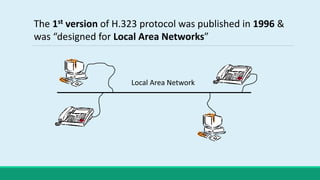
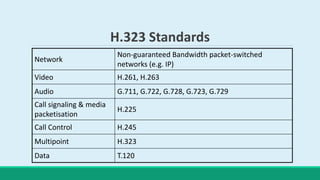
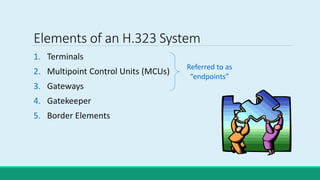
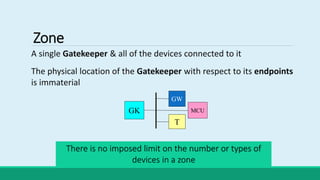
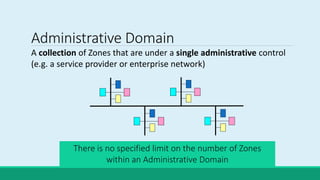
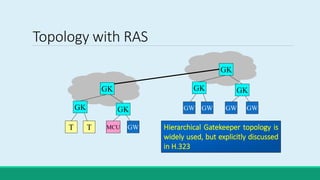
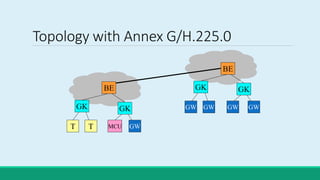
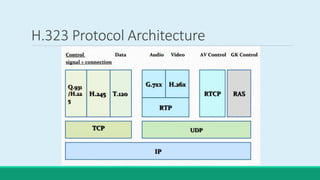
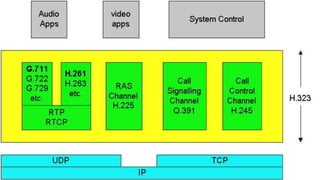
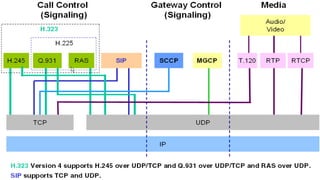
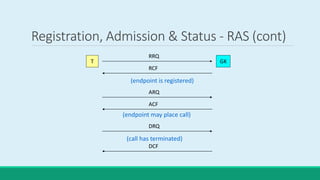
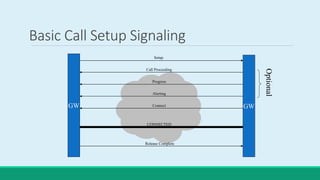
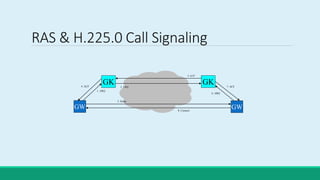
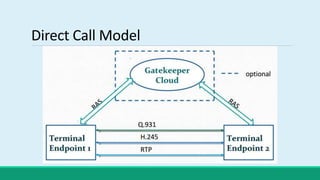
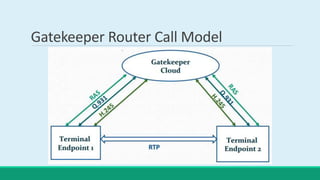
H.323 is a standard for multimedia communications over packet-based networks. It defines protocols for real-time audio, video and data communications between endpoints such as terminals, gateways and multipoint control units. As an umbrella standard, H.323 references other protocols for functions like call signaling, bandwidth negotiation and transmission of audio and video data. H.323 provides scalable and flexible multimedia communication capabilities and has been widely adopted for voice and video conferencing over both internet and private networks.