Embed presentation
Download to read offline

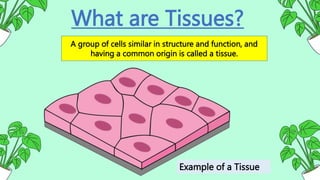

Our bodies contain over 30 trillion specialized cells that are organized into tissues. A tissue is a group of similar cells that work together to perform a specific function. There are two main types of tissues - plant tissues which are made of thick-walled, often dead cells that allow plants to grow throughout their lives, and animal tissues containing mostly living cells that enable animal mobility and heterotrophic nutrition but limit further growth after maturity.



