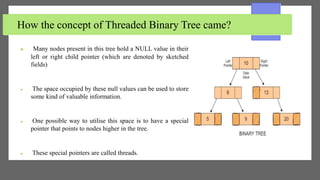
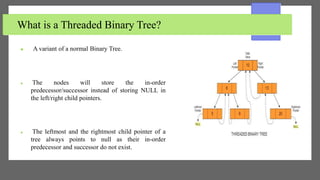
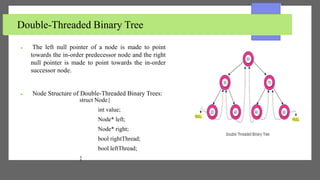
The document discusses threaded binary trees. It defines a threaded binary tree as a variant of a normal binary tree where nodes store their in-order predecessor or successor instead of NULL pointers. There are two types: single-threaded trees use threads only for right child pointers, while double-threaded trees use threads for both left and right child pointers. Threaded binary trees use memory efficiently and allow both forward and backward traversal without recursion, but have more complex insertion and deletion and use extra memory for the threads.