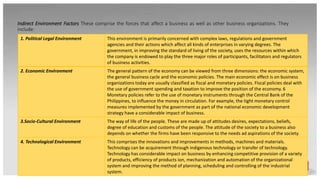
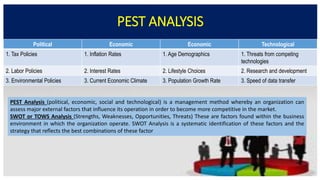
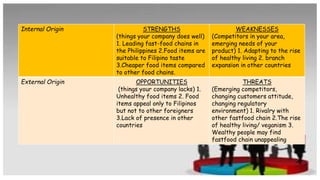
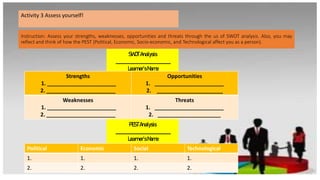
The document discusses various internal and external forces that influence local and international business, using PEST and SWOT analyses. It defines the internal environment as including owners, board of directors, employees, culture, and physical work environment. The external environment includes suppliers, distributors, customers, competitors, and factors like political, economic, social, and technological conditions. PEST analysis assesses these broader factors, while SWOT analysis examines internal strengths and weaknesses and external opportunities and threats. Activities guide applying these analytical tools to better understand a business environment.