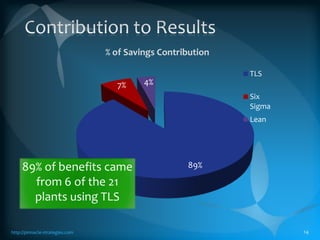
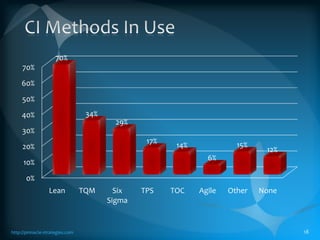
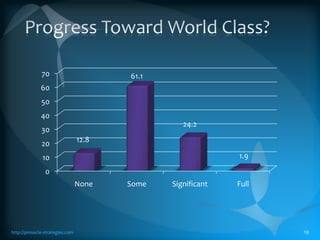
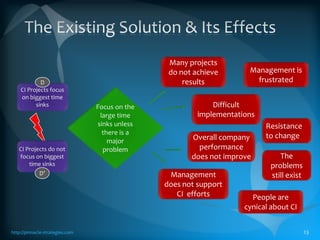
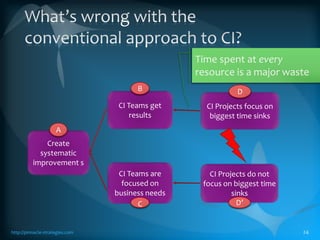
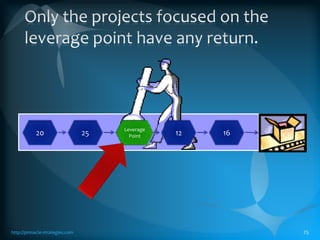
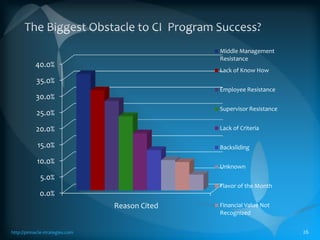
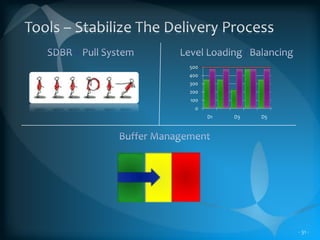
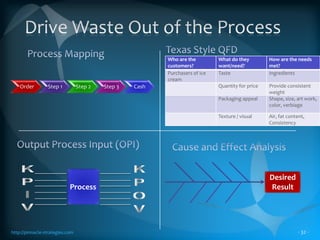
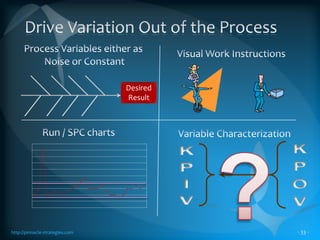
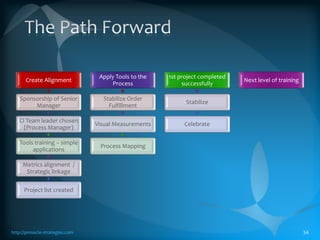
The document discusses the TLS (Theory of Constraints) methodology, highlighting its superior results in process management compared to other approaches like Lean and Six Sigma. It emphasizes that successful improvement arises from focusing on leverage points within processes rather than merely managing changes. TLS aims to foster a culture of continuous improvement aligned with global strategies, leading to significant organizational performance enhancements without major capital investments.