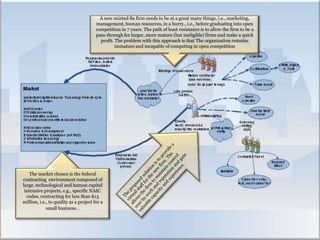
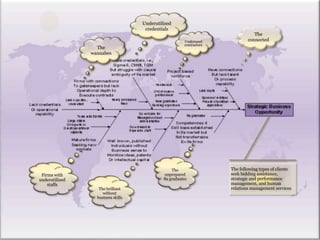
This proposal suggests using strategic and performance management tools to market virtual human resources services to technology and human capital intensive firms. The approach involves three phases: 1) Identifying strategic opportunities to address clients' competency deficits, 2) Matching clients to opportunities, and 3) Engaging clients. Services initially provide virtual human resources and bidding assistance. As clients grow, services expand to strategic management, performance management, and risk management, helping clients evolve from a focus on time-based competition to strategic competition. Key performance indicators track progress in resolving competency barriers across financial, customer, internal, and learning/growth perspectives.