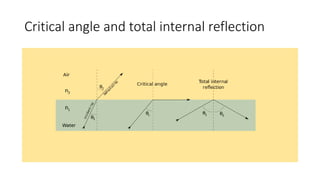
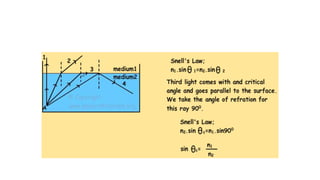
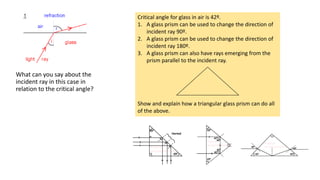
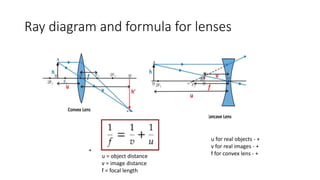
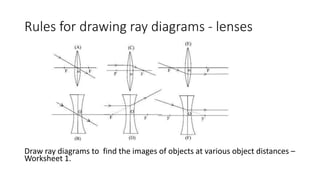
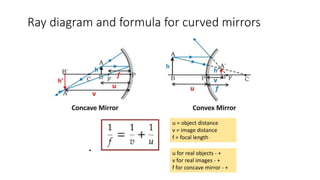
This document provides an overview of key topics in geometrical optics, including reflection, refraction via Snell's law, total internal reflection, and the formation of images using lenses and mirrors. Specifically, it discusses how plane mirrors, convex mirrors, concave mirrors, convex lenses, and concave lenses form images, and the types of optical instruments that use these principles. It also mentions drawing ray diagrams to show image formation using lenses and mirrors.