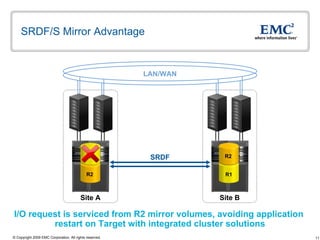
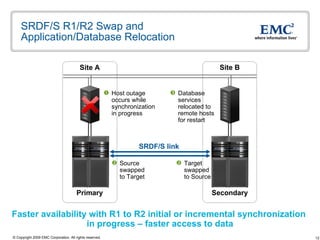
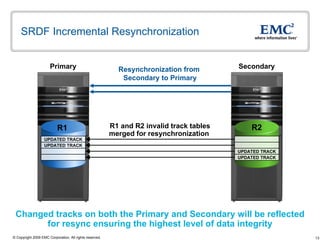
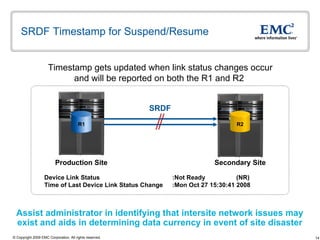
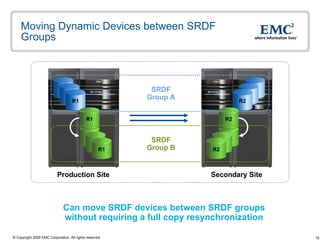
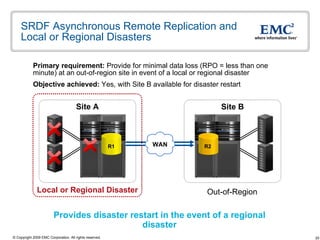
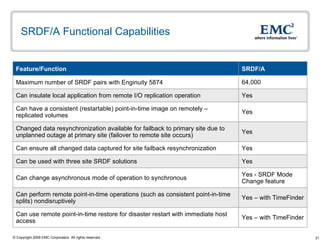
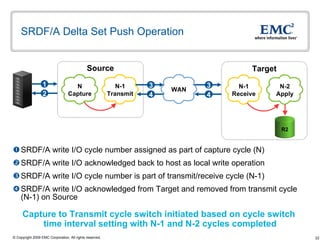
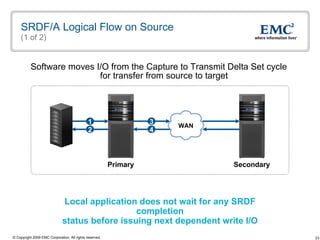
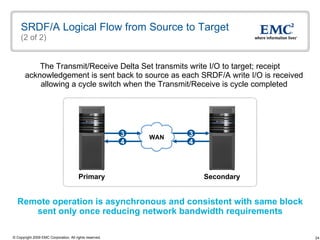
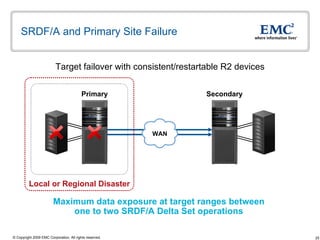
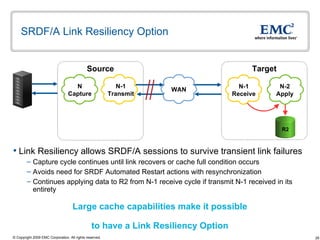
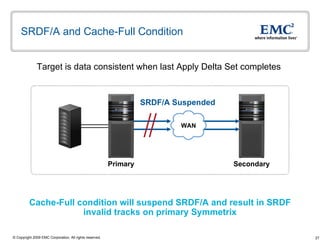
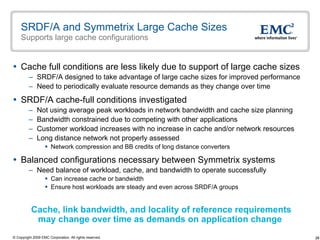
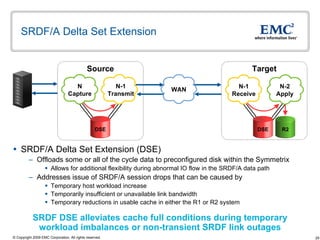
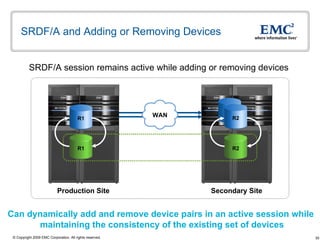
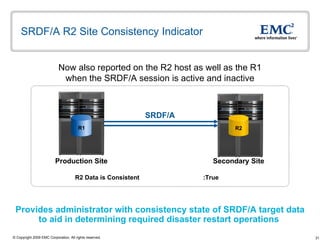
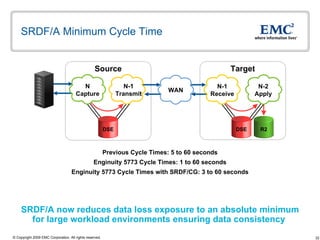
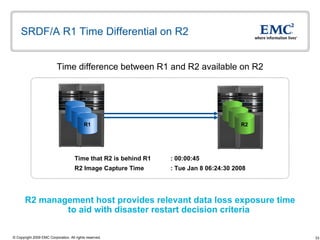
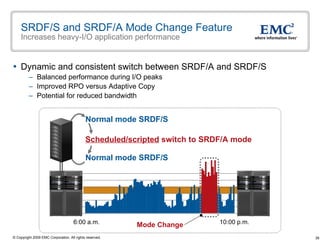
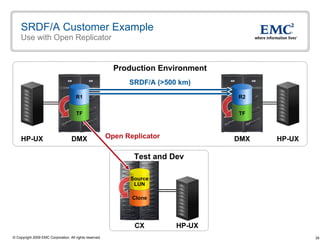
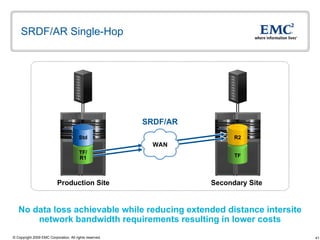
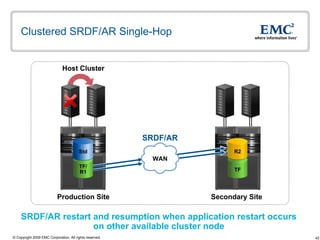
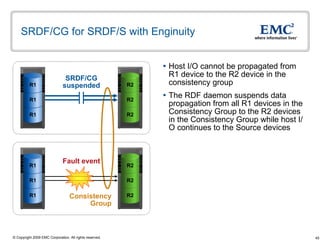
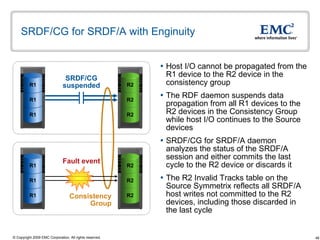
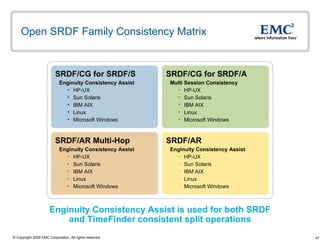
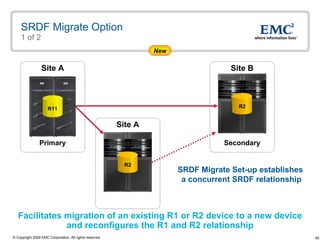
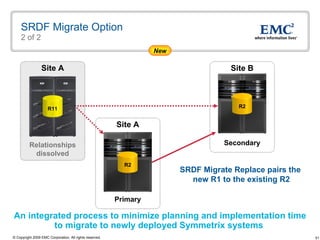
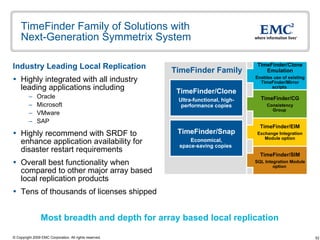
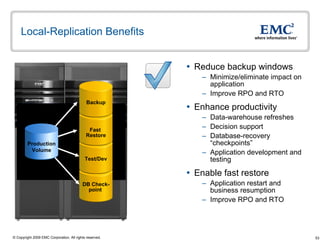
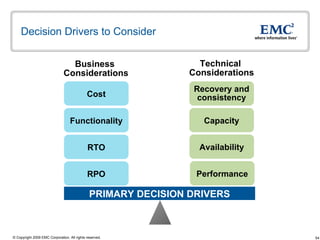
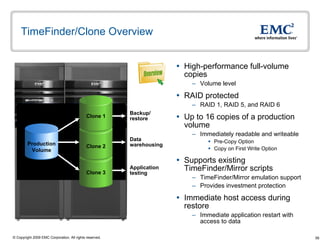
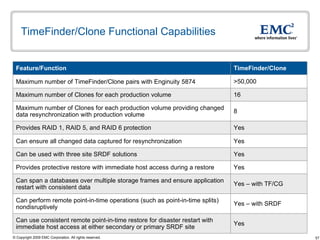
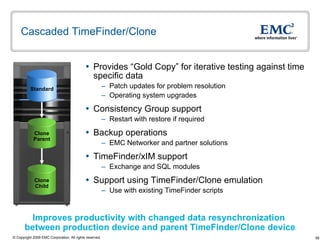
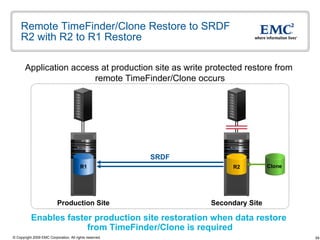
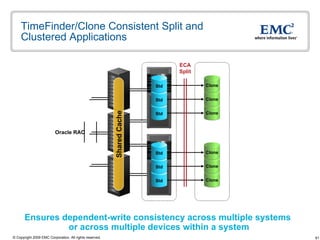
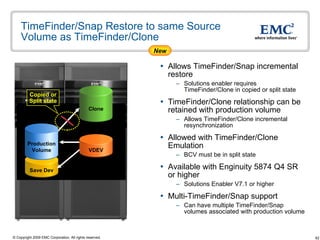
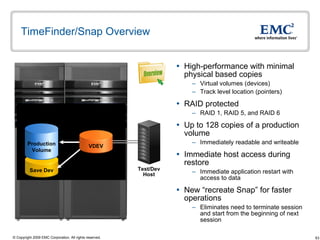
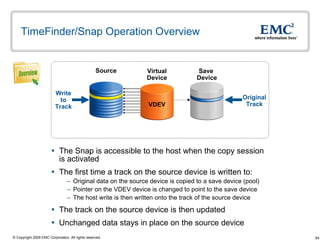
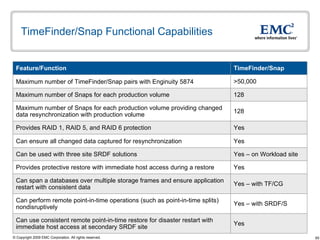
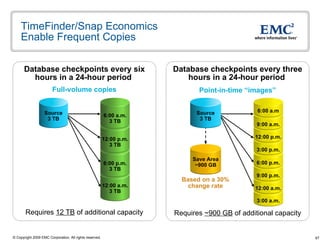
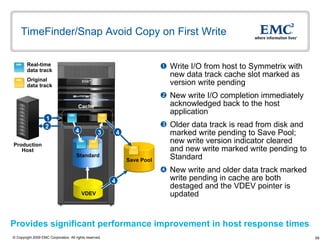
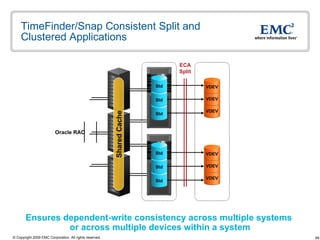
The document discusses EMC's SRDF and TimeFinder technologies for remote data replication and recovery. It provides an overview of SRDF/S synchronous replication which allows zero data loss recovery, and SRDF/A asynchronous replication which provides recovery with minimal data loss. It describes the key capabilities and benefits of both technologies for disaster recovery and business continuity.