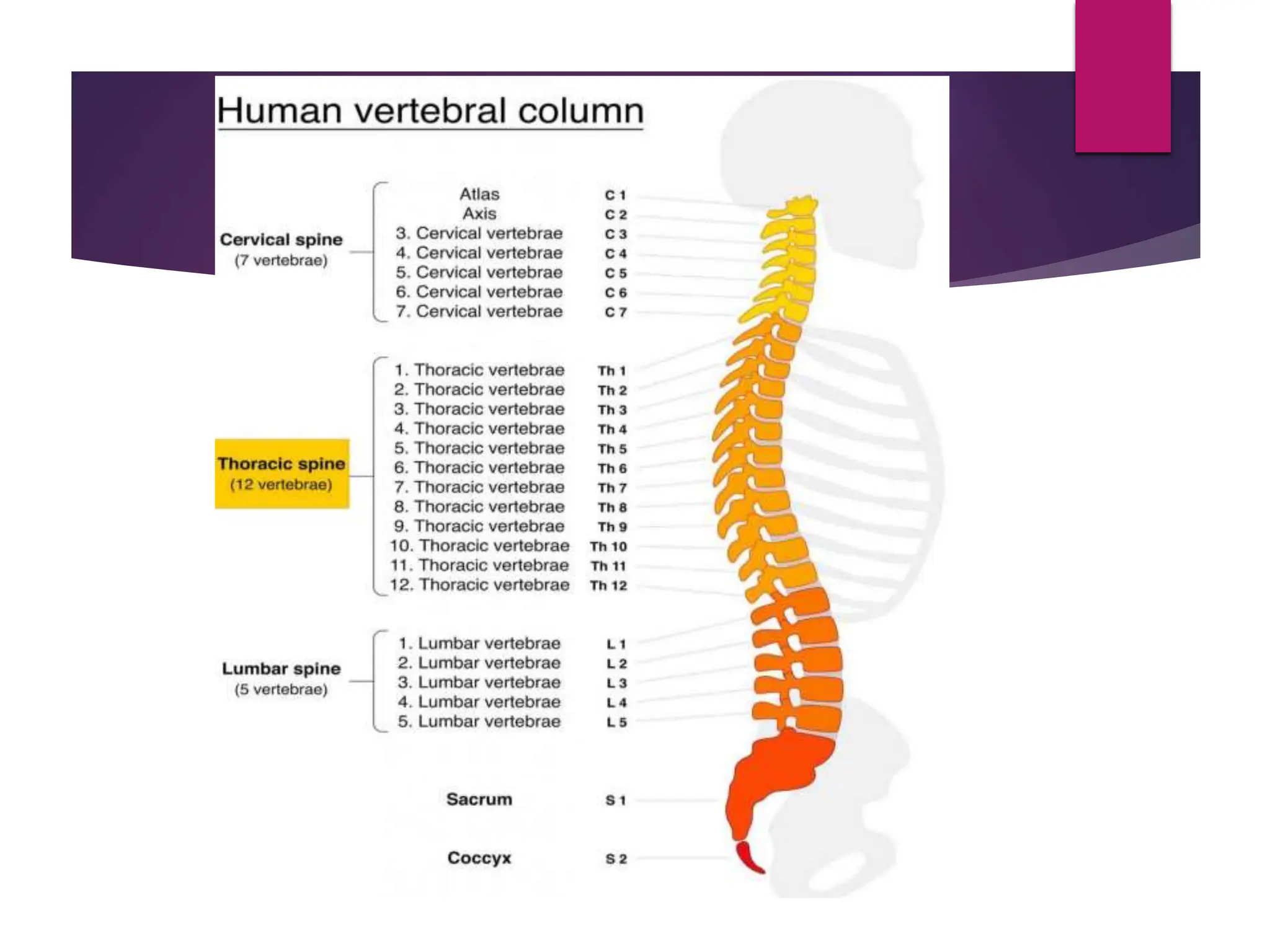
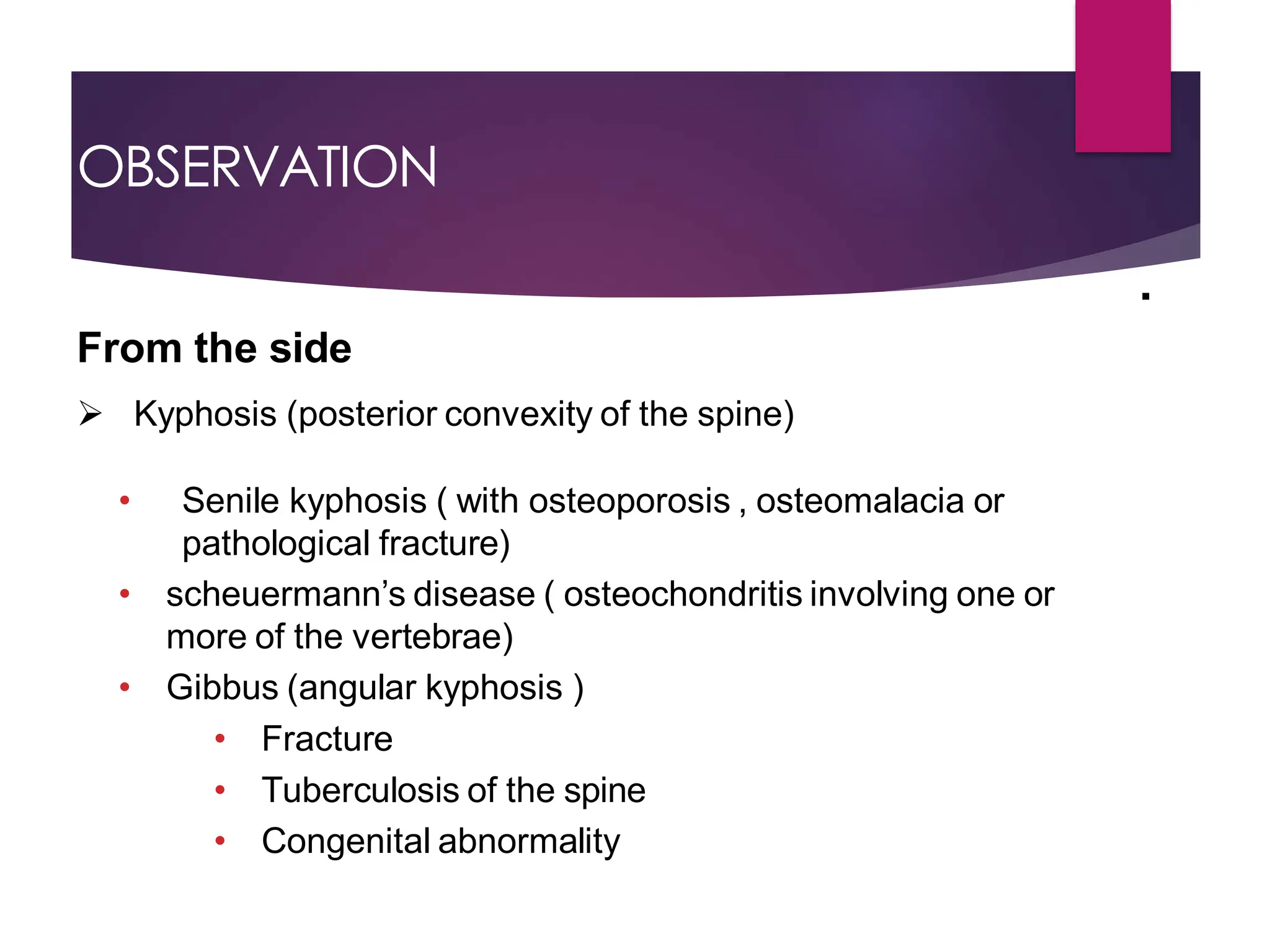
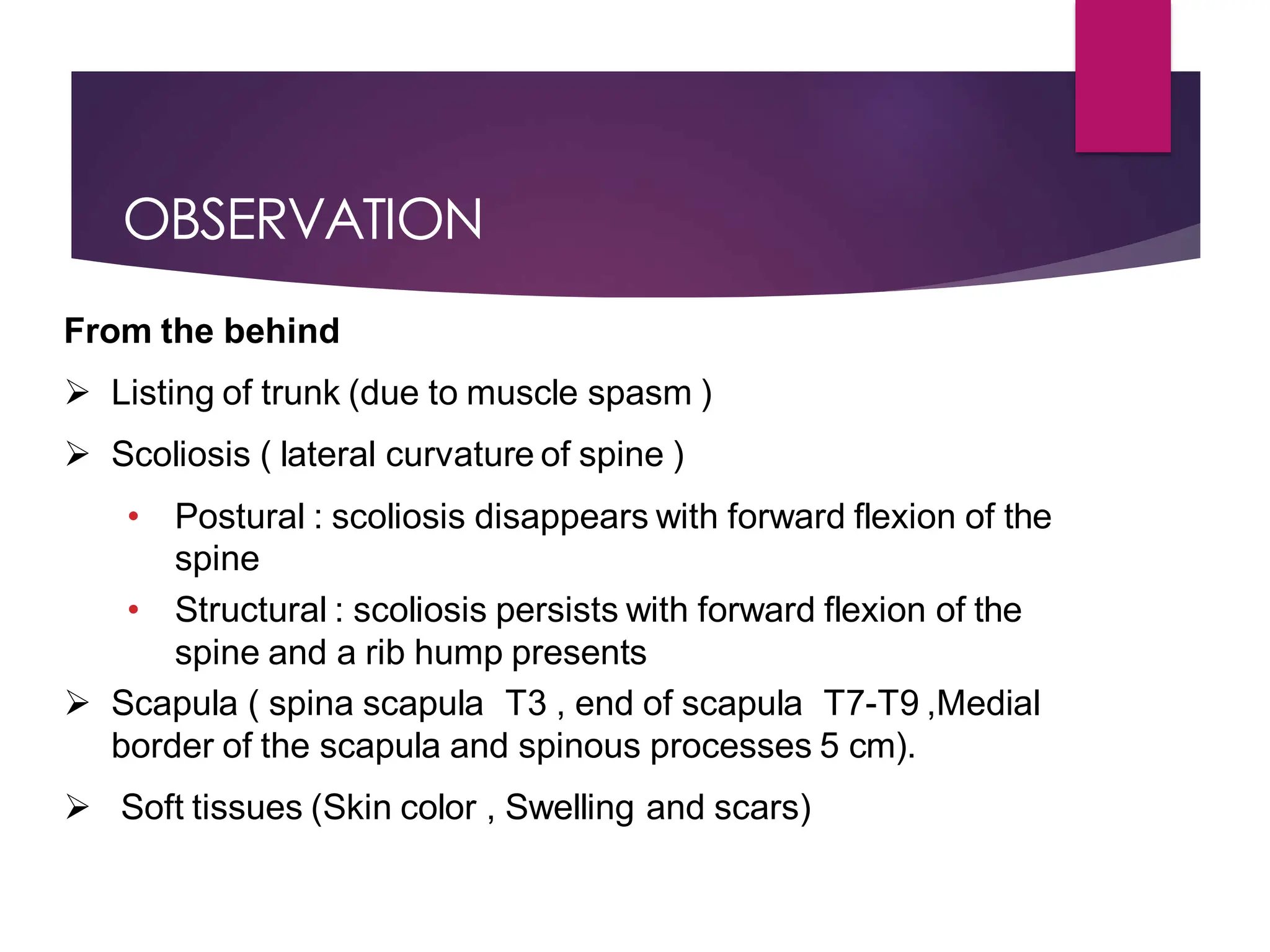
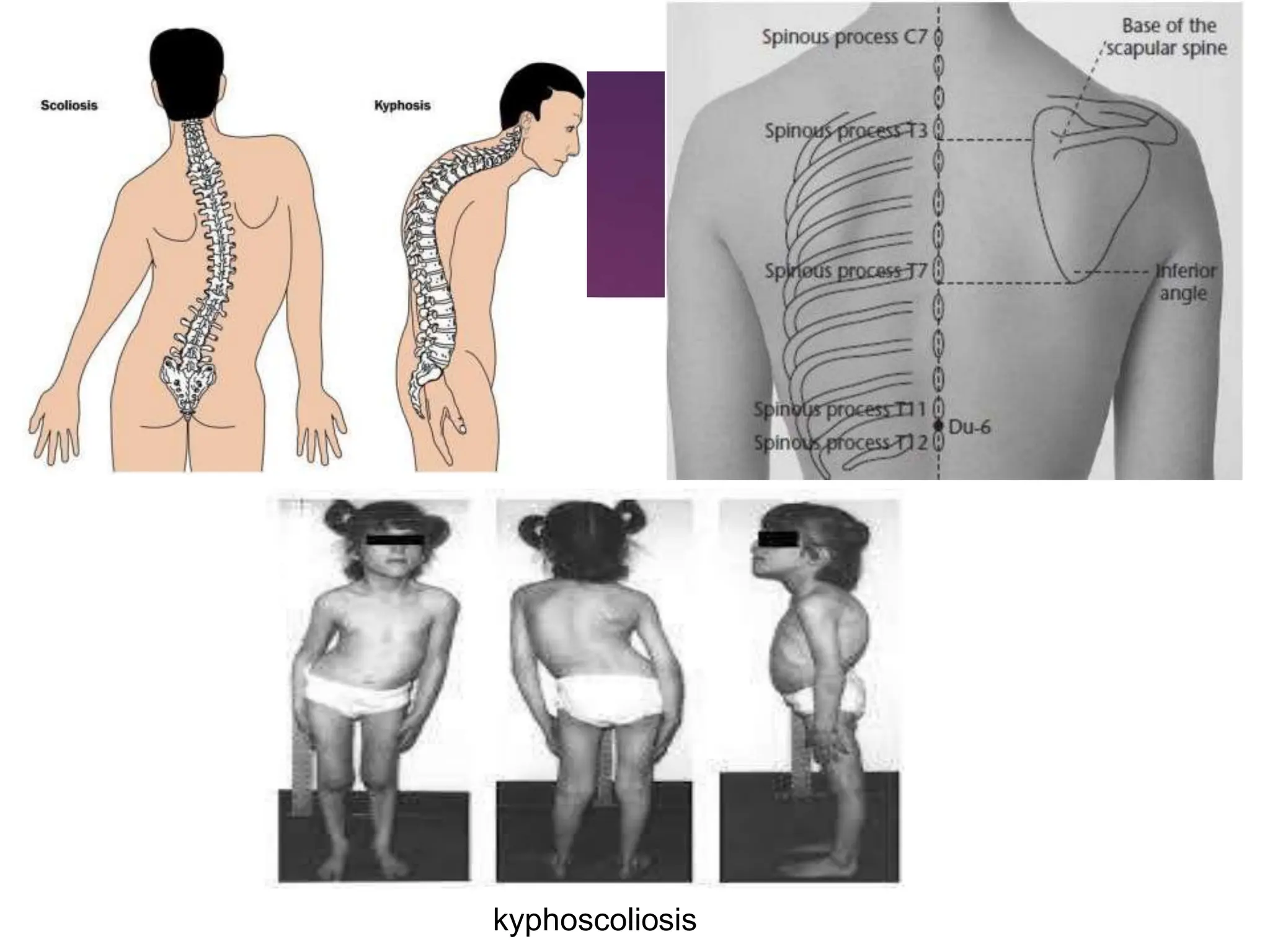
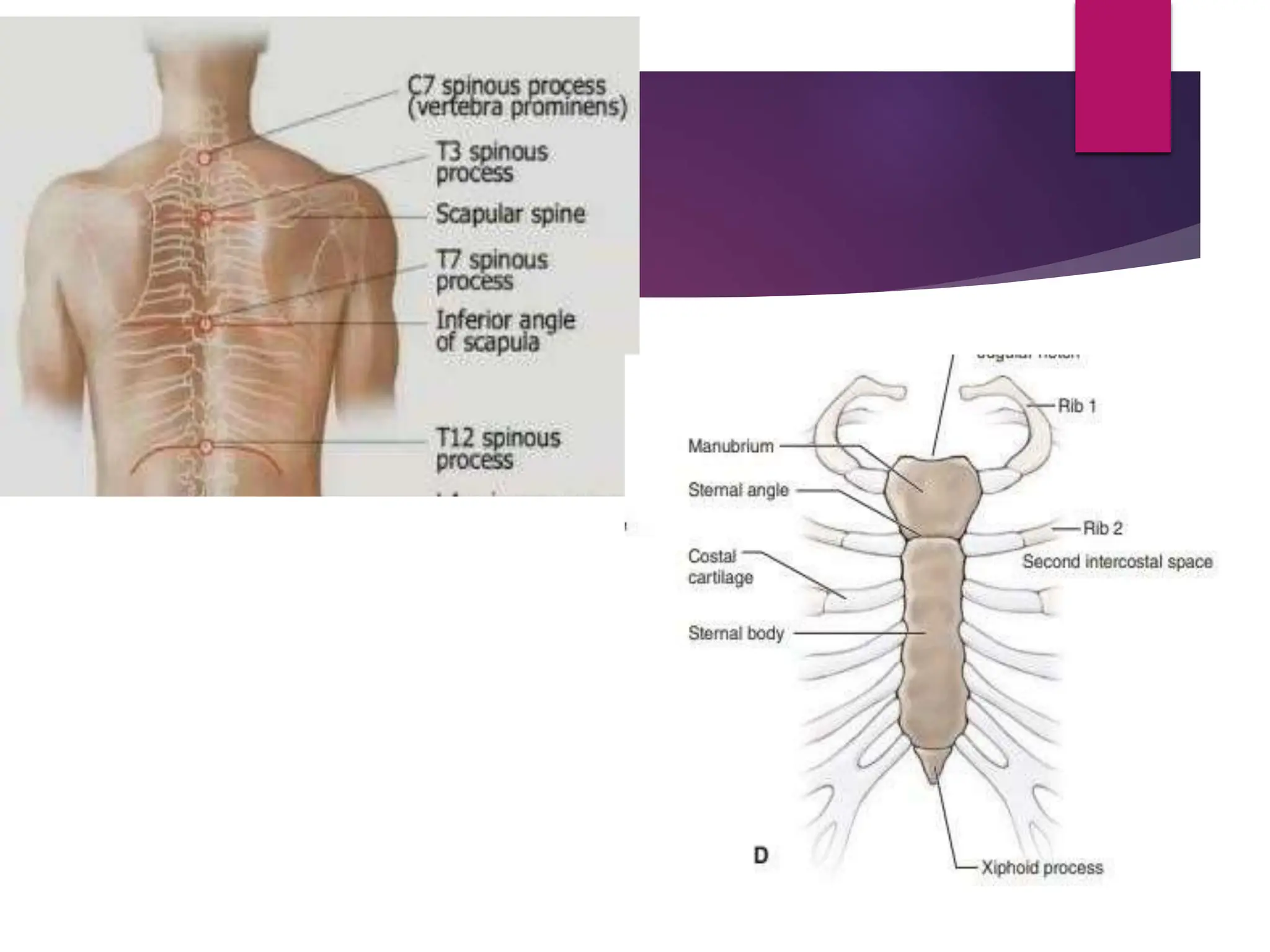
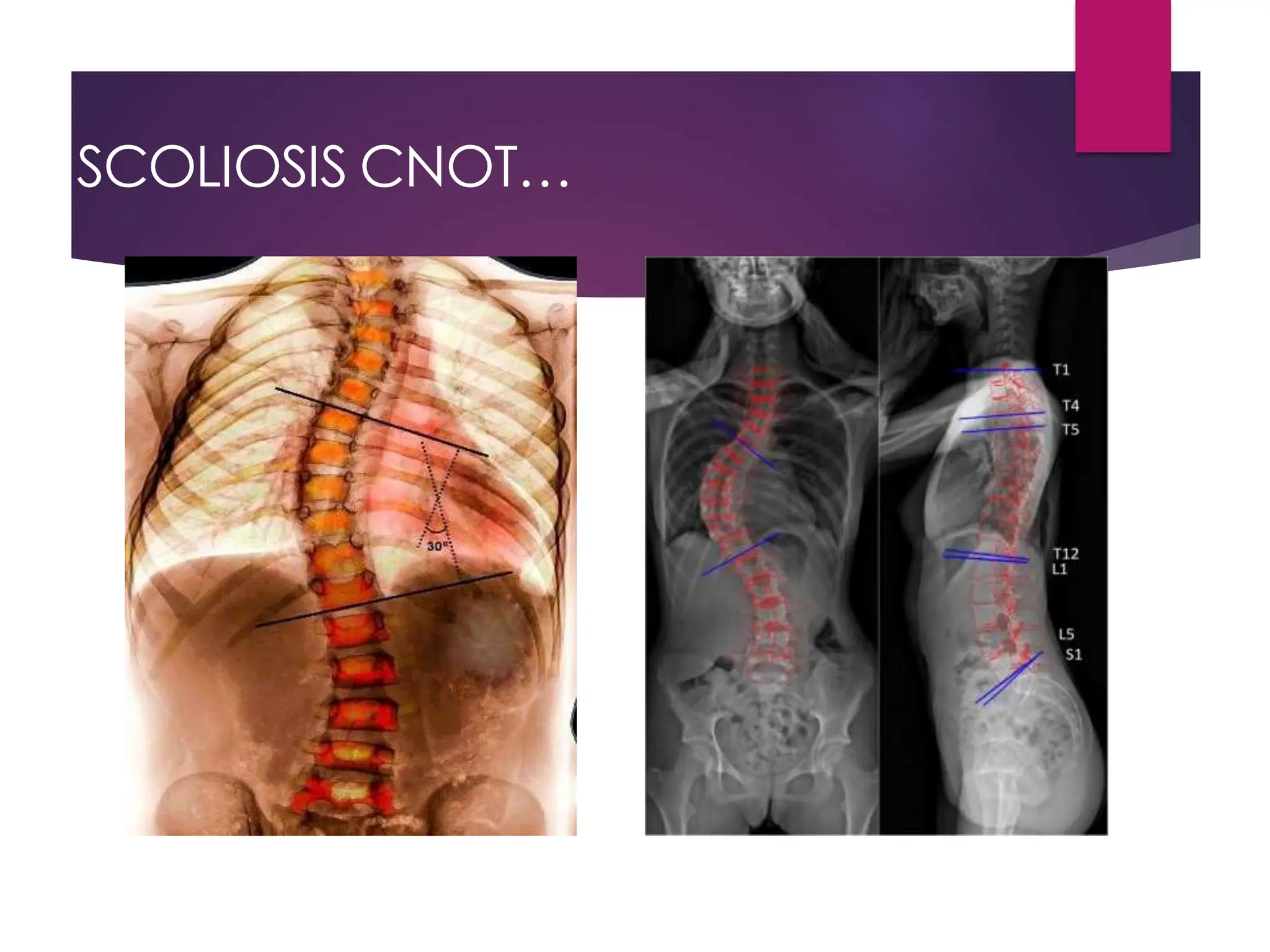
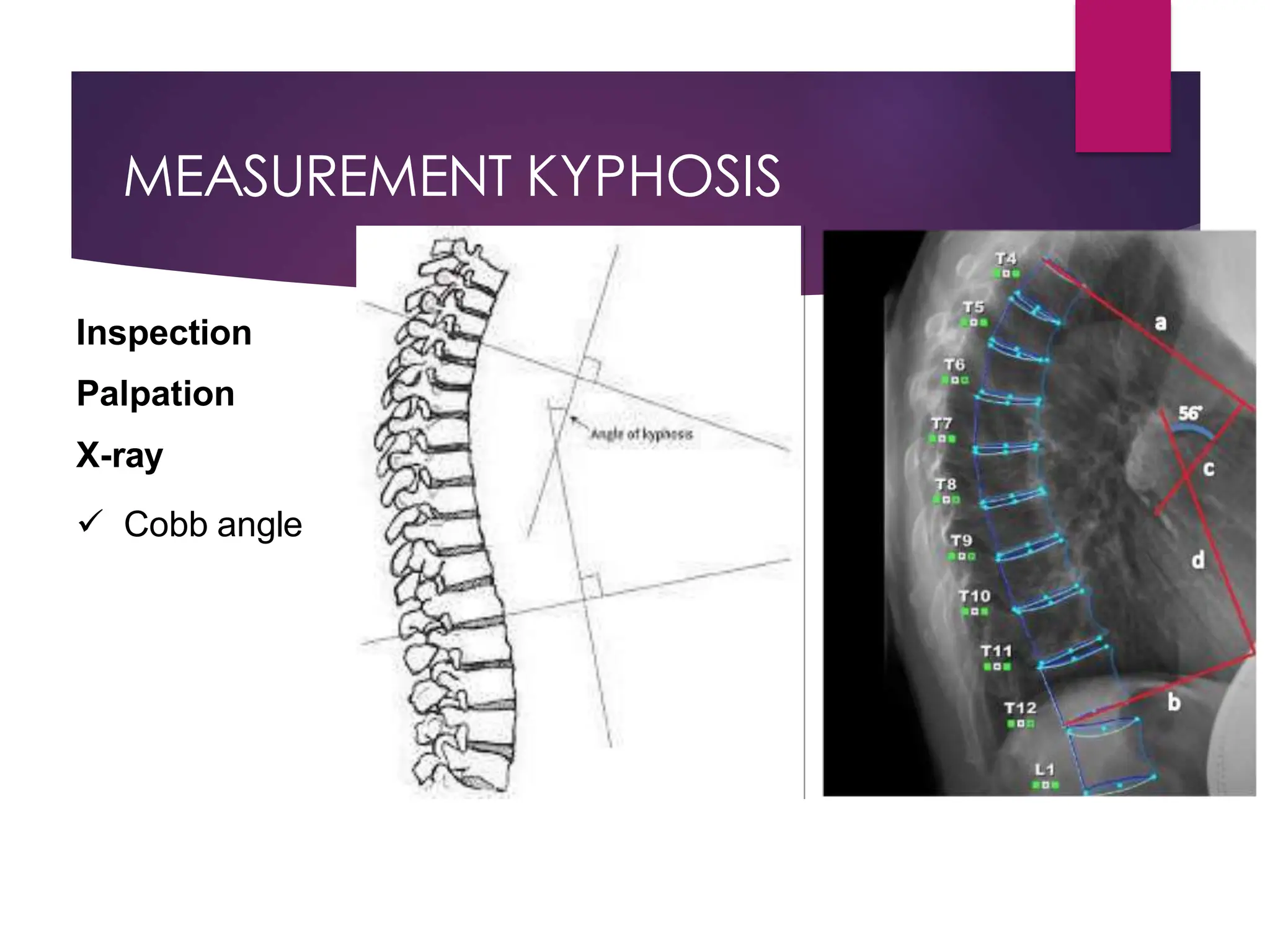
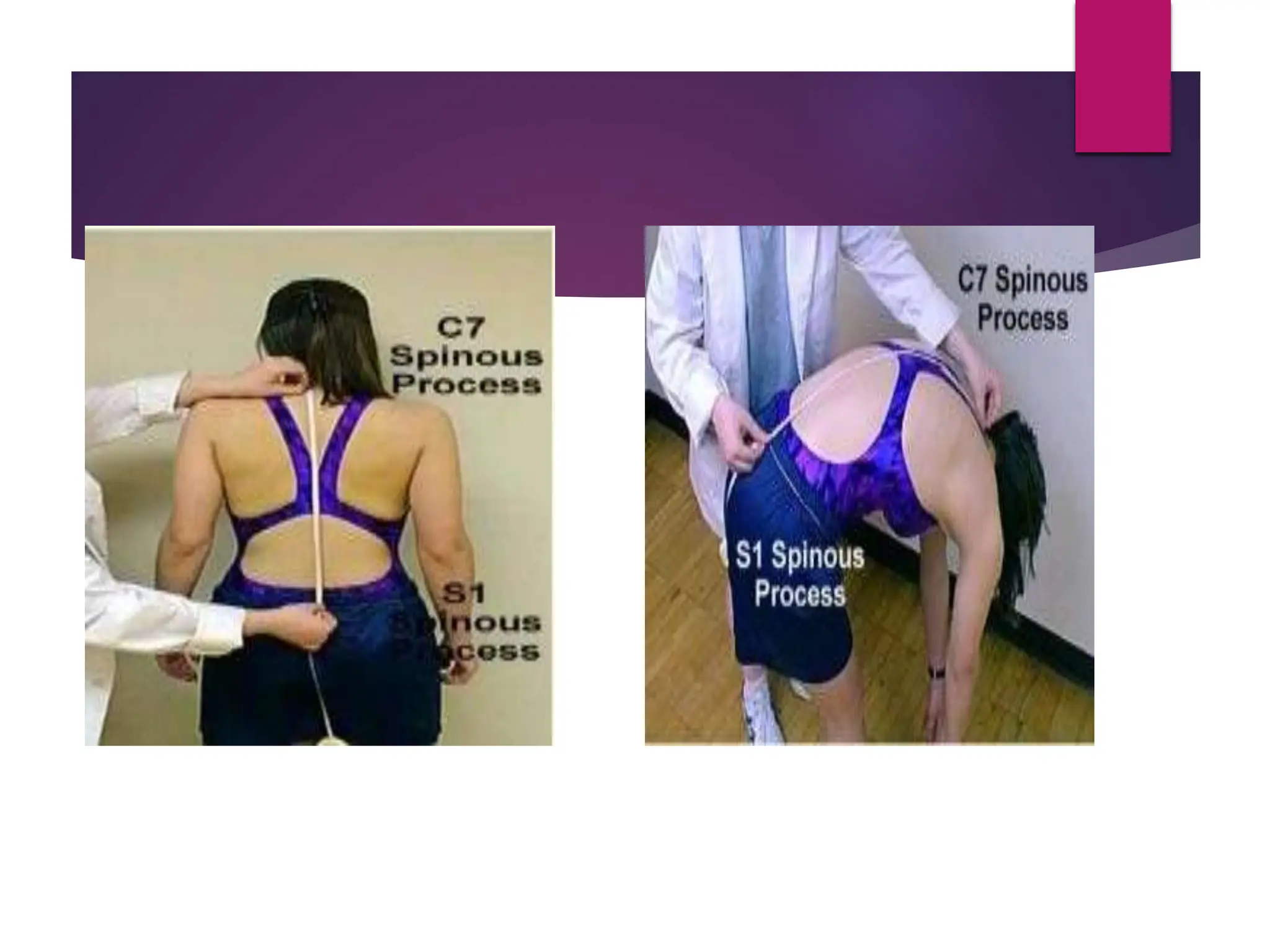
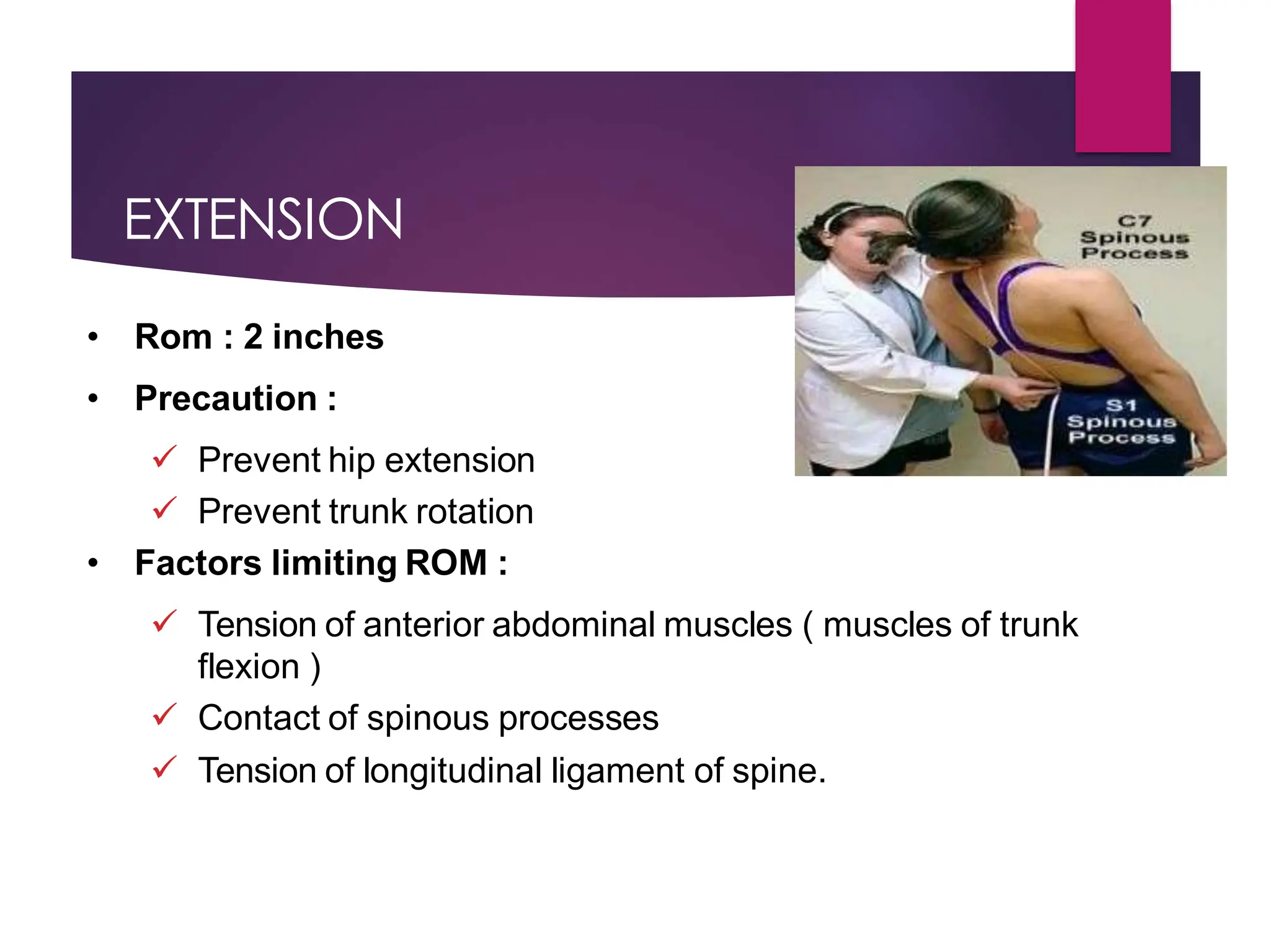
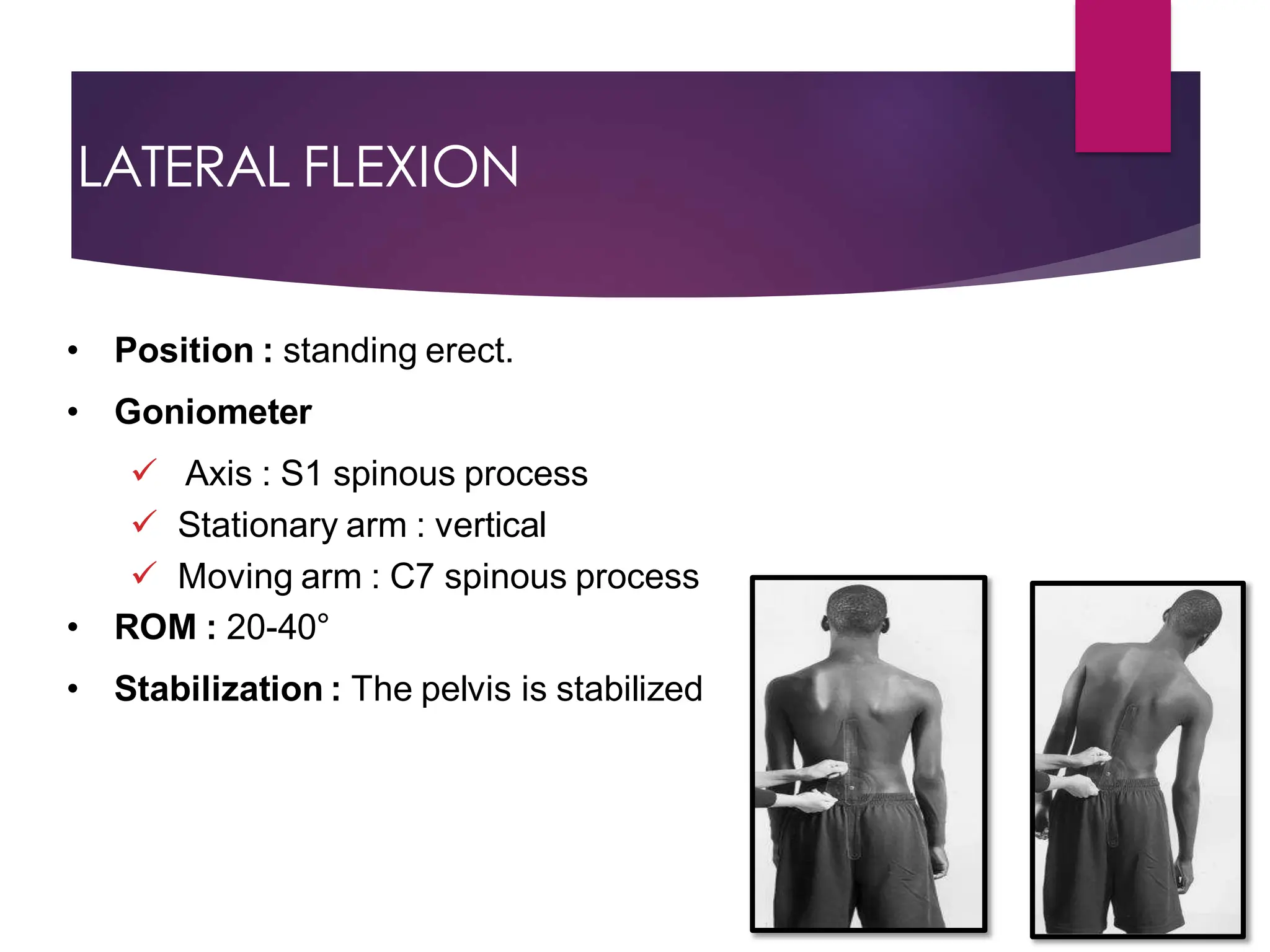
The document discusses the thoracic spine, detailing its anatomical structure, including its 12 vertebrae, the kyphotic curve, and its role in the thoracic cage. It highlights various conditions affecting the thoracic spine, such as kyphosis, scoliosis, and their associated symptoms and examinations, including inspection and palpation techniques, special tests like the Adams forward bend test, and measurement methods. Additionally, it covers factors affecting range of motion (ROM) and precautions necessary during assessments.