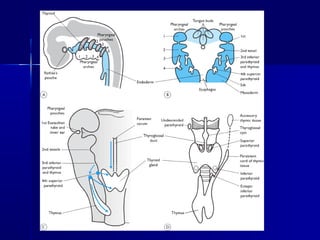
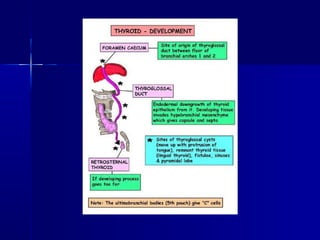
The thyroid gland originates from endodermal cells on the midline pharyngeal floor between the 24th day of gestation. It initially develops caudal to the tuberculum impar from the 1st pharyngeal arch on the floor of the developing pharynx. The thyroid primordium starts as a simple midline thickening that forms the thyroid diverticulum. During descent, the thyroid gland forms its mature bilobed shape connected by an isthmus as it reaches its final location in the neck by the 7th gestational week. Parafollicular C cells are derived from the ultimobranchial body which fuses with the thyroid gland and disseminates its cells.