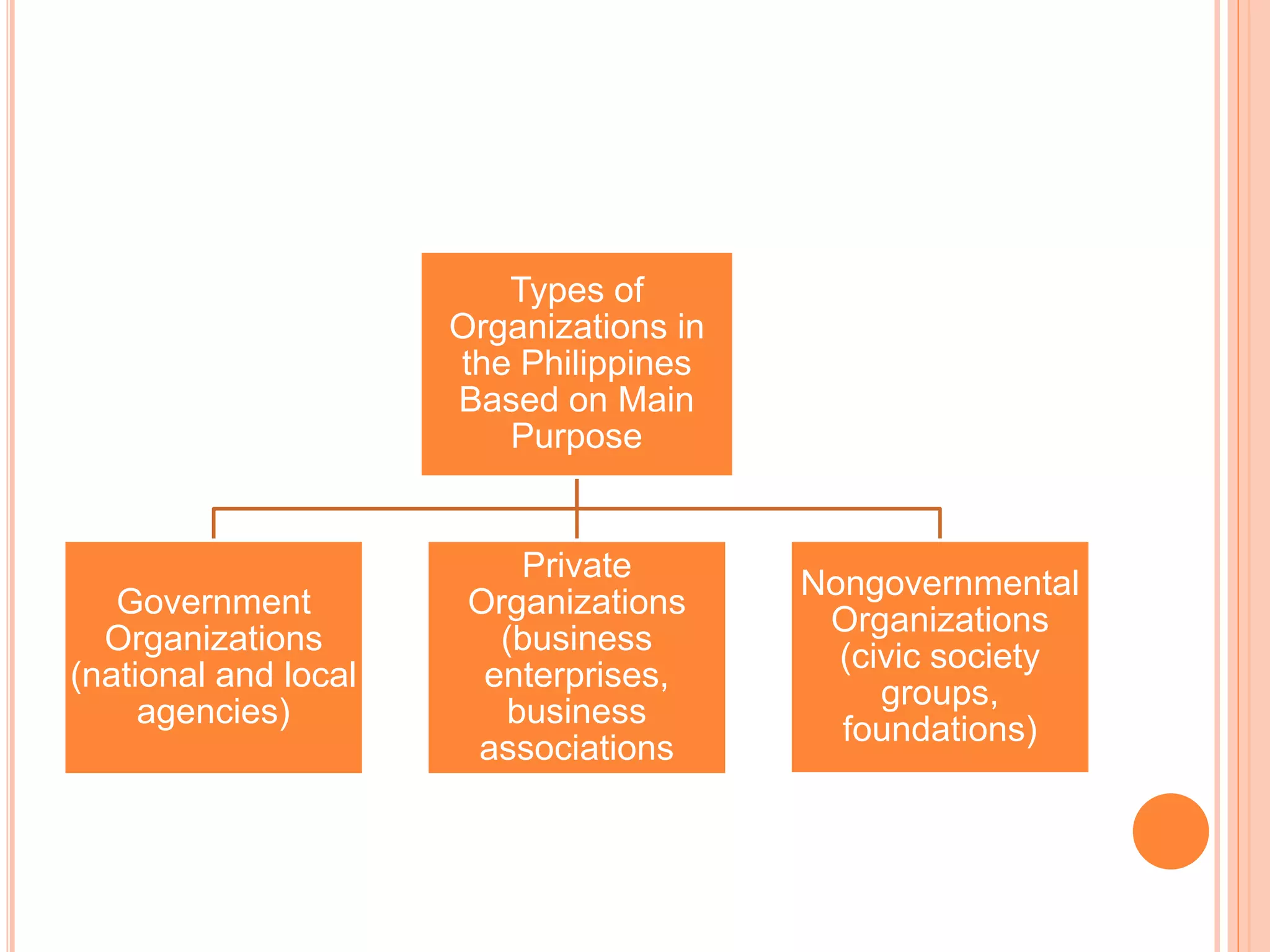
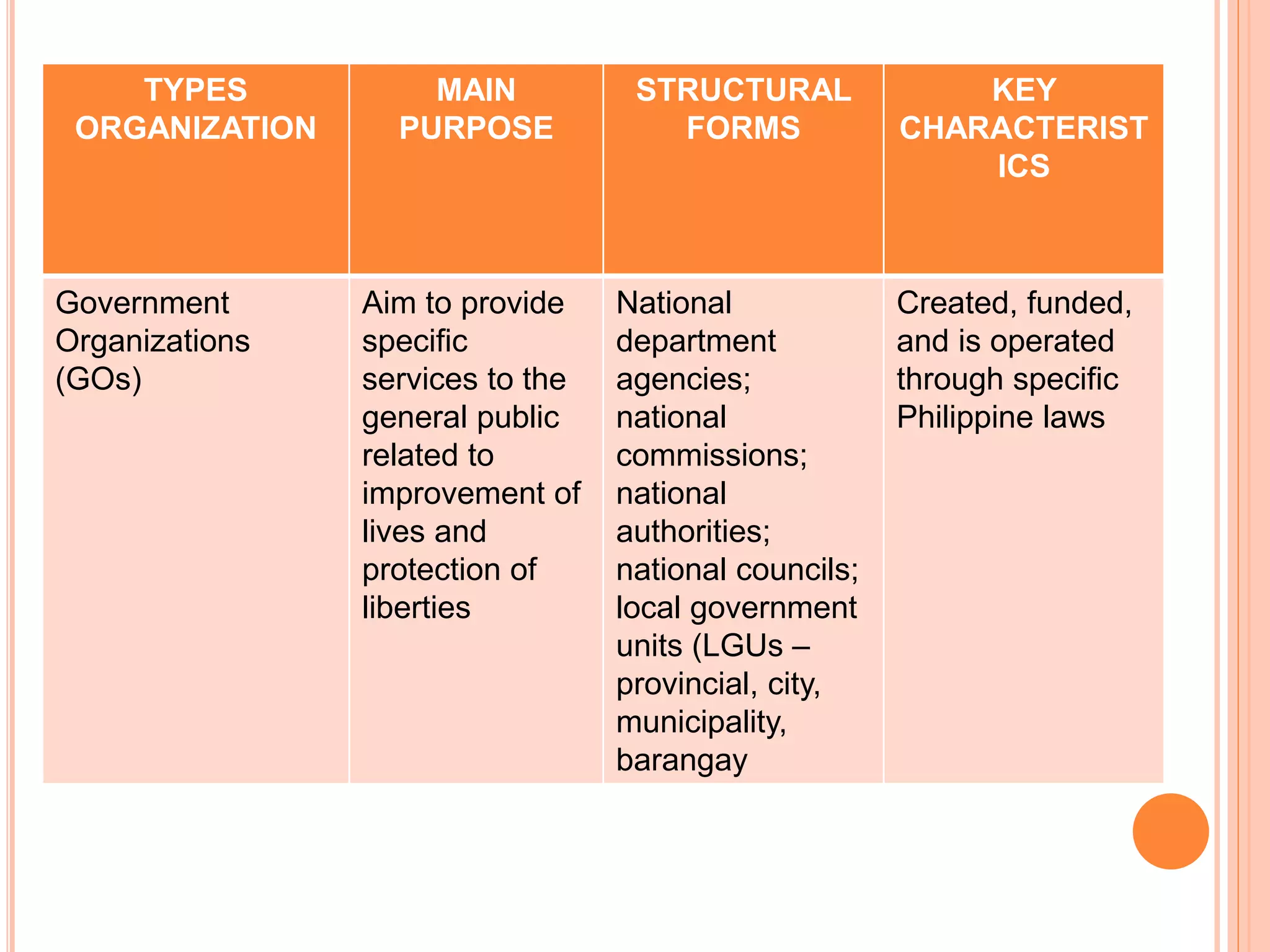
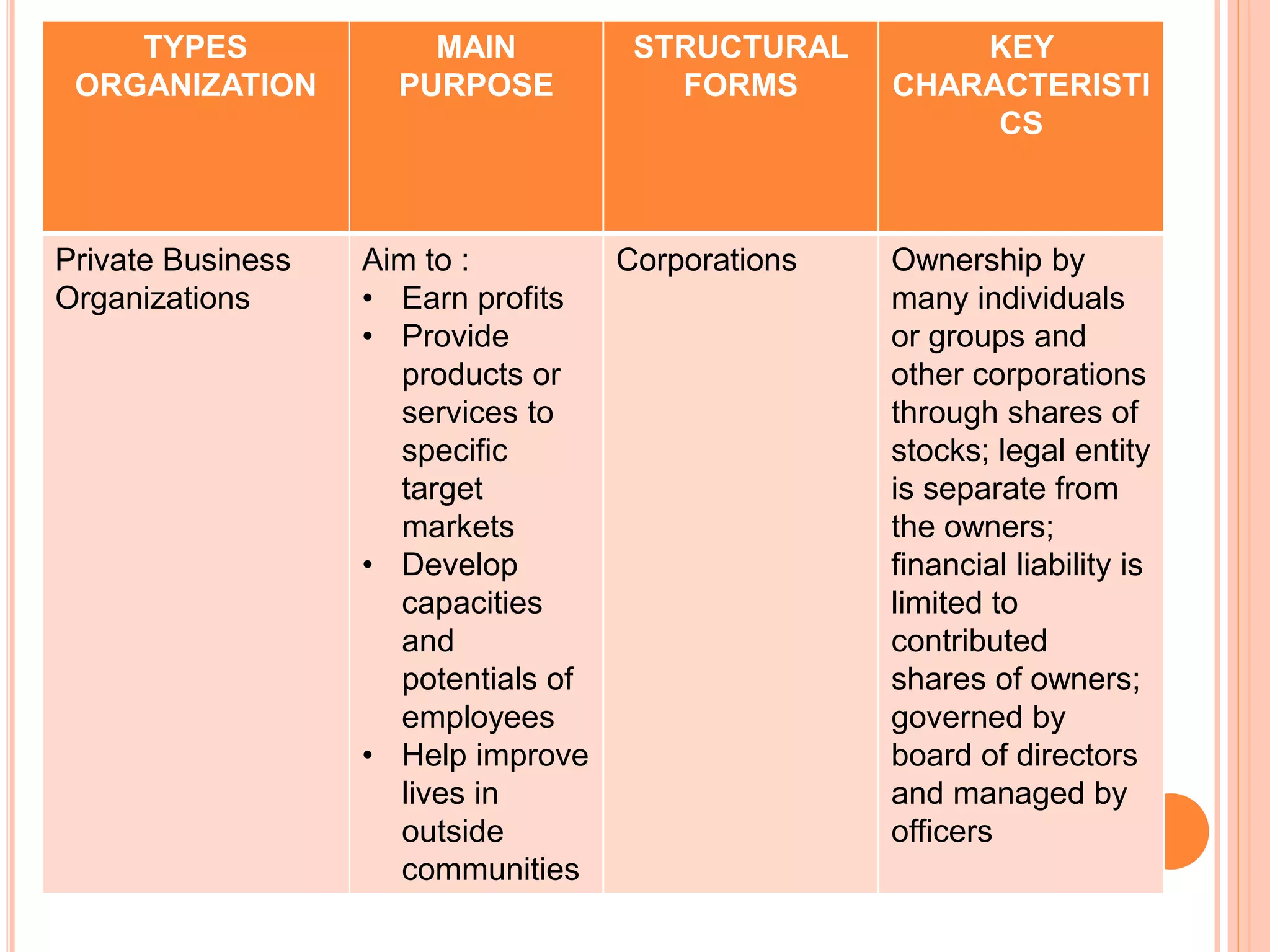
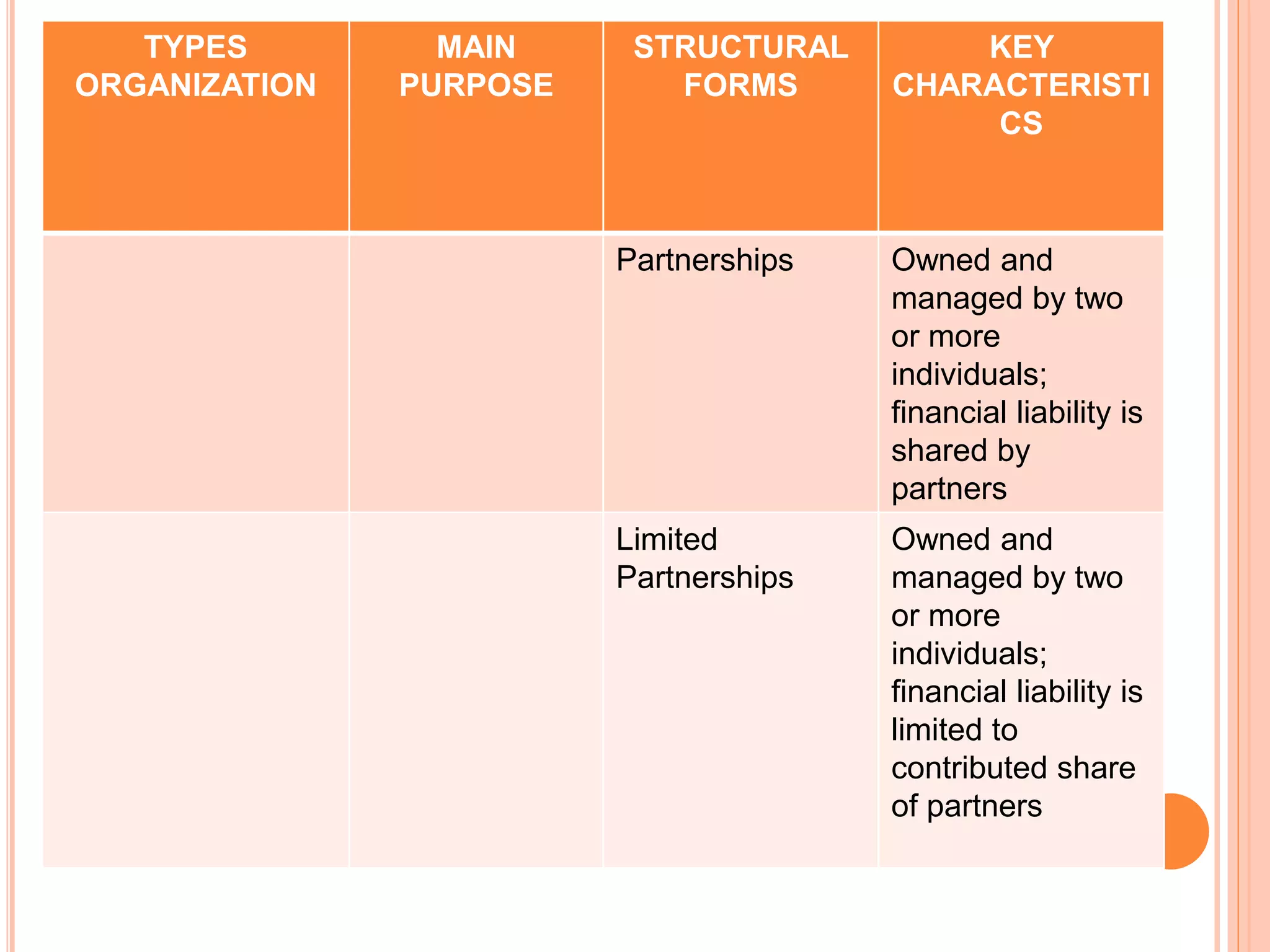
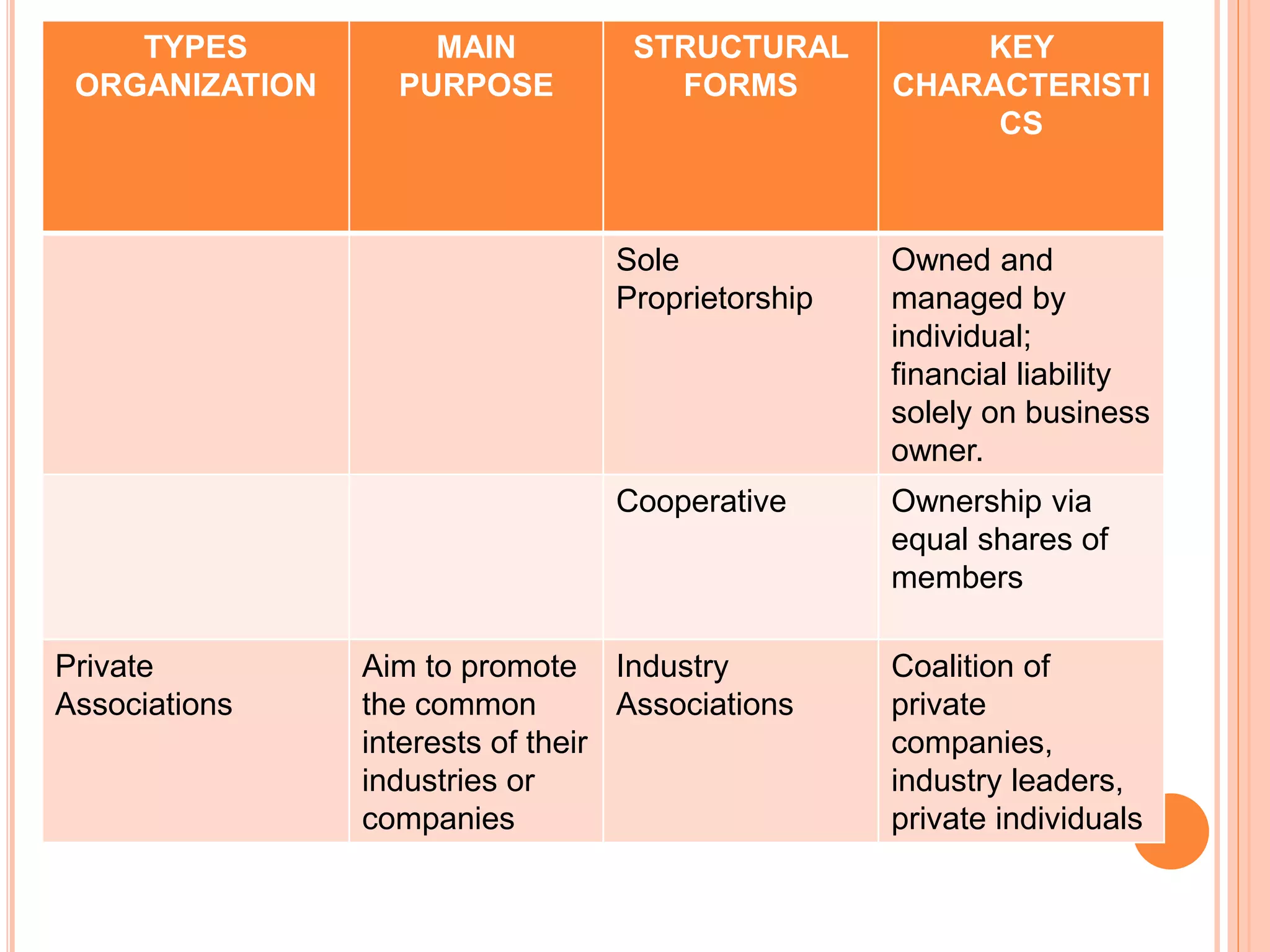
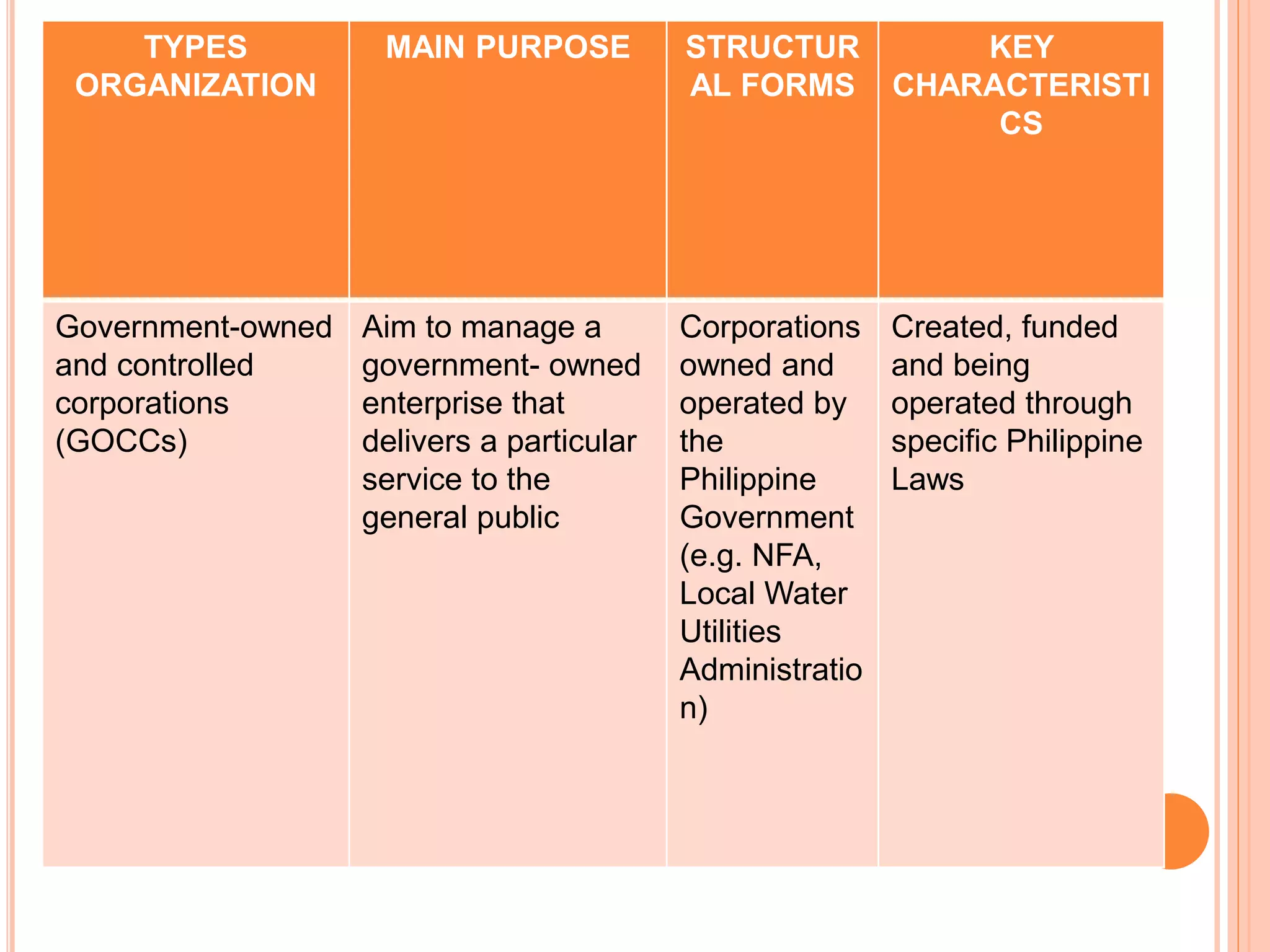
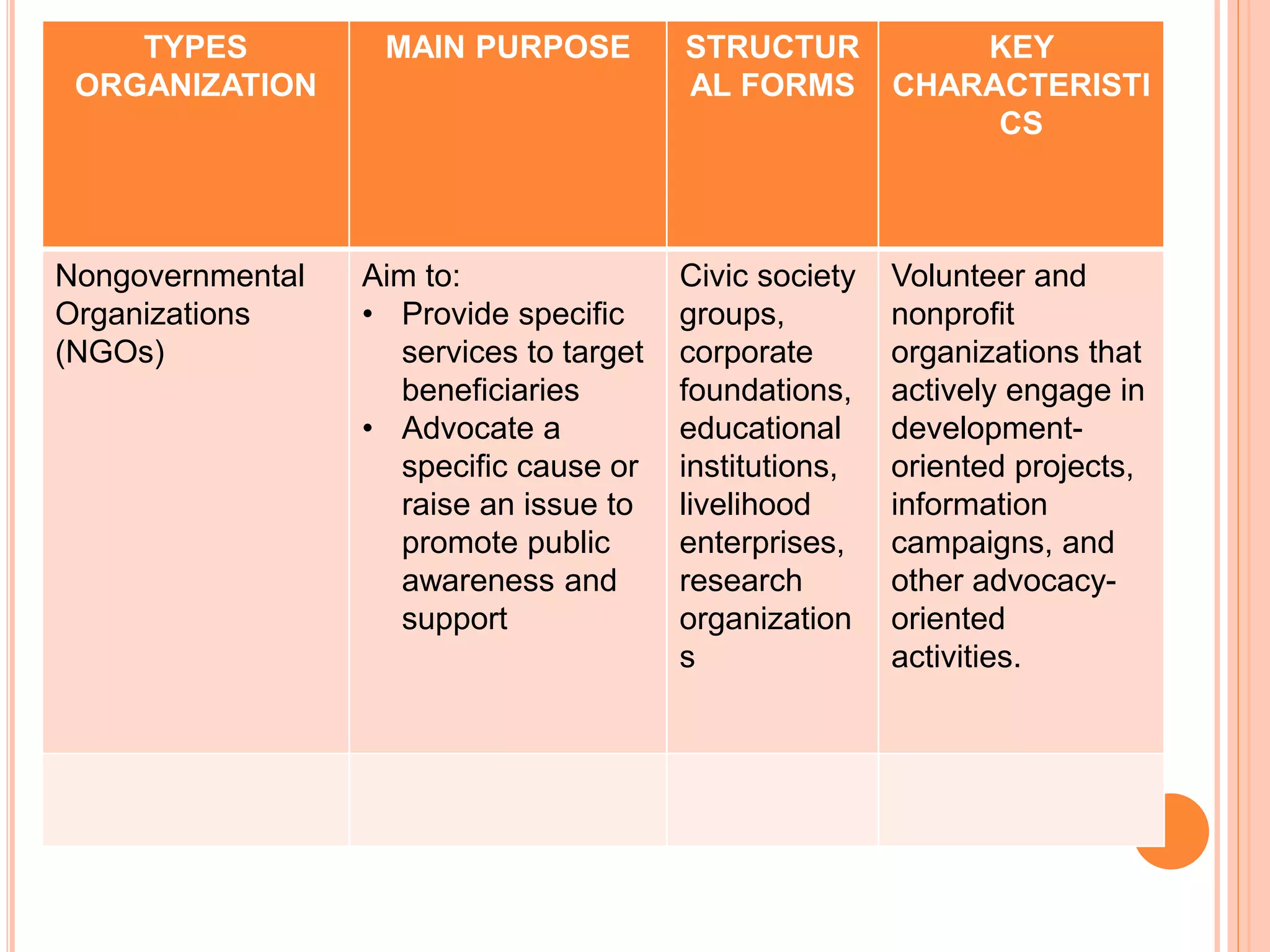
Government organizations, private organizations, and nongovernmental organizations are the main types of organizations in the Philippines. Government organizations include national and local agencies and aim to provide public services. Private organizations include business enterprises that earn profits and business associations that promote industry interests. NGOs serve target beneficiaries and include civic groups, foundations, and social enterprises. The document further discusses the different forms that these organizations can take such as corporations, partnerships, sole proprietorships, cooperatives, and government-owned corporations, along with their key characteristics.