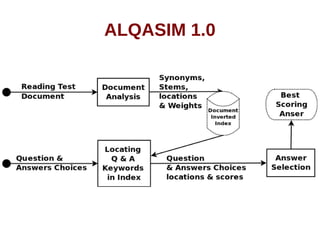
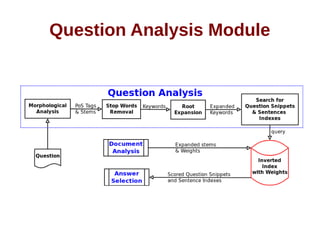
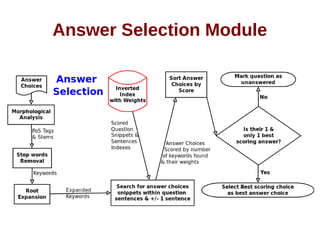
The document discusses the significance of Arabic question answering (QA) systems, which are essential for providing accurate and swift answers to the over 350 million native Arabic speakers. It outlines the QA pipeline, focusing on the importance of answer selection and validation to mitigate error propagation and enhance performance. The document also details the development of the QA4MRE protocol and its implementation in systems like Alqasim 1.0 and Alqasim 2.0, examining their respective methodologies and evaluation results.









![Related Works [continued]
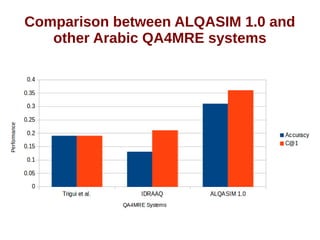
● Abouenour et al. 2012 (IDRAAQ)
– Accuracy : 0.13
– C@1 : 0.21
● Used JIRS (Java Information Retrieval System) for
passage retrieval (Distance Density N-gram Model)
● Semantic expansion using Arabic WordNet (AWN)
● Did not use the CLEF background collections](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/thesispresentation-140929152637-phpapp01/85/Answer-Selection-and-Validation-for-Arabic-Questions-12-320.jpg)
![Related Works [continued]
● Trigui et al. 2012:
– Accuracy : 0.19
– C@1 : 0.19
● Has not marked any questions as unanswered
● Retrieves the passages that have the question keywords and
aligns them with the answer choices
● Finds the best answer choice in the retrieved passages
● Expands the answer choices that could not be found in the
retrieved passages using some inference rules on the
background collection
● Depends on the background collection as it offers enough
redundancy for the passage retrieval module](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/thesispresentation-140929152637-phpapp01/85/Answer-Selection-and-Validation-for-Arabic-Questions-13-320.jpg)
![Related Works [continued]
● Bhaskar et al. 2012 (on the English test-set)
– Accuracy : 0.53
– C@1 : 0.65
● Combines each answer choice with the question in
a hypothesis
● Searches for the hypothesis keywords in the
document
● Uses textual entailment to rank the retrieved
passages](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/thesispresentation-140929152637-phpapp01/85/Answer-Selection-and-Validation-for-Arabic-Questions-14-320.jpg)
![Related Works [continued]
● The 2 Arabic QA4MRE systems
– Use the typical QA pipeline that depend mainly on
passage retrieval
– Do not analyze the reading test document
● The English system (Bhaskar et al.)
– Analyzes the reading test document
– Uses many English specific NLP tools that are not
found in Arabic (at least in the public domain) like:
● semantic parsing
● semantic role labeling
● dependency analysis](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/thesispresentation-140929152637-phpapp01/85/Answer-Selection-and-Validation-for-Arabic-Questions-15-320.jpg)


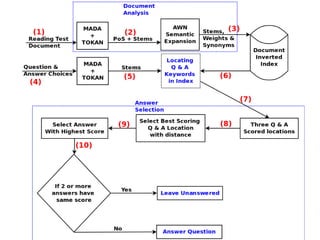

![ALQASIM 1.0 Pros & Cons [continued]
● ALQASIM 1.0 could not identify the question snippet
because its keywords are a bit far from each other.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/thesispresentation-140929152637-phpapp01/85/Answer-Selection-and-Validation-for-Arabic-Questions-22-320.jpg)

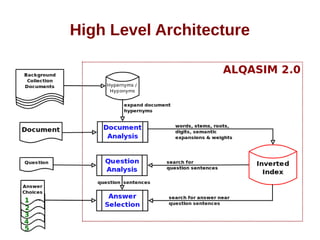
![ALQASIM 2.0 [continued]
A basic ontology of hypernyms and their hyponyms
generated automatically from the background
collection](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/thesispresentation-140929152637-phpapp01/85/Answer-Selection-and-Validation-for-Arabic-Questions-28-320.jpg)

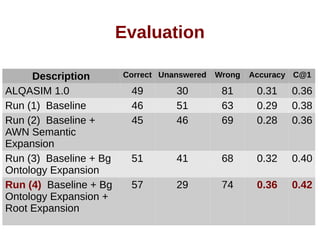
![Evaluation [continued]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/thesispresentation-140929152637-phpapp01/85/Answer-Selection-and-Validation-for-Arabic-Questions-33-320.jpg)
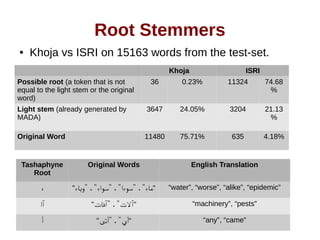
![Evaluation [continued]
Root Stemmer Accuracy C@1
ALQASIM 2.0 without root expansion 0.32 0.4
ISRI 0.36 0.42
Khoja 0.32 0.4
Tashaphyne 0.31 0.36](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/thesispresentation-140929152637-phpapp01/85/Answer-Selection-and-Validation-for-Arabic-Questions-34-320.jpg)