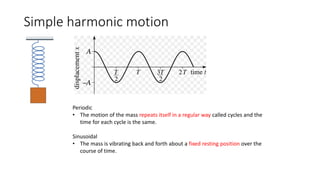
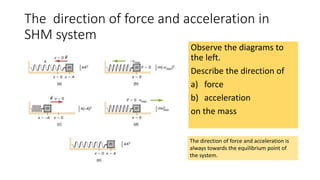
1) Simple harmonic motion (SHM) is the periodic motion of an object where its acceleration is always towards the equilibrium position and is proportional to the distance from that position.
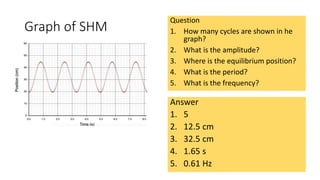
2) SHM is characterized by sinusoidal motion with a fixed amplitude, period, and frequency. The motion repeats in cycles of equal time periods.
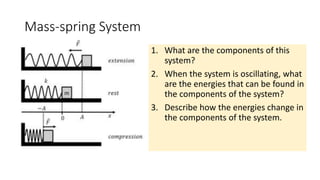
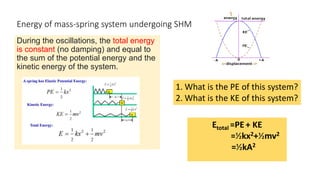
3) A mass undergoing SHM has maximum velocity when passing through the equilibrium position and zero velocity at the extreme positions, with velocity changing direction at the equilibrium position.