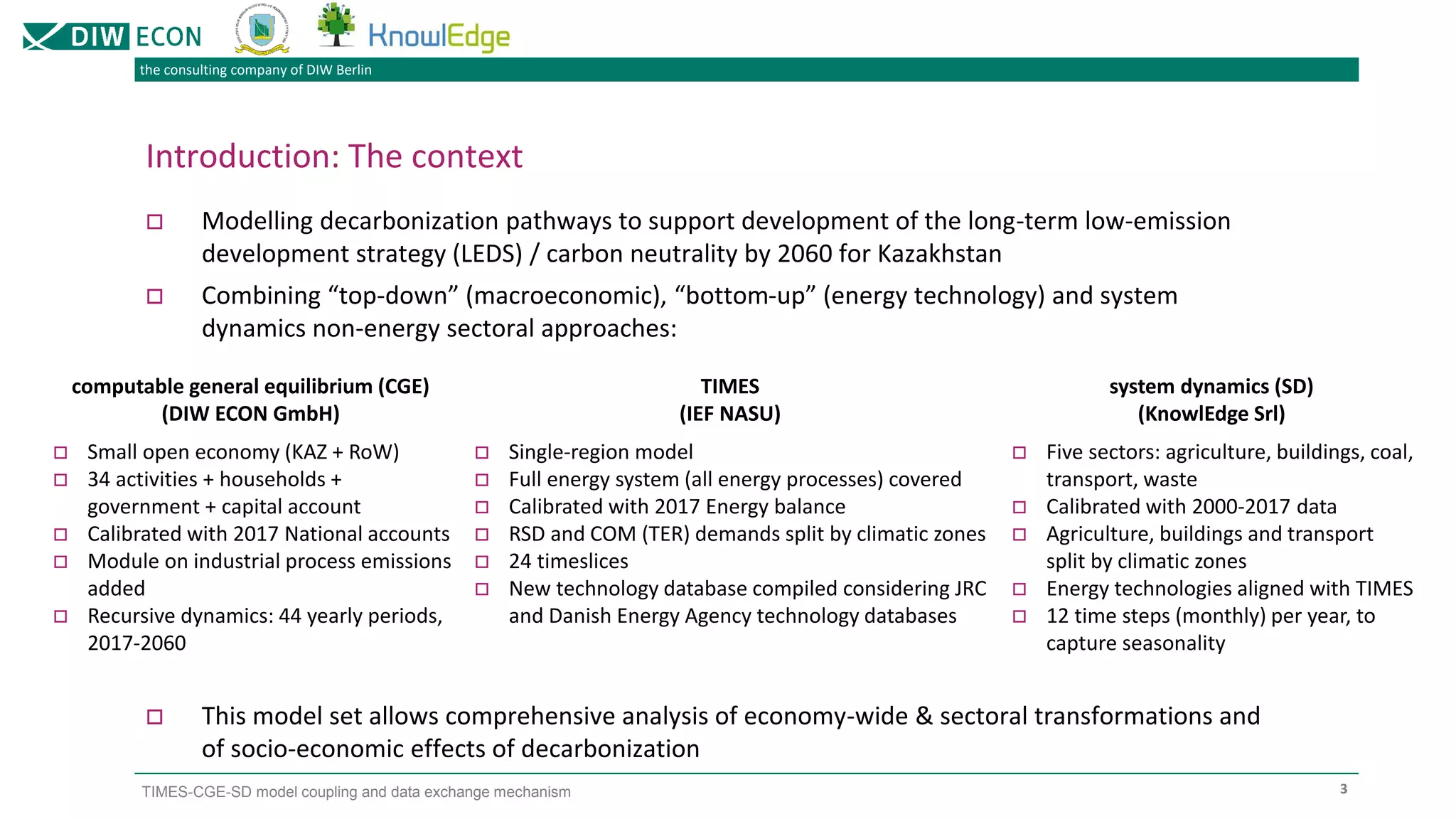
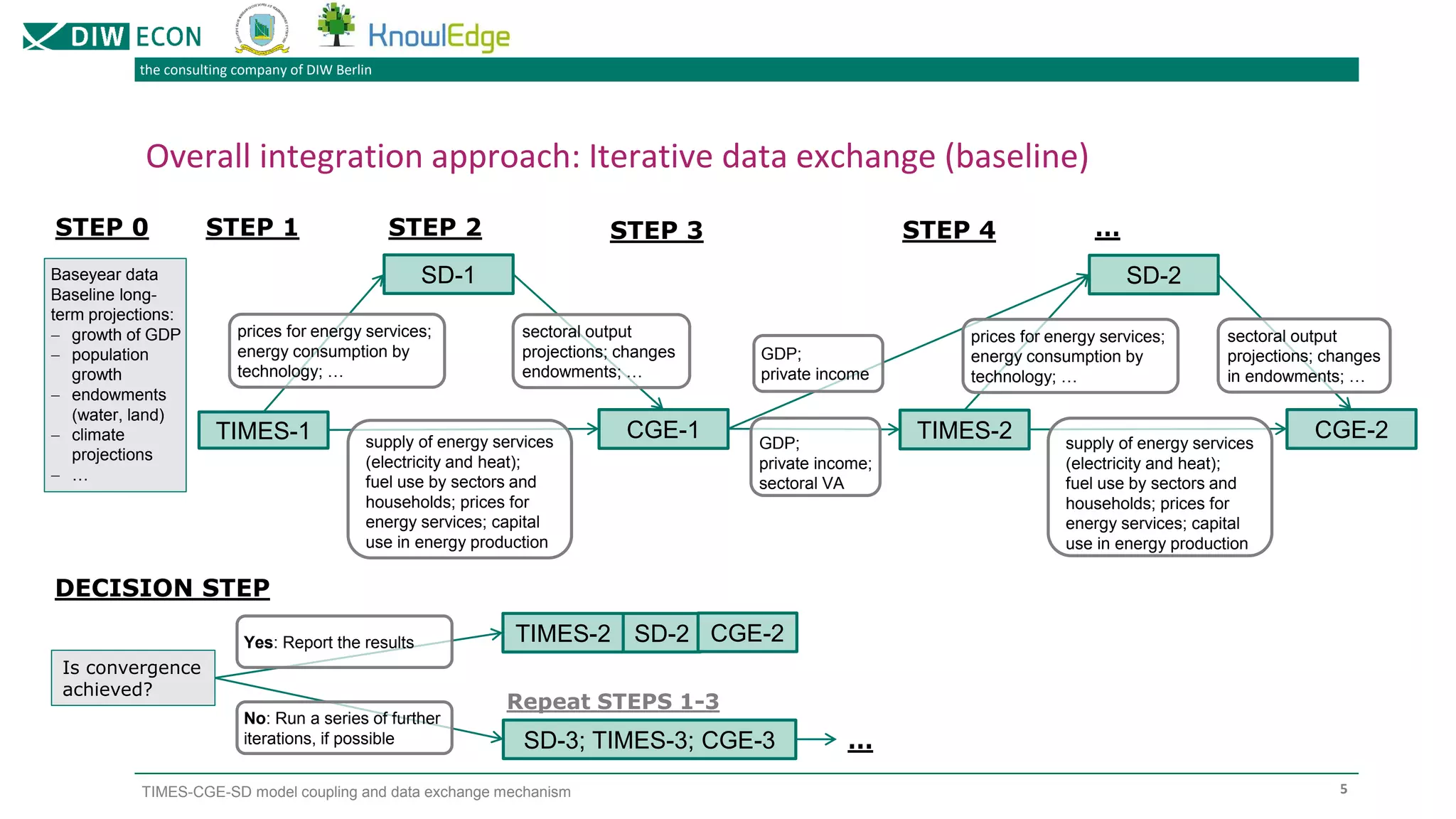
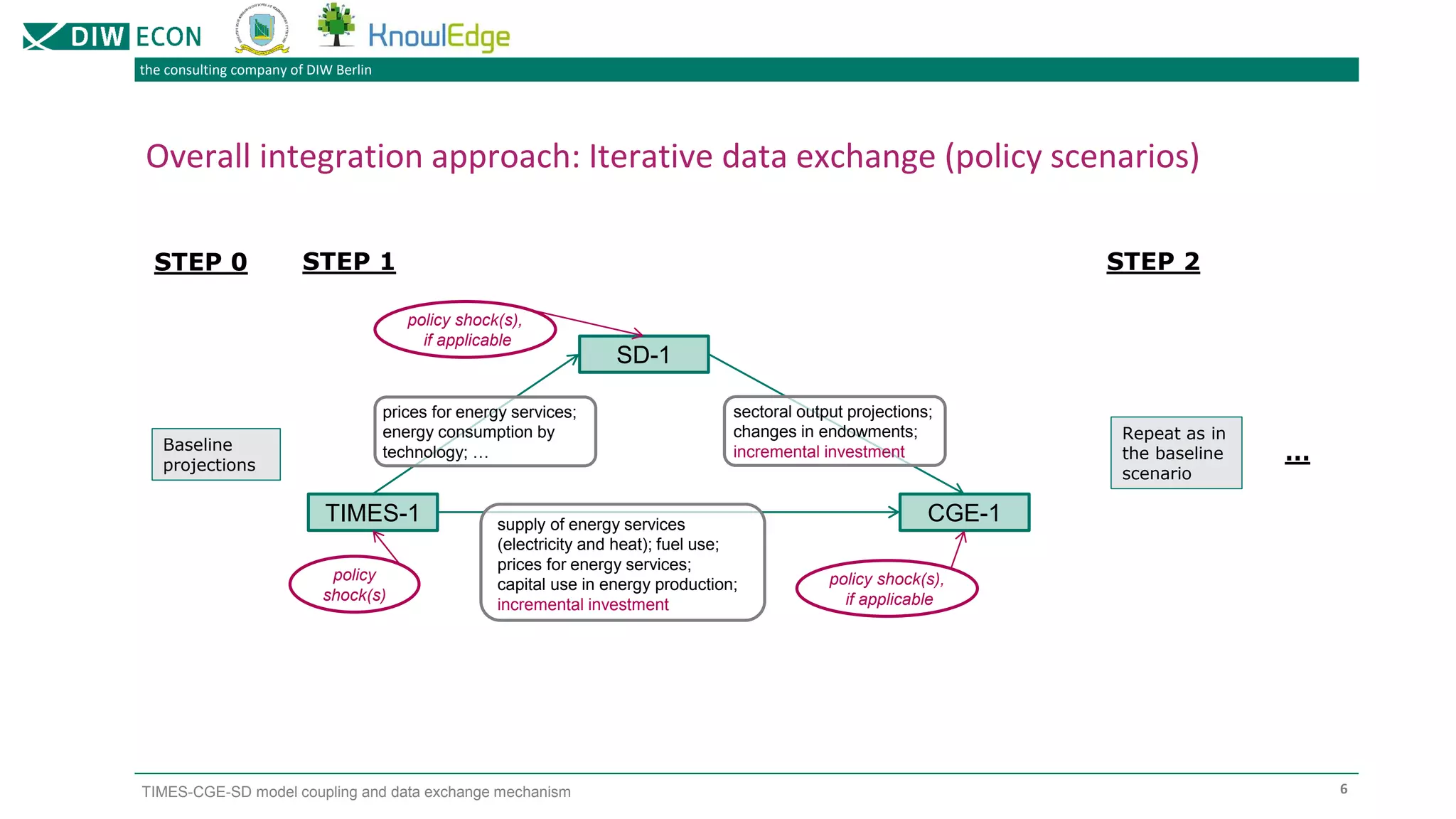
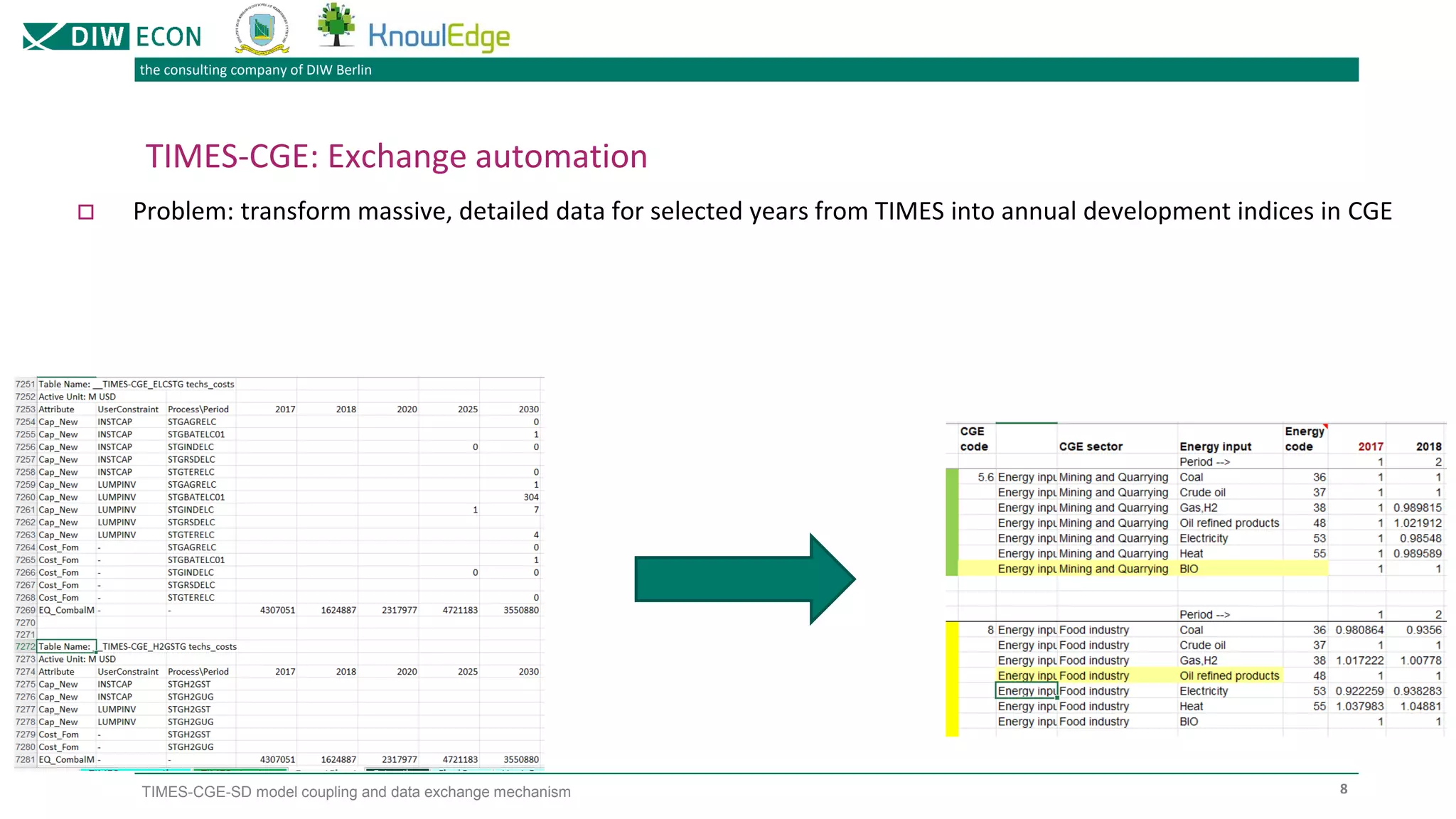
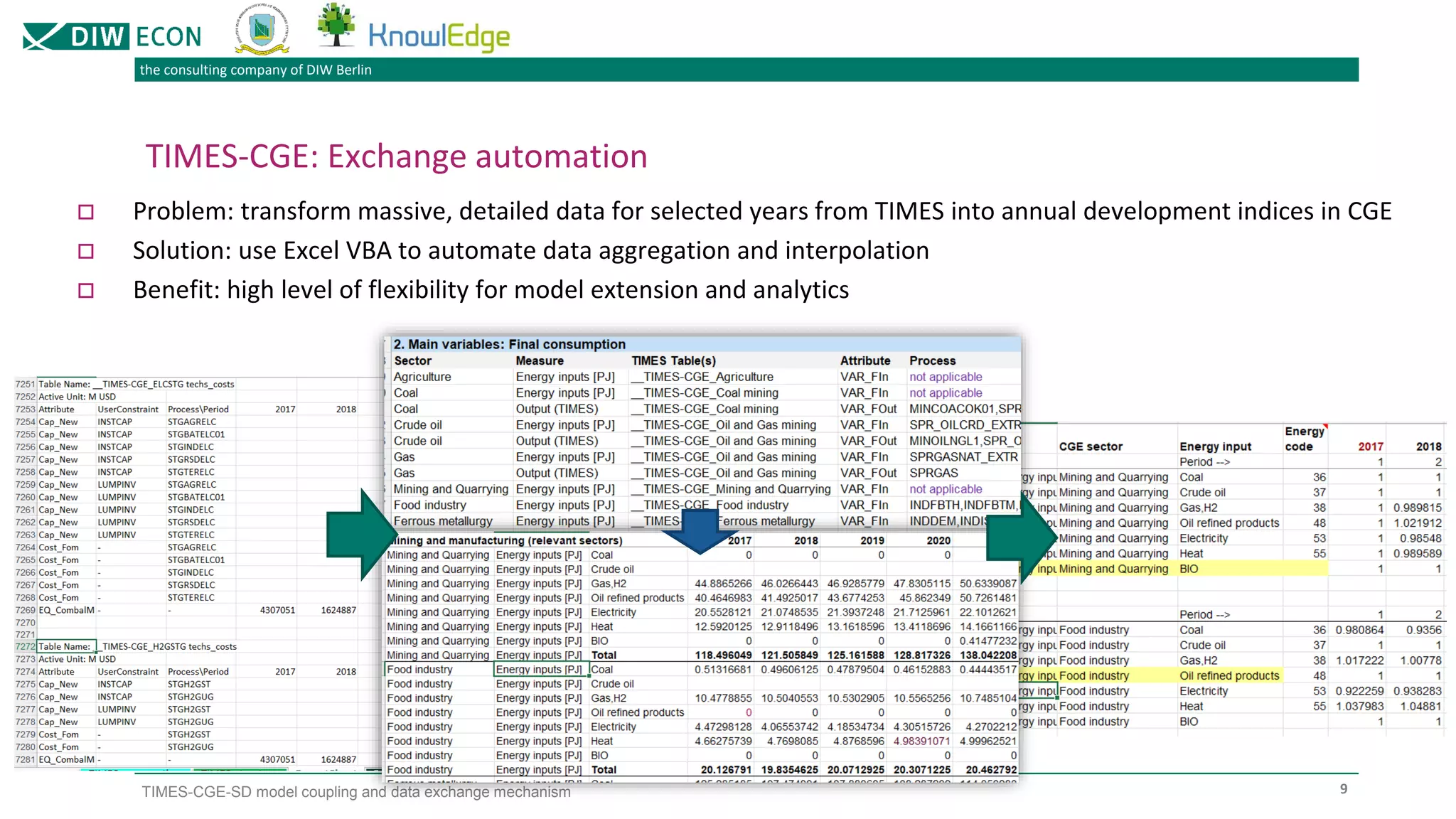
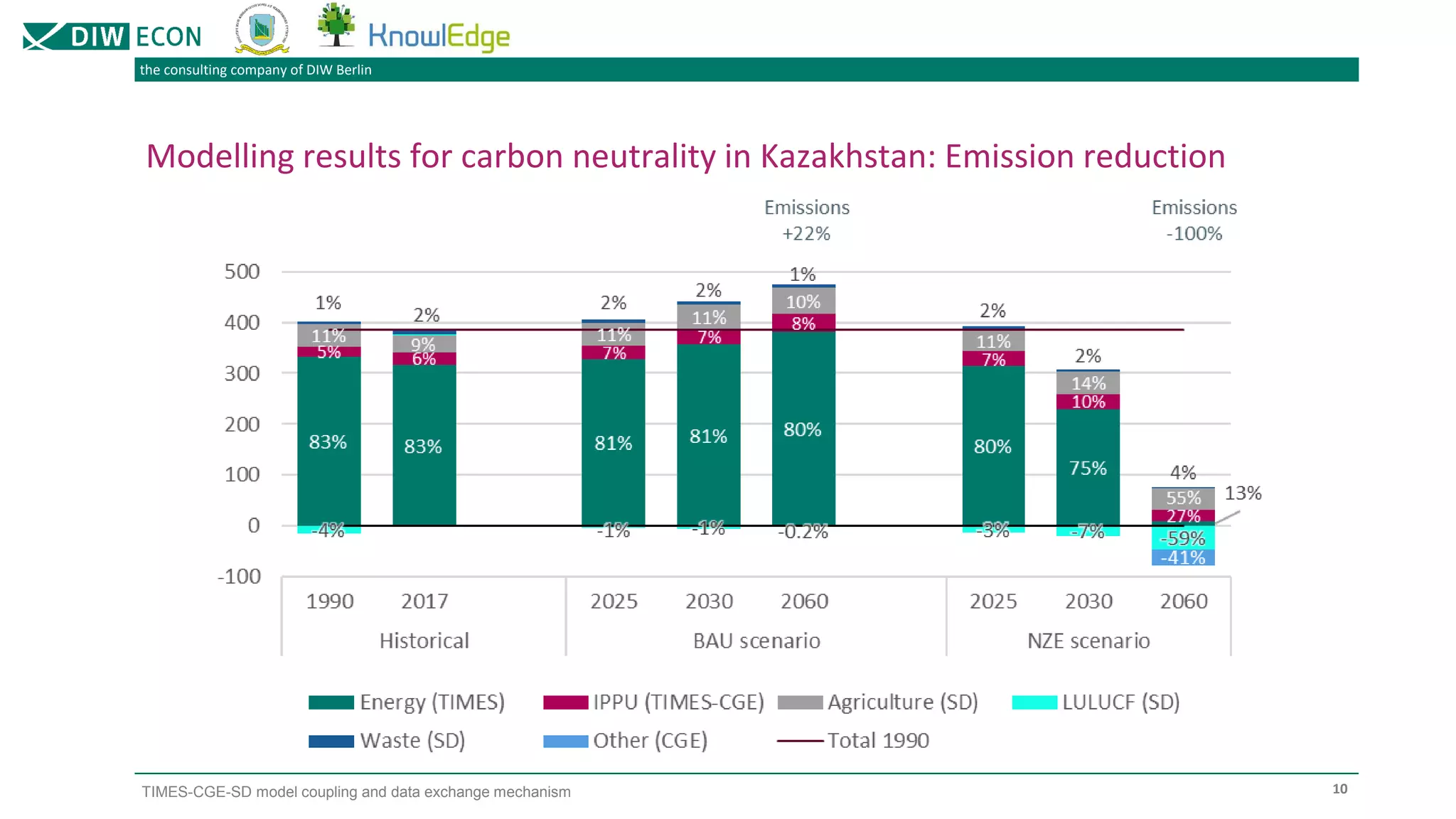
The document outlines a project focused on modeling decarbonization pathways to support Kazakhstan's long-term low-emission development strategy aimed at achieving carbon neutrality by 2060. It describes the integration of three modeling approaches (CGE, TIMES, and system dynamics) to analyze economic transformations and socio-economic effects of decarbonization. Additionally, it details the iterative data exchange process between models and presents challenges and solutions for effective model coupling.