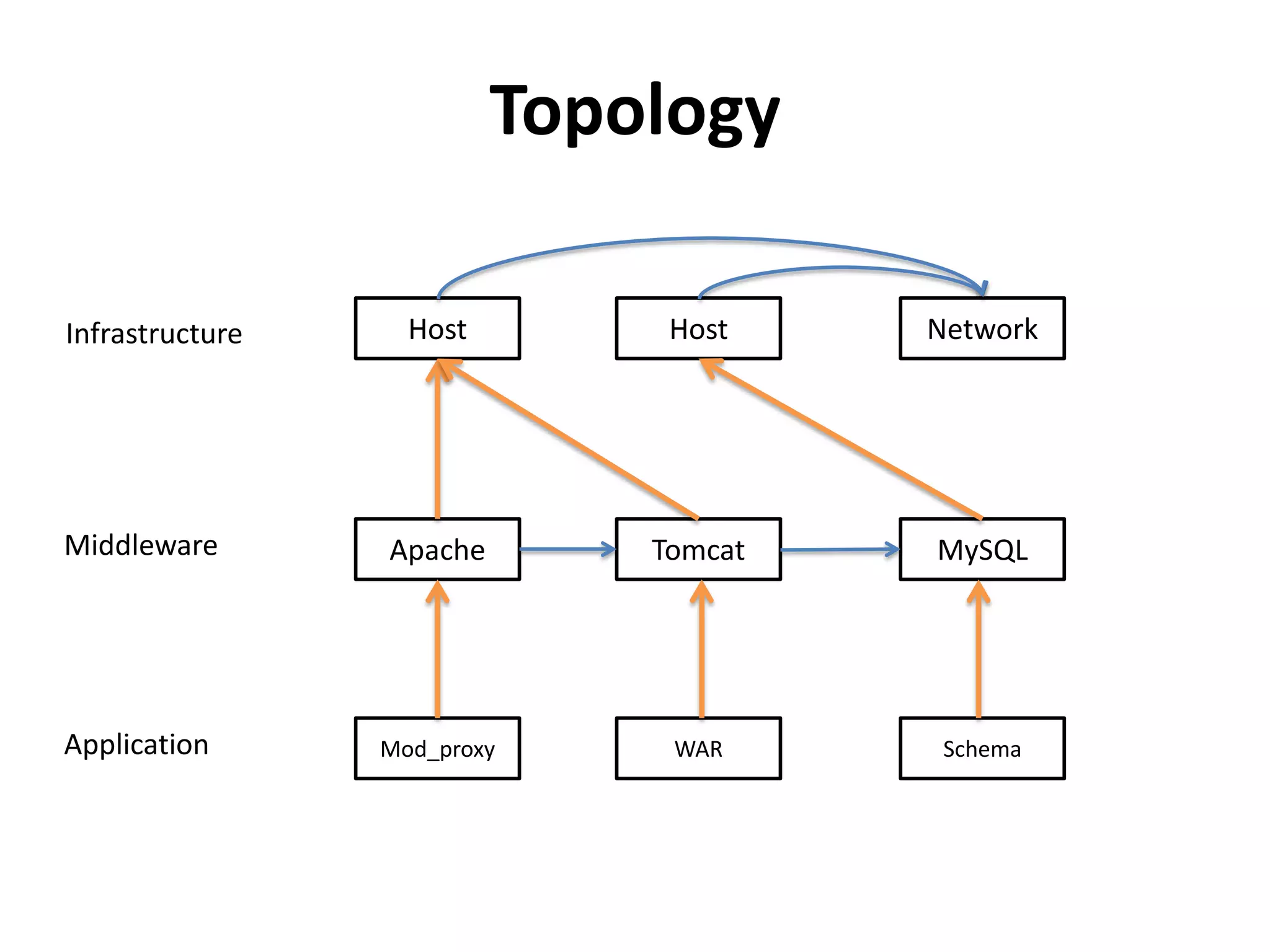
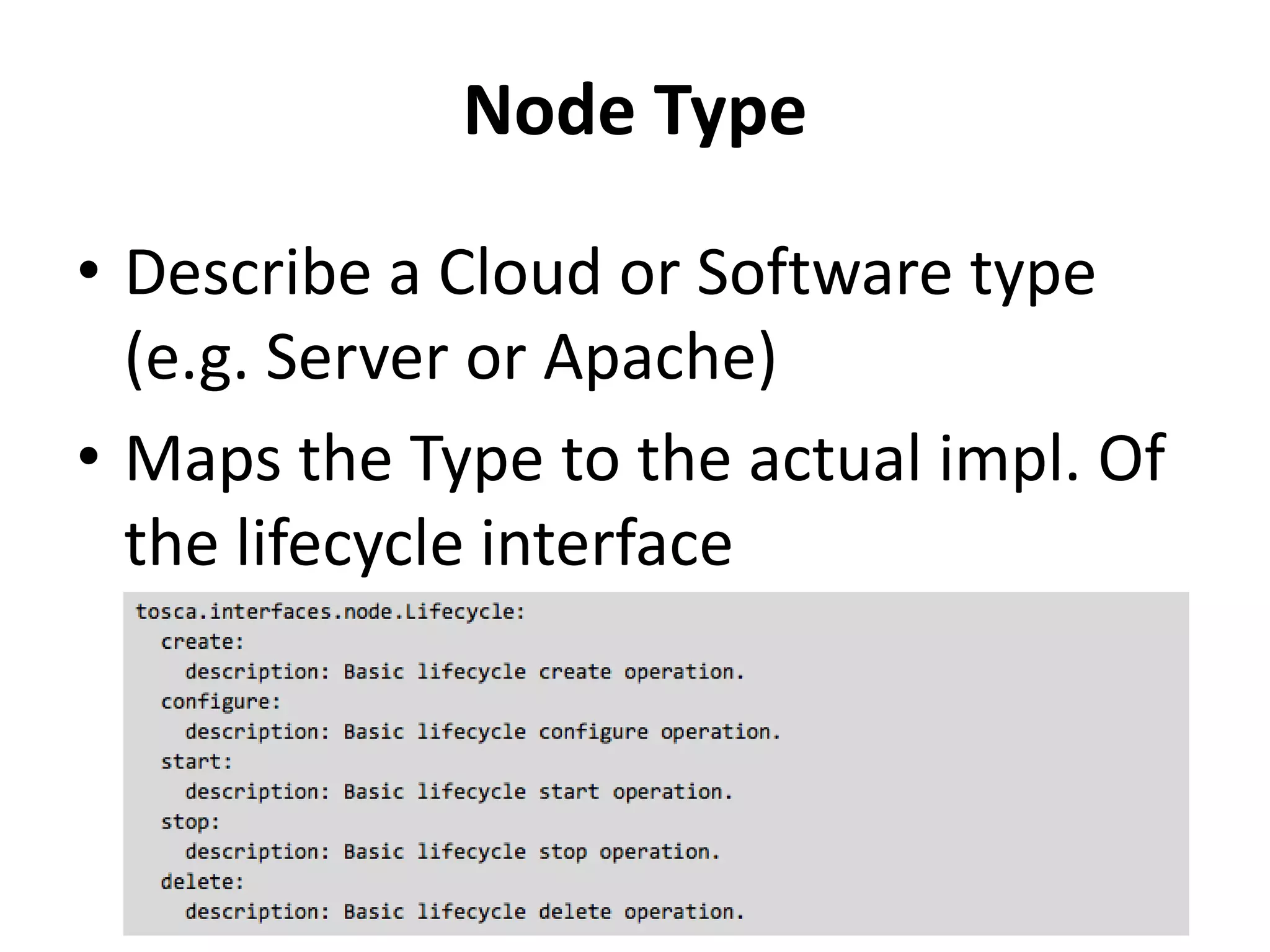
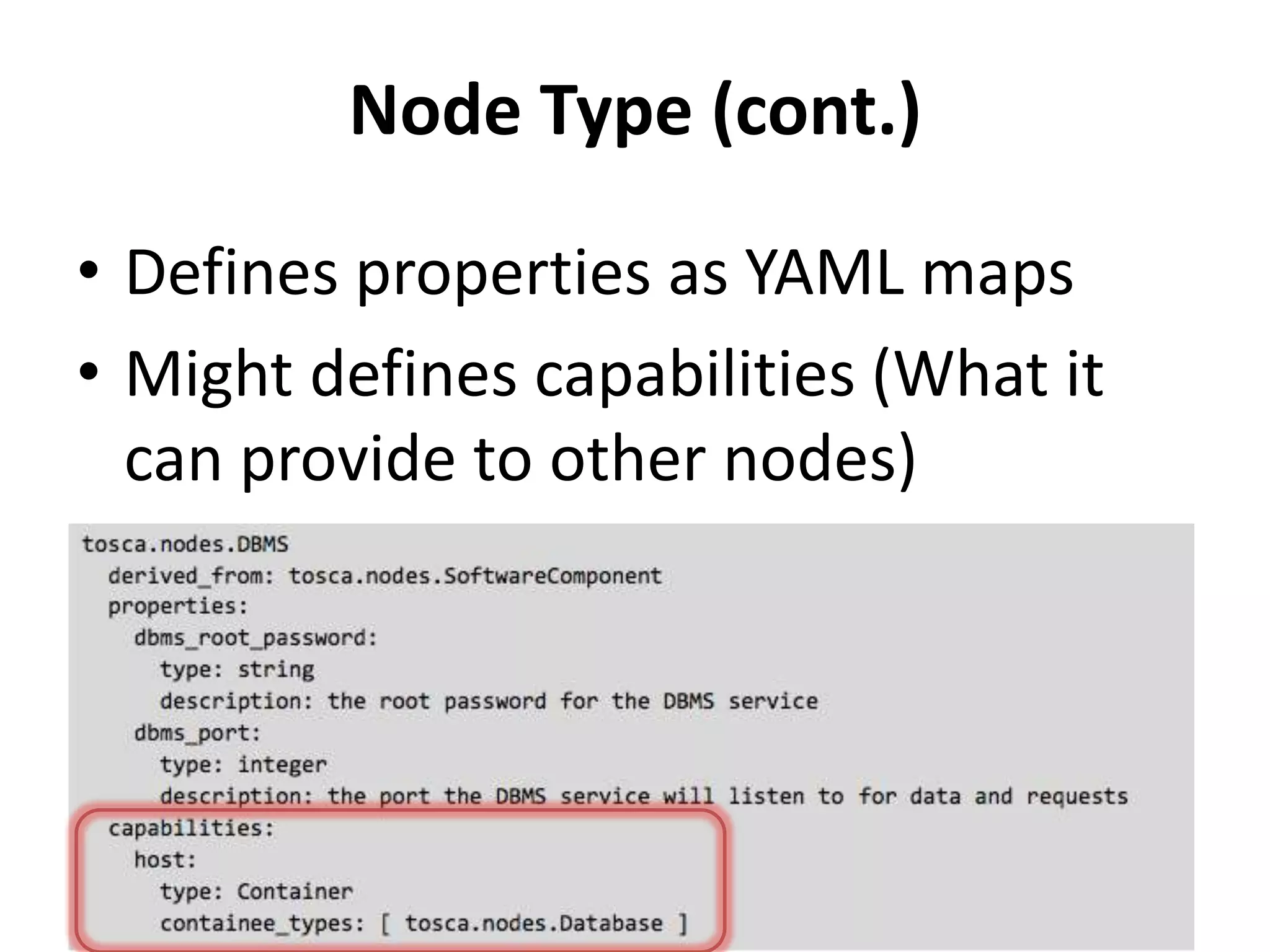
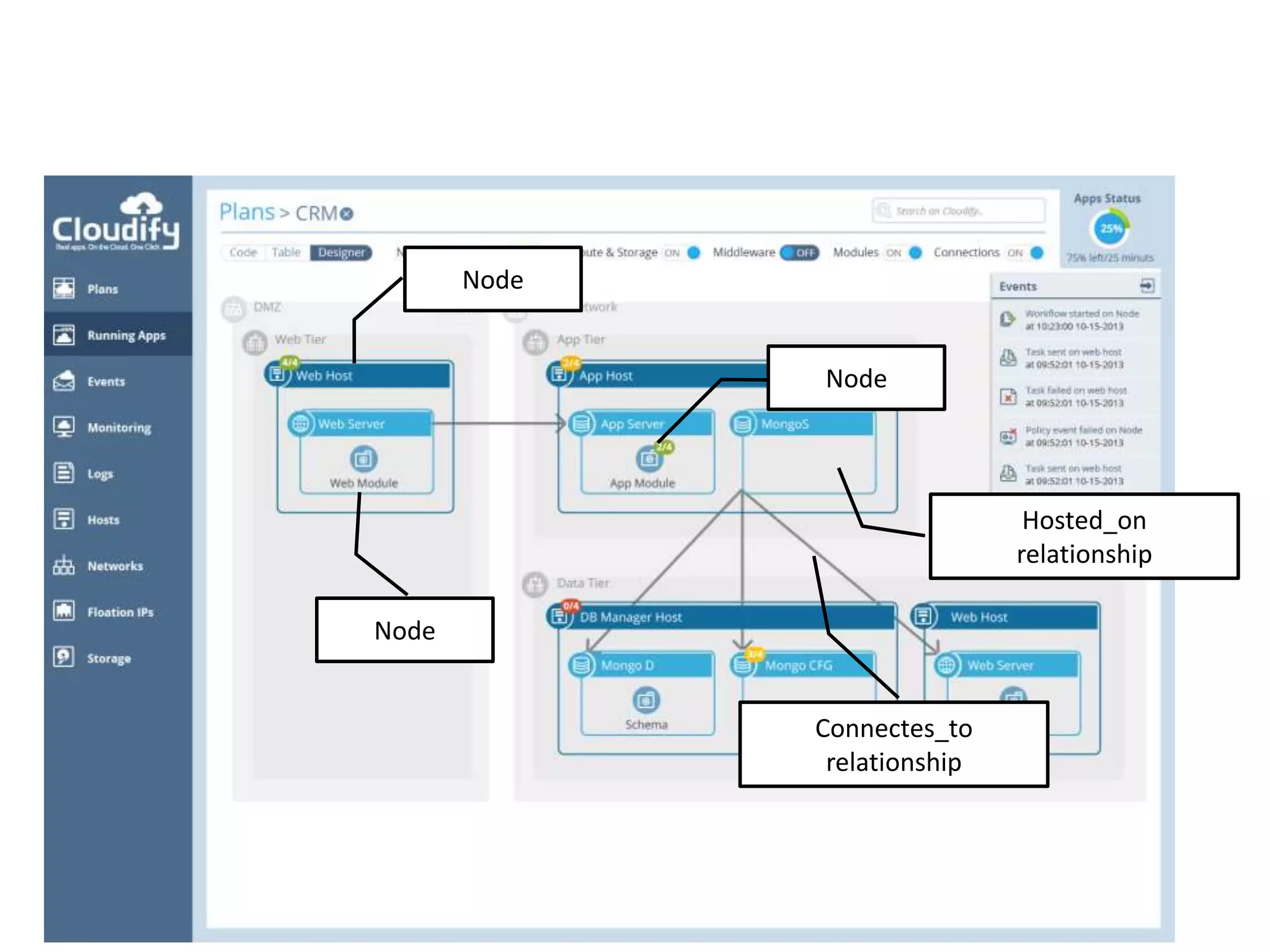
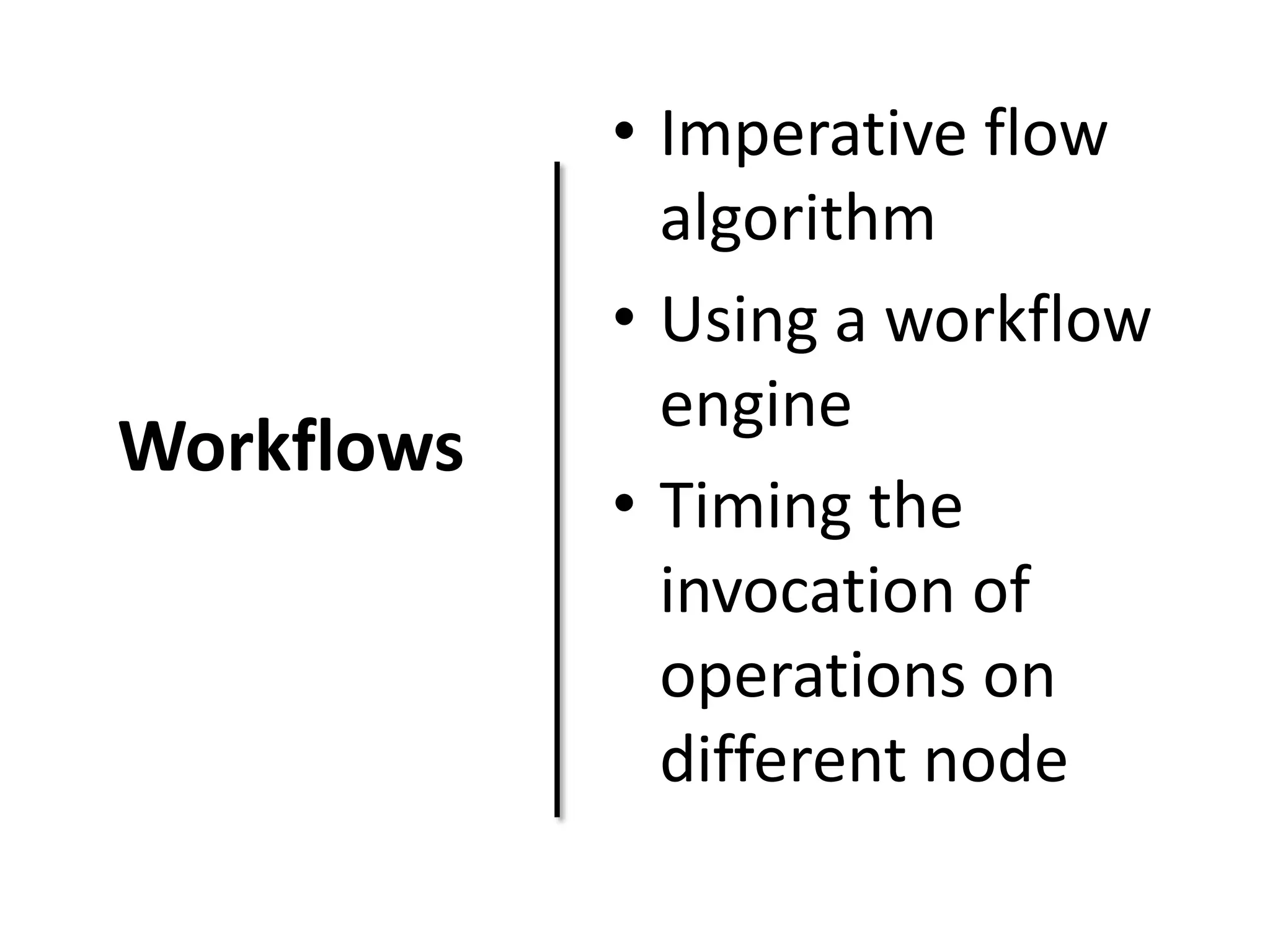
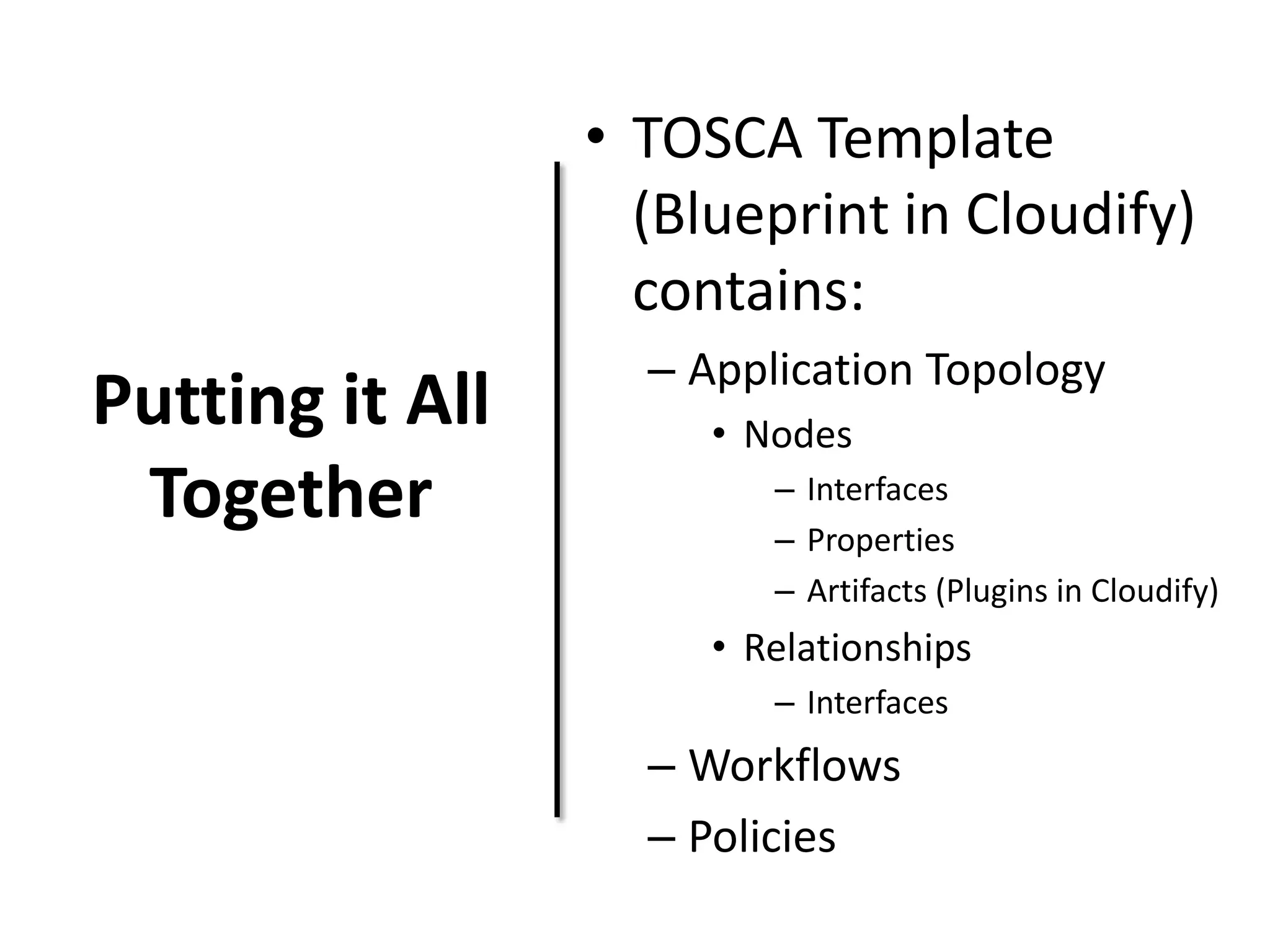
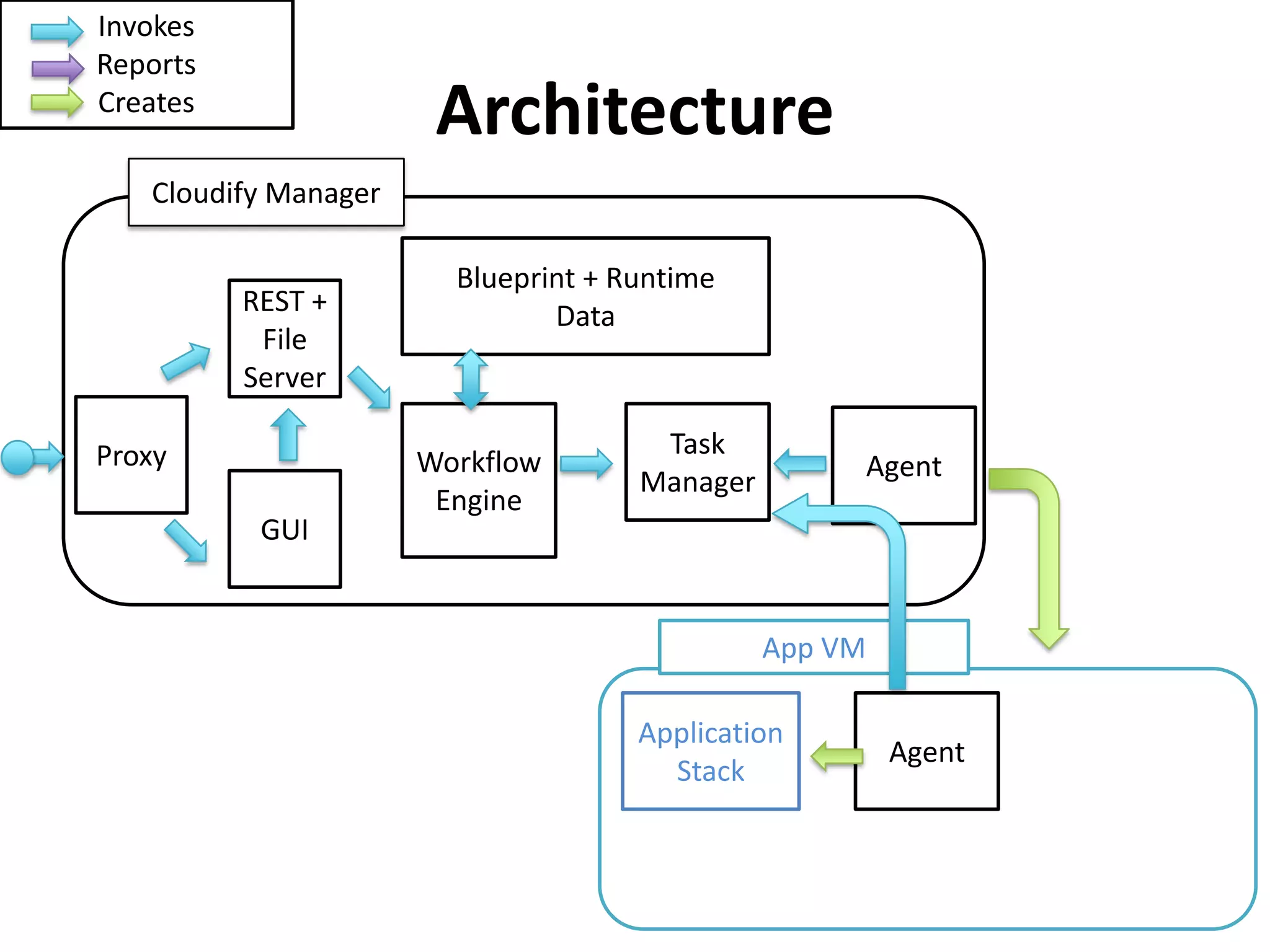
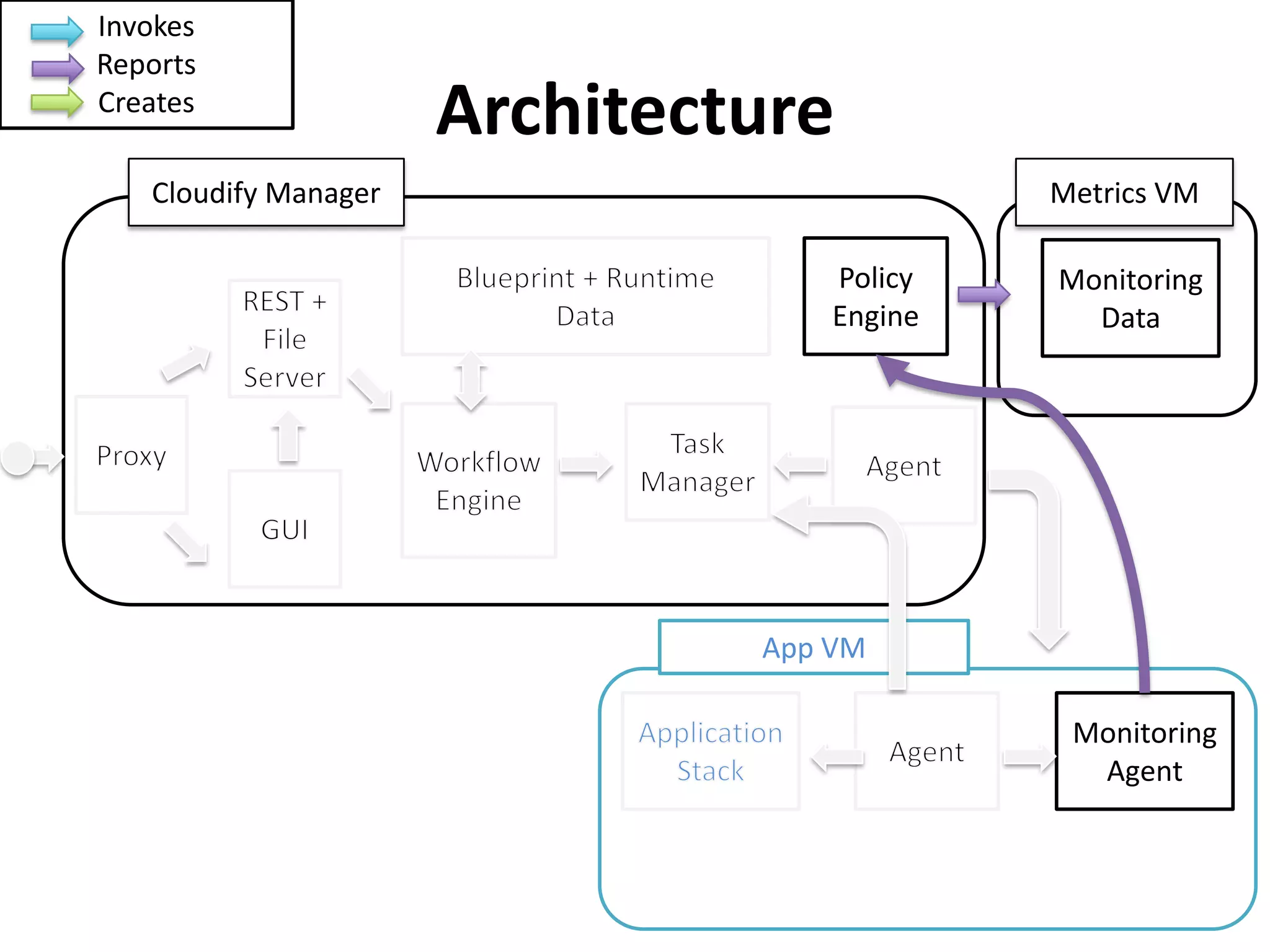
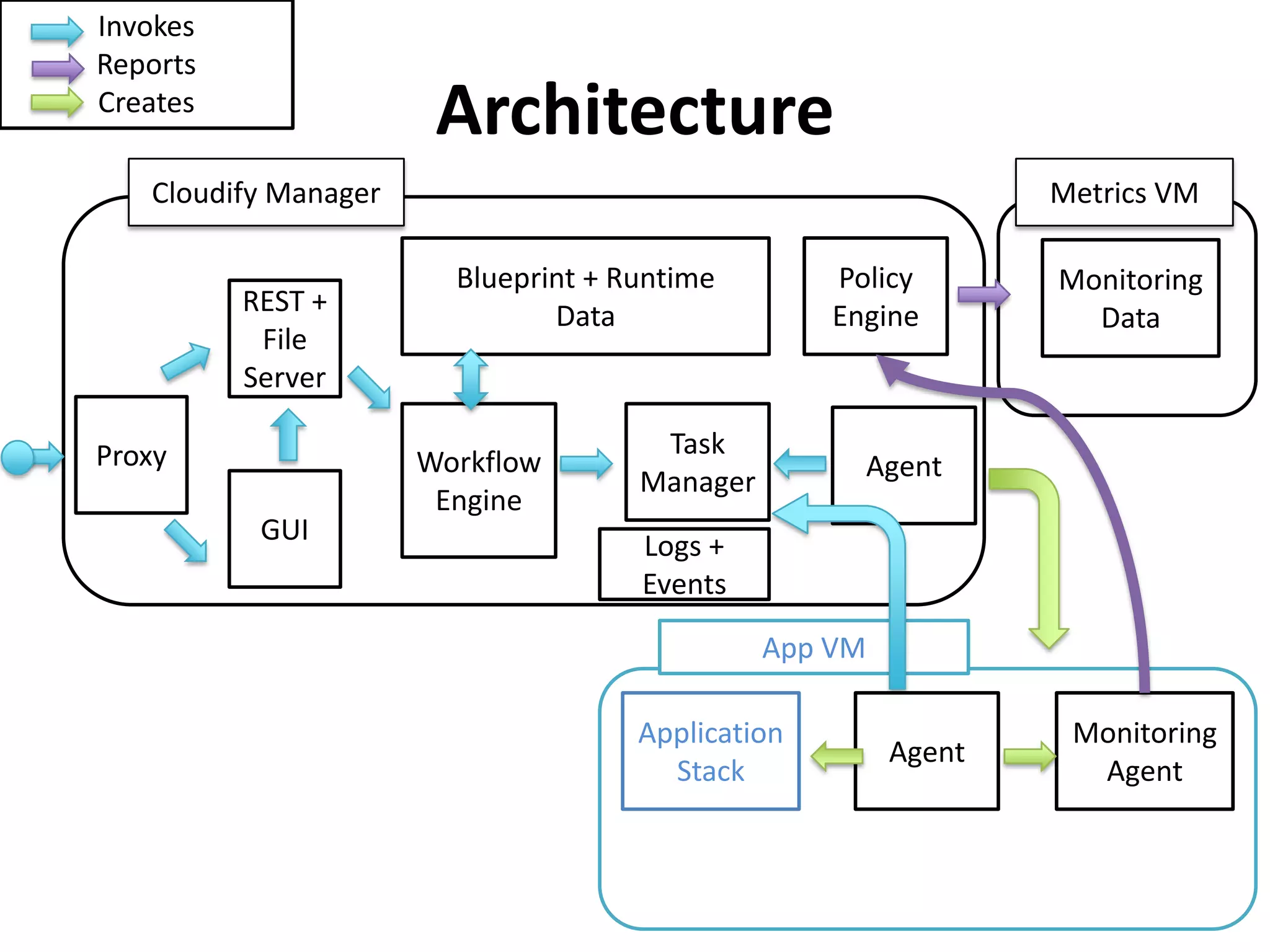
This document discusses TOSCA (Topology and Orchestration Specification for Cloud Applications), a standard for describing application deployment workflows in a portable way across multiple cloud platforms. It describes the key components of TOSCA including node types, node templates, relationship types, topology templates, policies, and workflows. TOSCA aims to automate and standardize the orchestration of installing, configuring, and deploying applications across different cloud environments and tools.