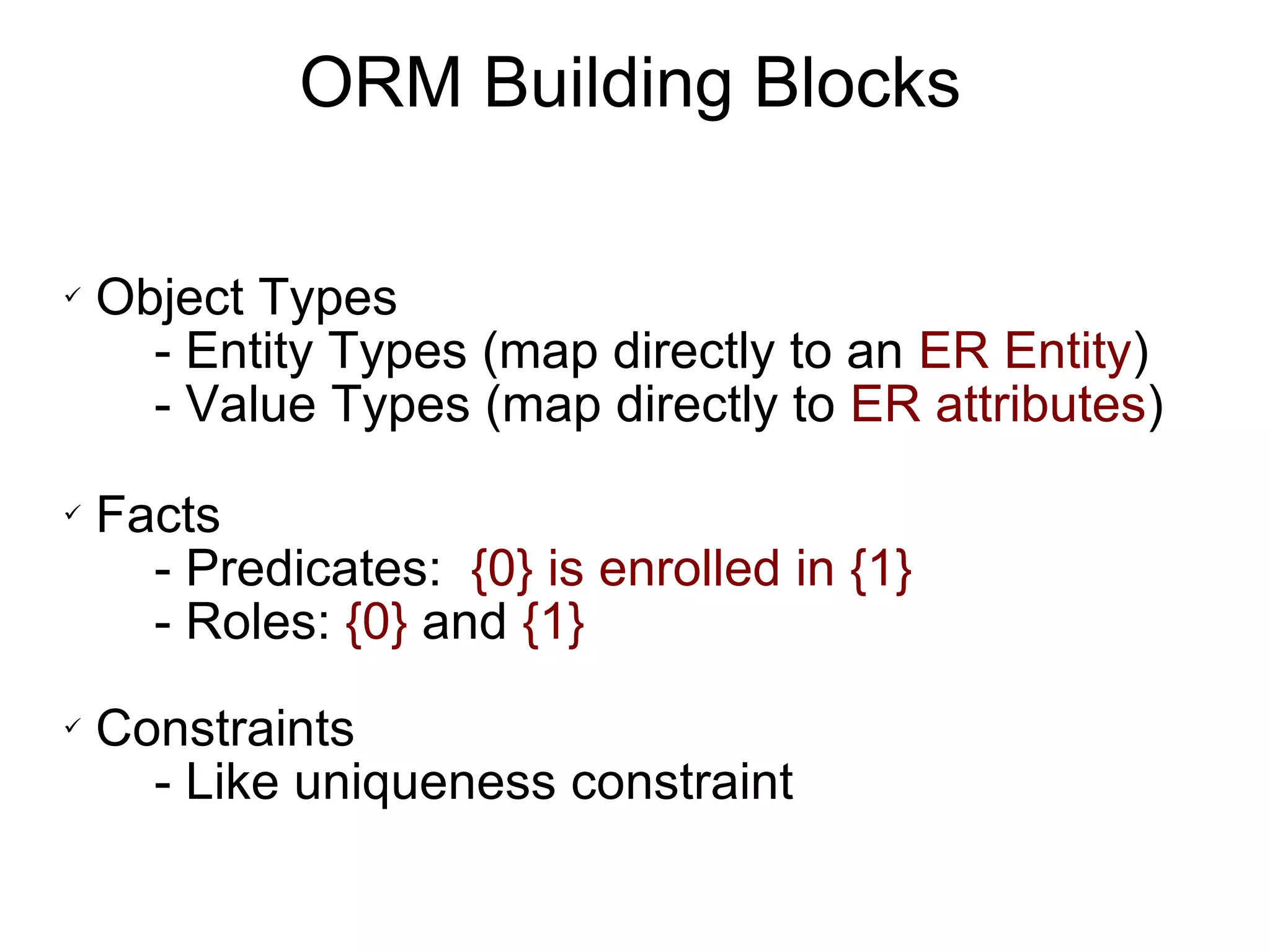
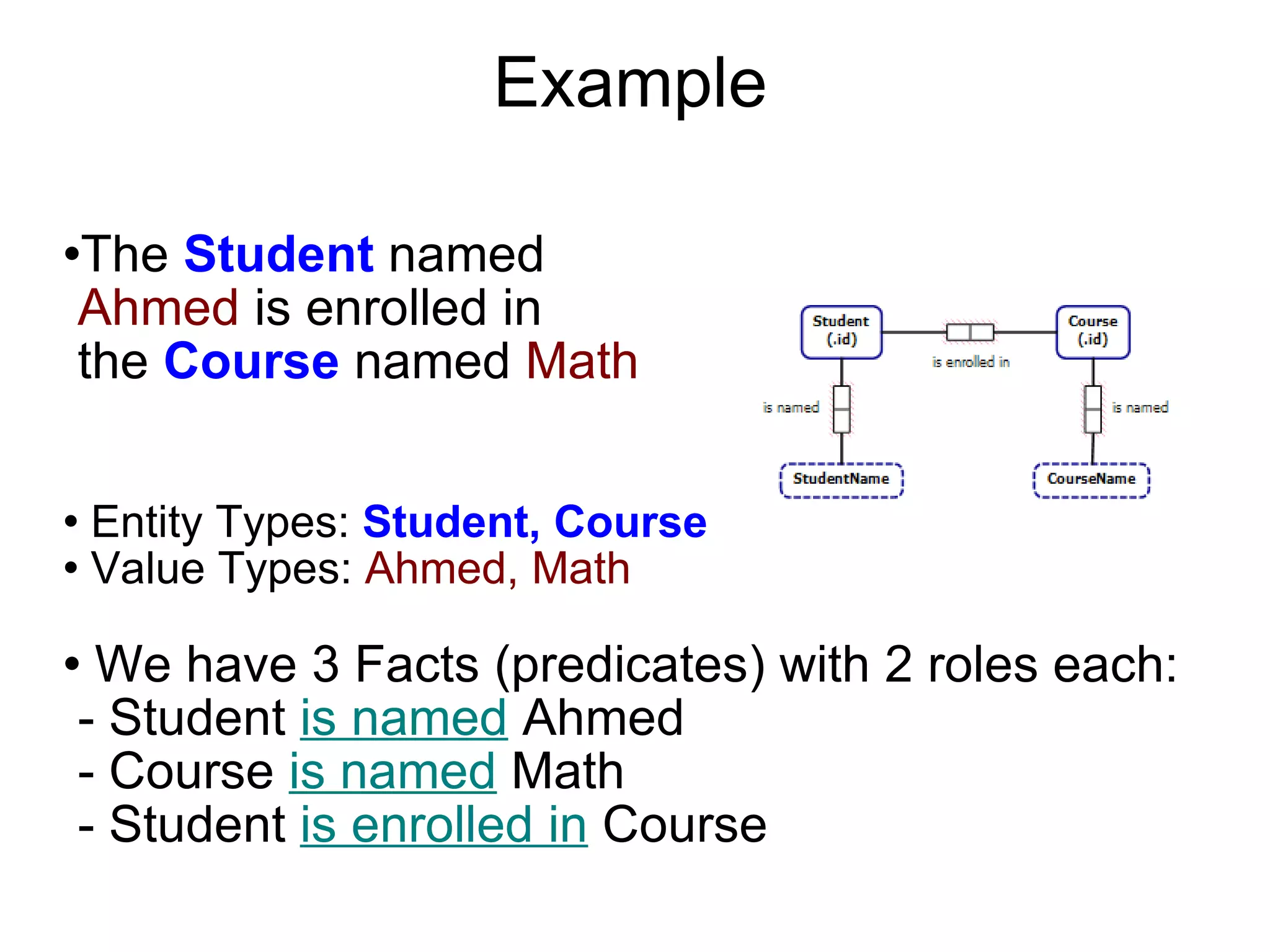
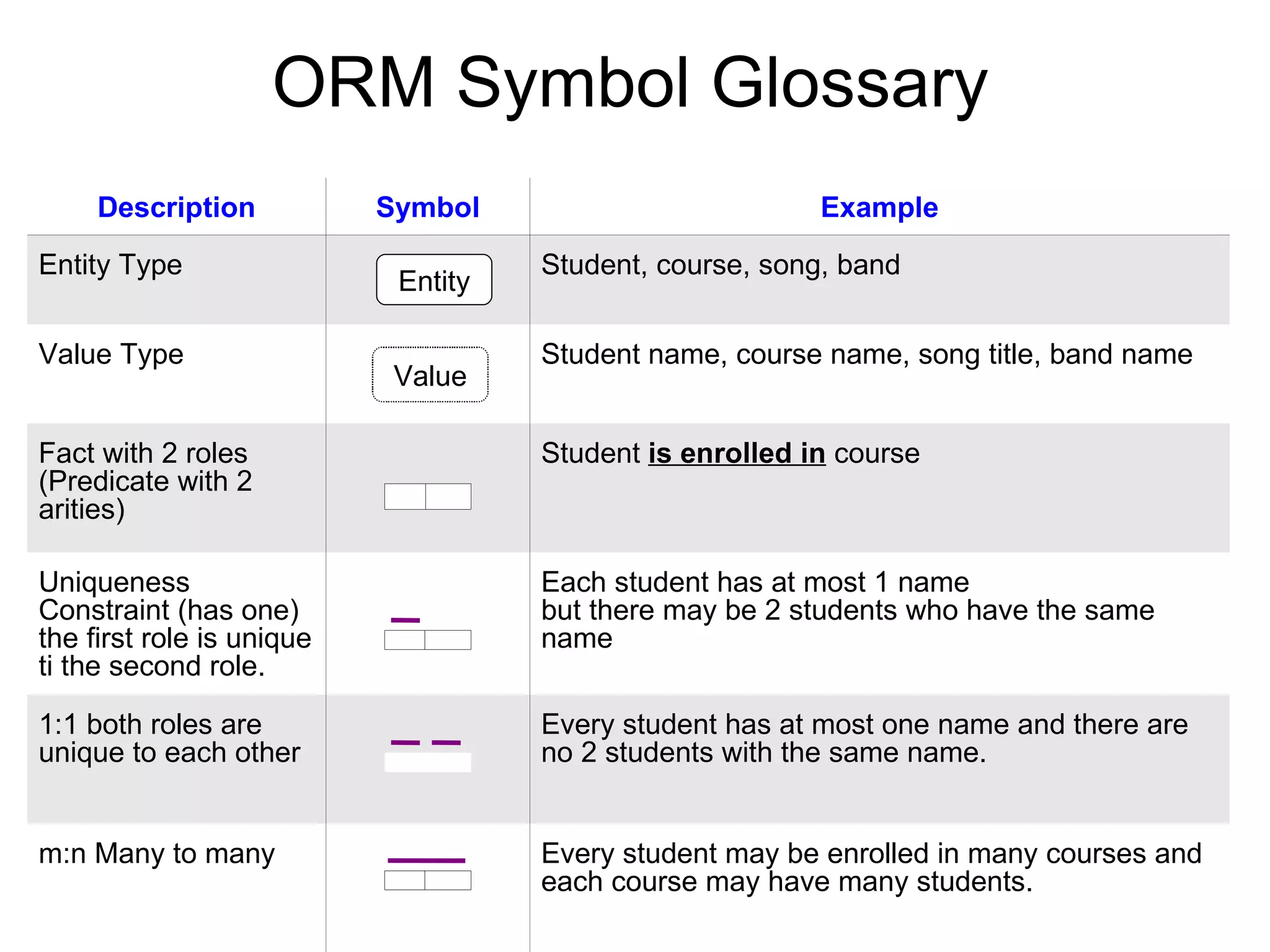
Object Role Modeling (ORM) is a conceptual method for designing and querying database models in non-technical terms, facilitating communication and validation with teams and clients. It utilizes building blocks such as entity types, value types, and facts to model applications systematically. ORM is adaptable to other modeling techniques like ER and UML, and it effectively captures business rules and constraints.