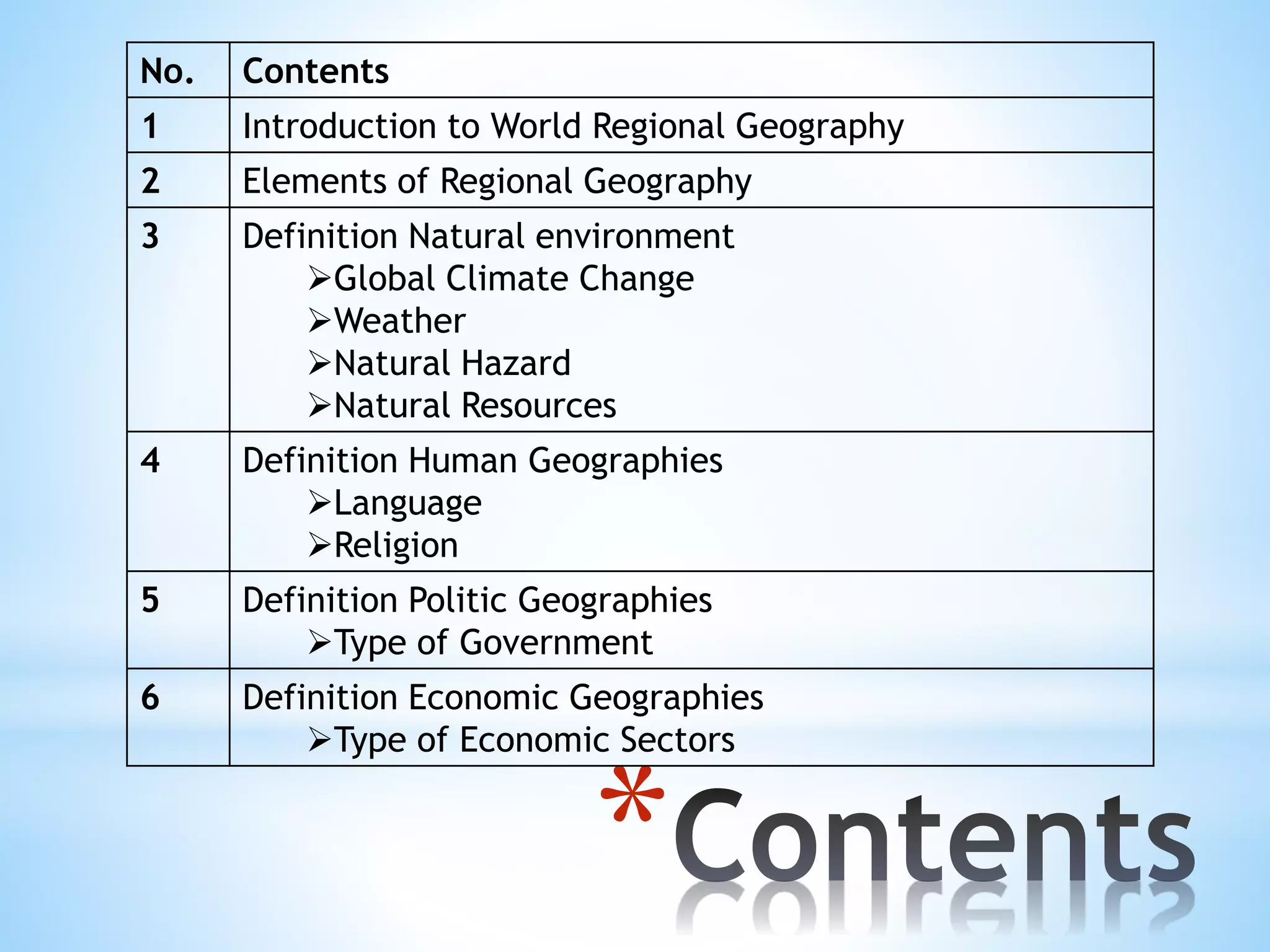
This document summarizes the key elements of regional geography. It discusses four main categories: natural environment, human geographies, political geographies, and economic geographies. The natural environment section defines this concept and provides examples like global climate change, weather, natural hazards, and natural resources. Human geographies examines languages and religions spoken around the world. Political geographies analyzes the different forms of government such as monarchy, democracy, and authoritarianism. Finally, economic geographies explores the primary, secondary, tertiary, and quaternary sectors of the world's economy.