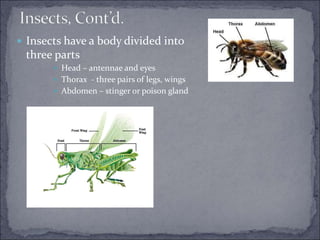
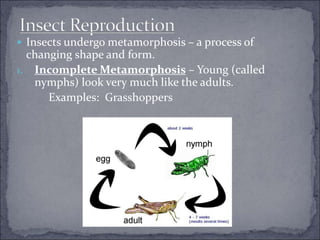
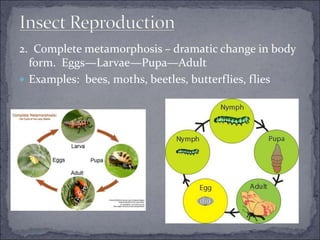
Arthropods are the most successful phylum, with over 750,000 species. They have segmented bodies, jointed appendages, and a tough exoskeleton. There are three main groups of arthropods: crustaceans, which are primarily aquatic and have two pairs of antennae; spiders and their relatives, which lack antennae and have fangs and pedipalps; and insects, which undergo incomplete or complete metamorphosis and have three body sections.