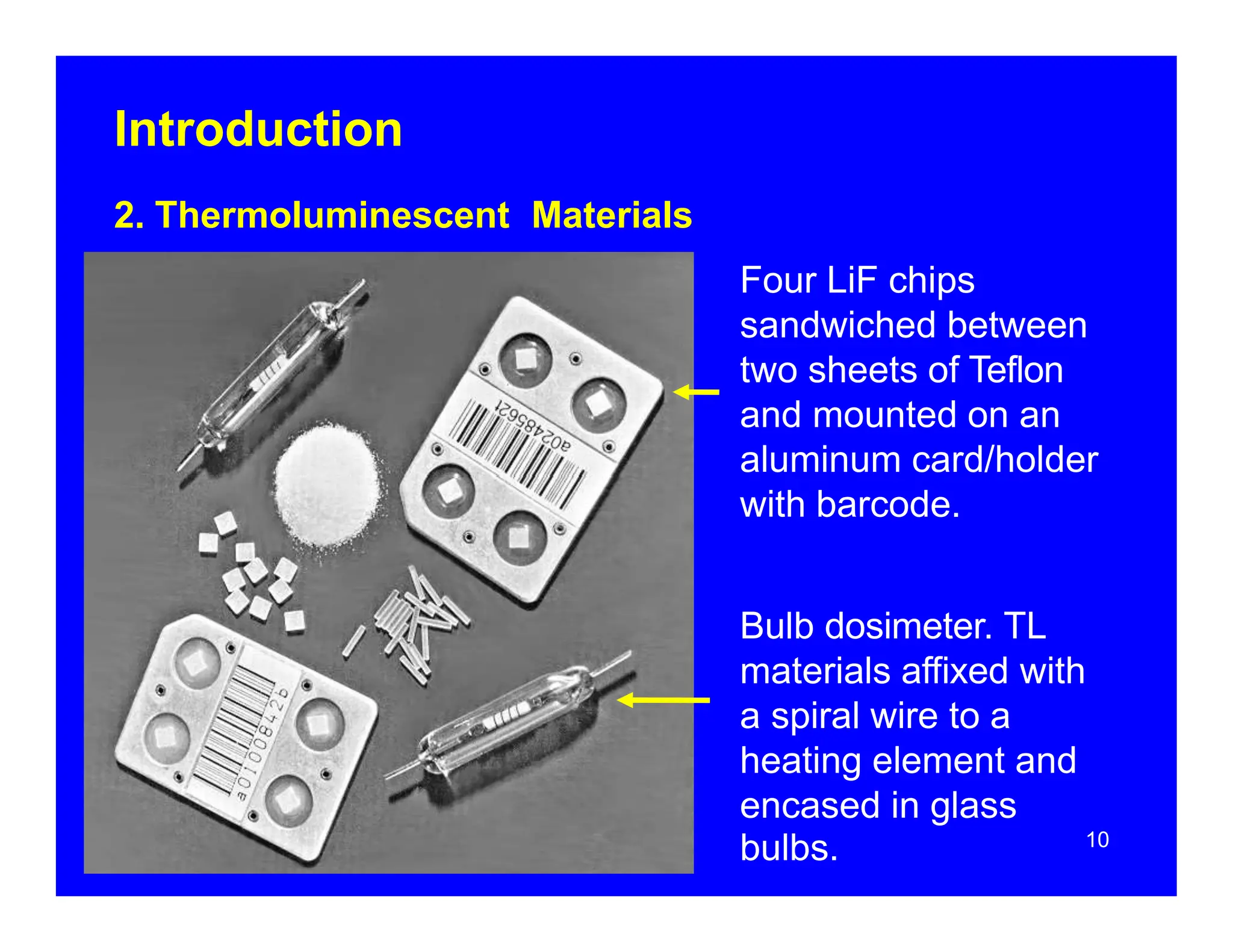
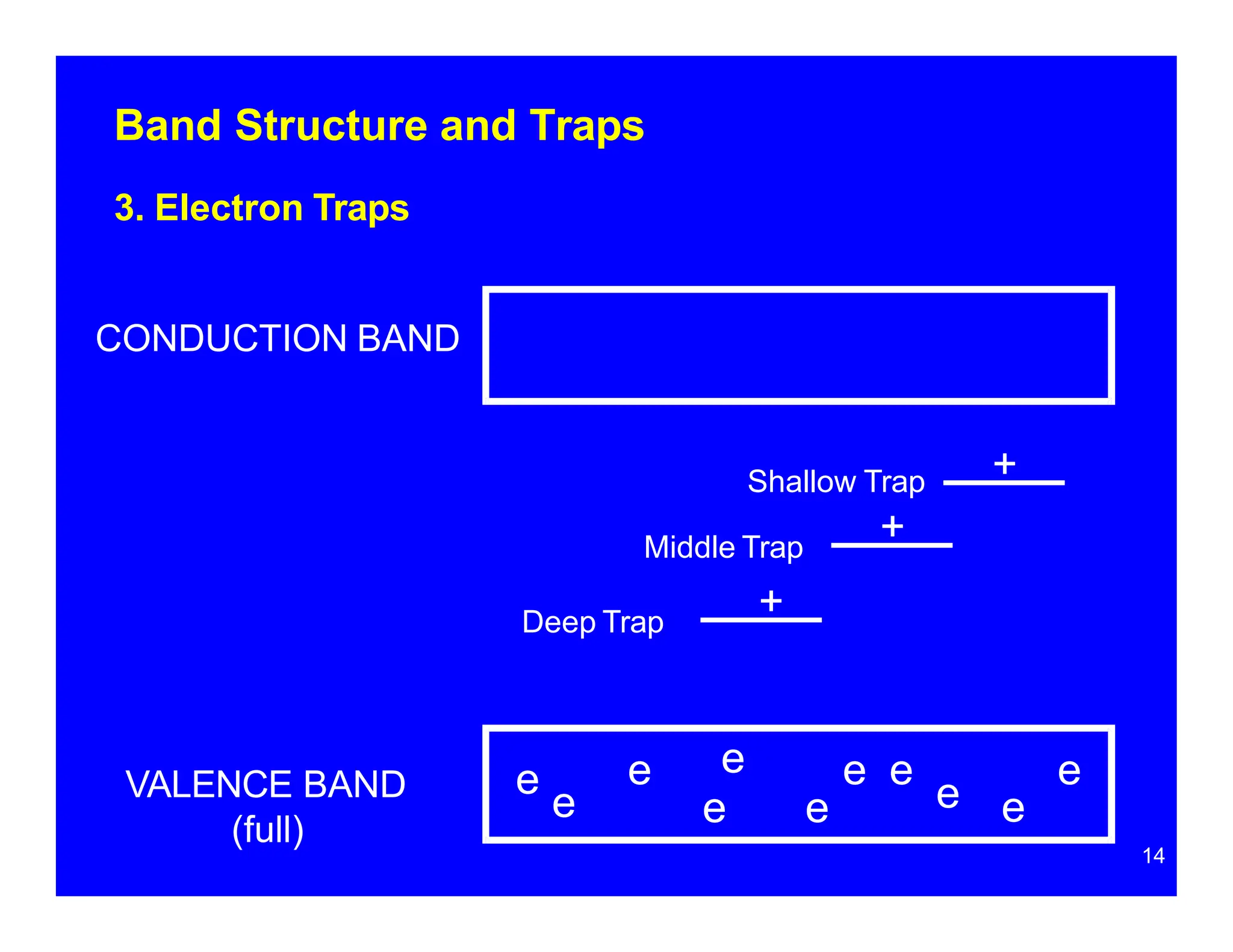
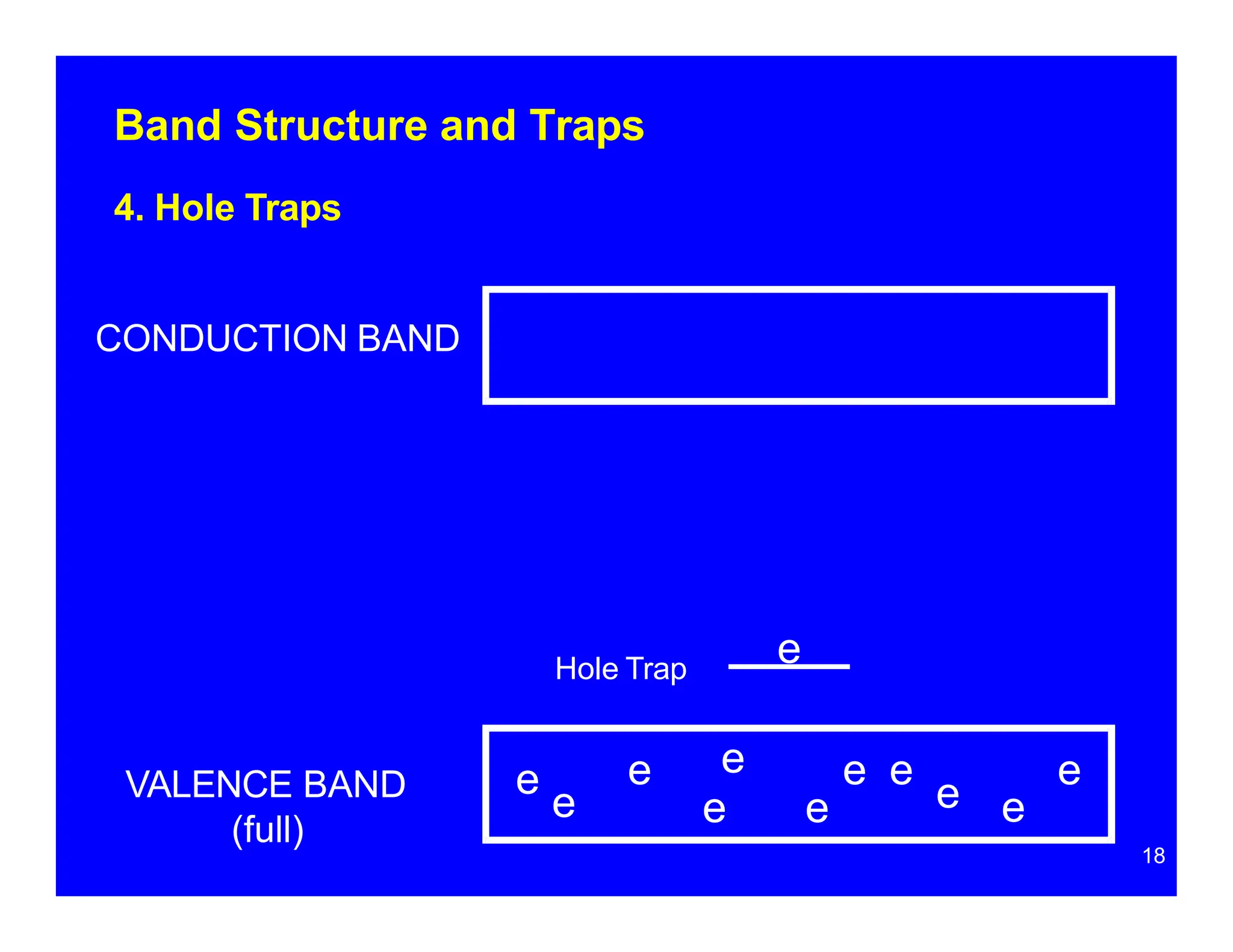
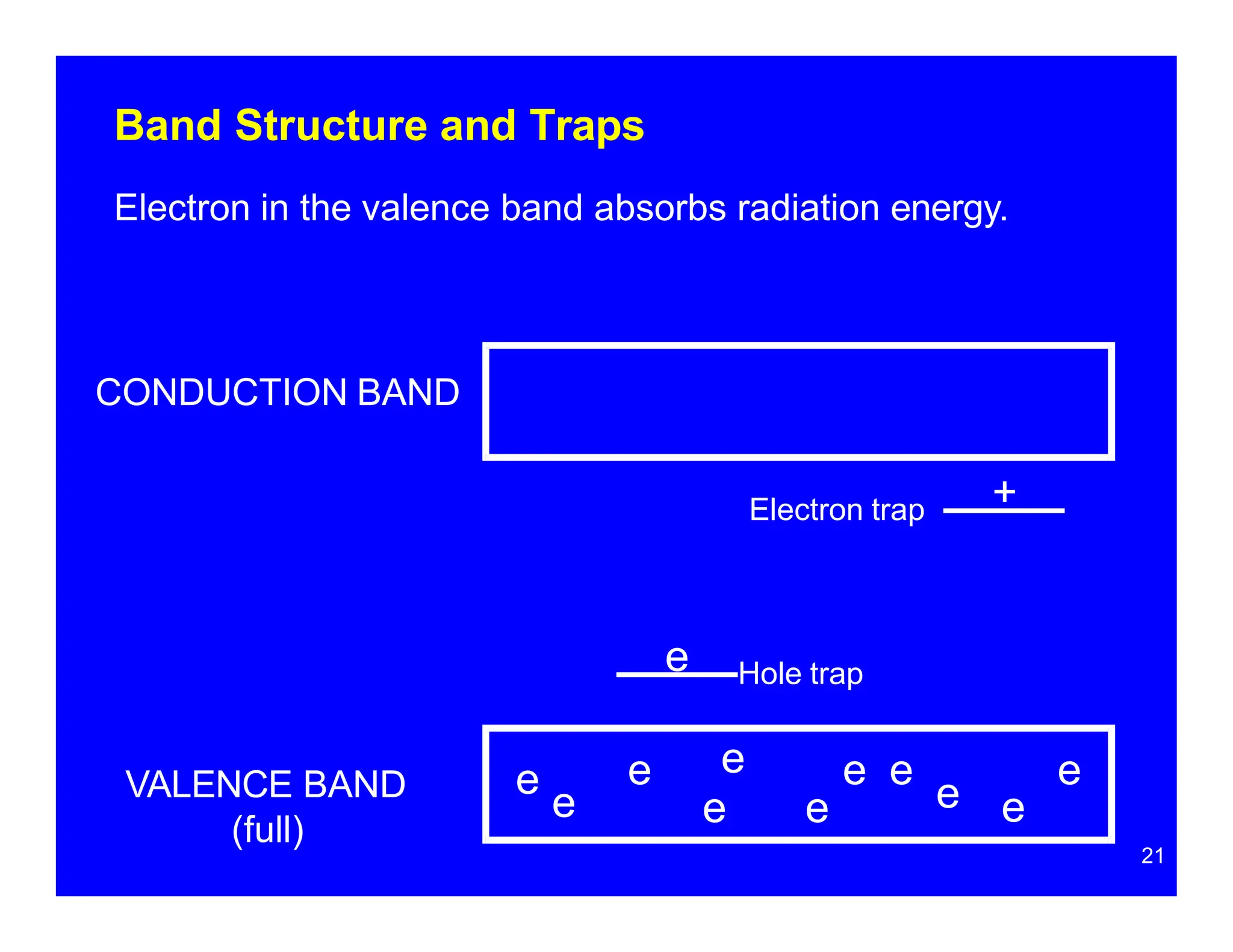
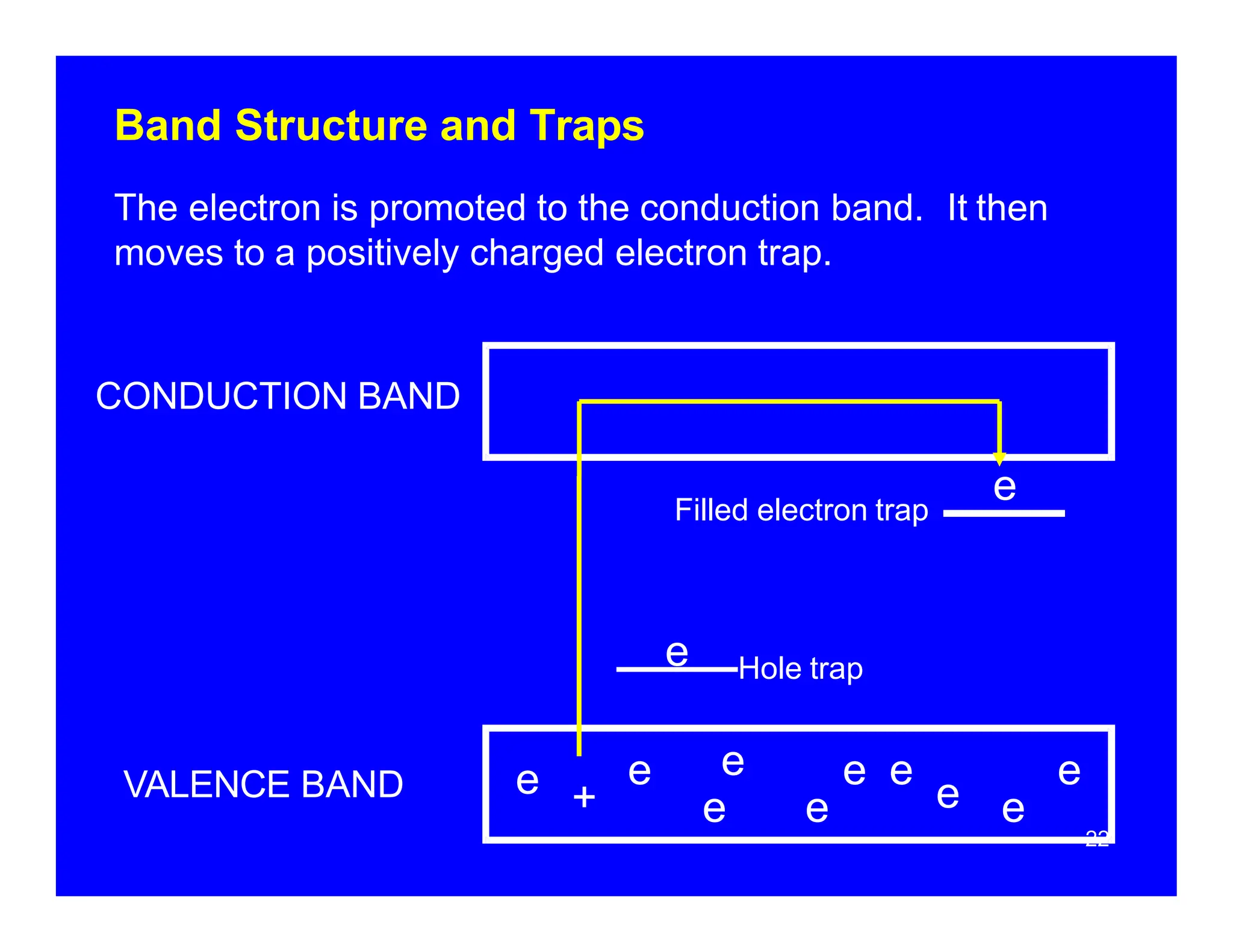
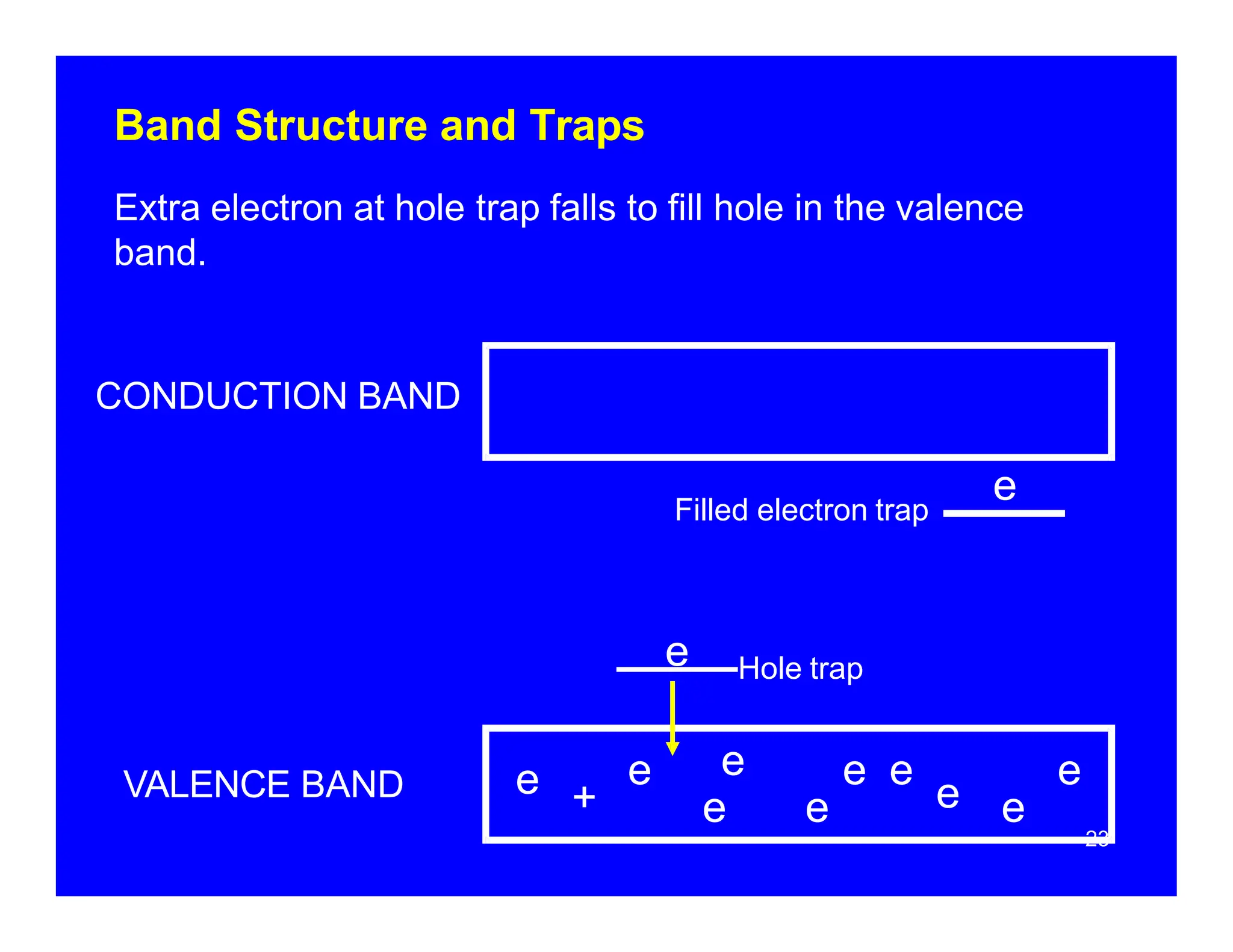
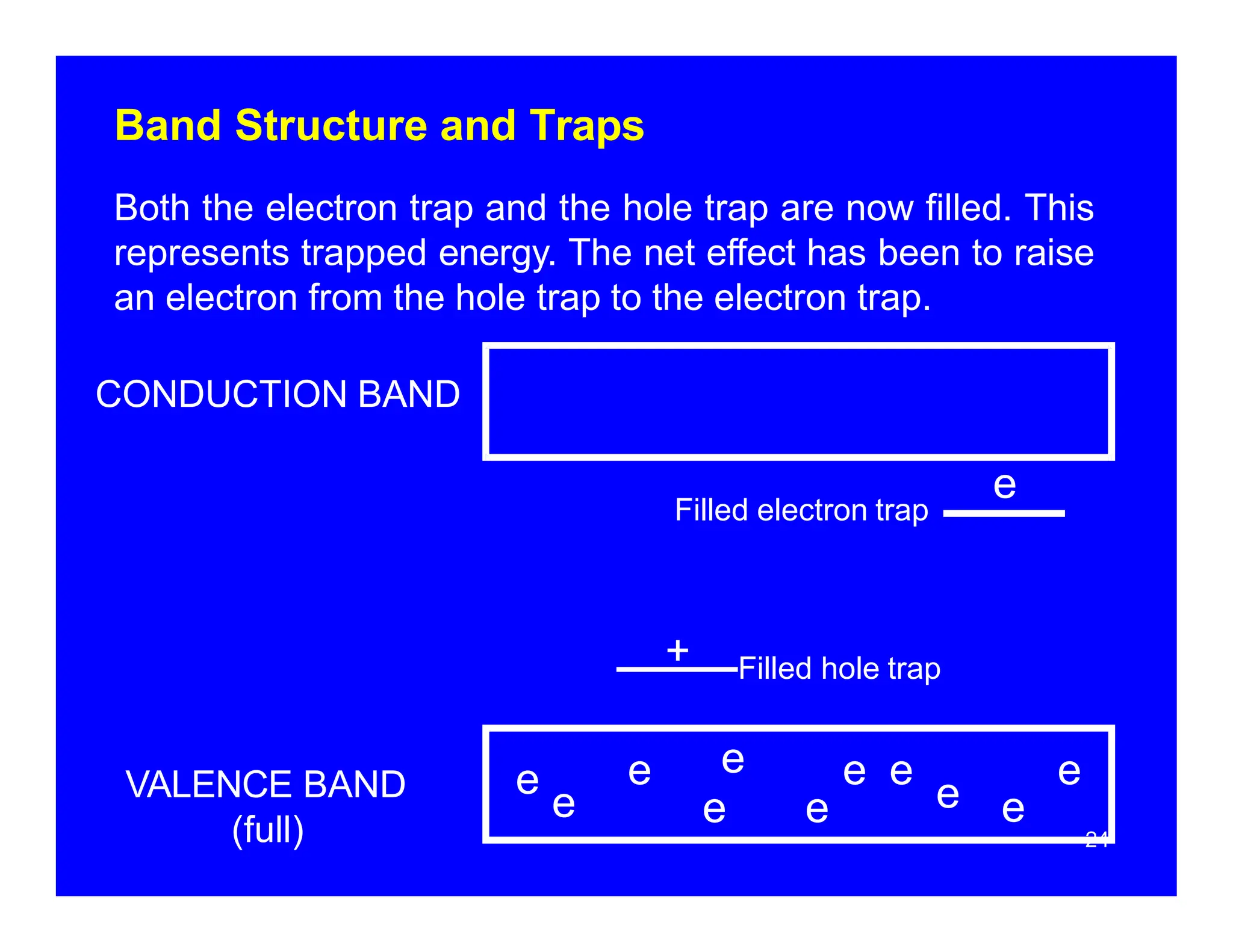
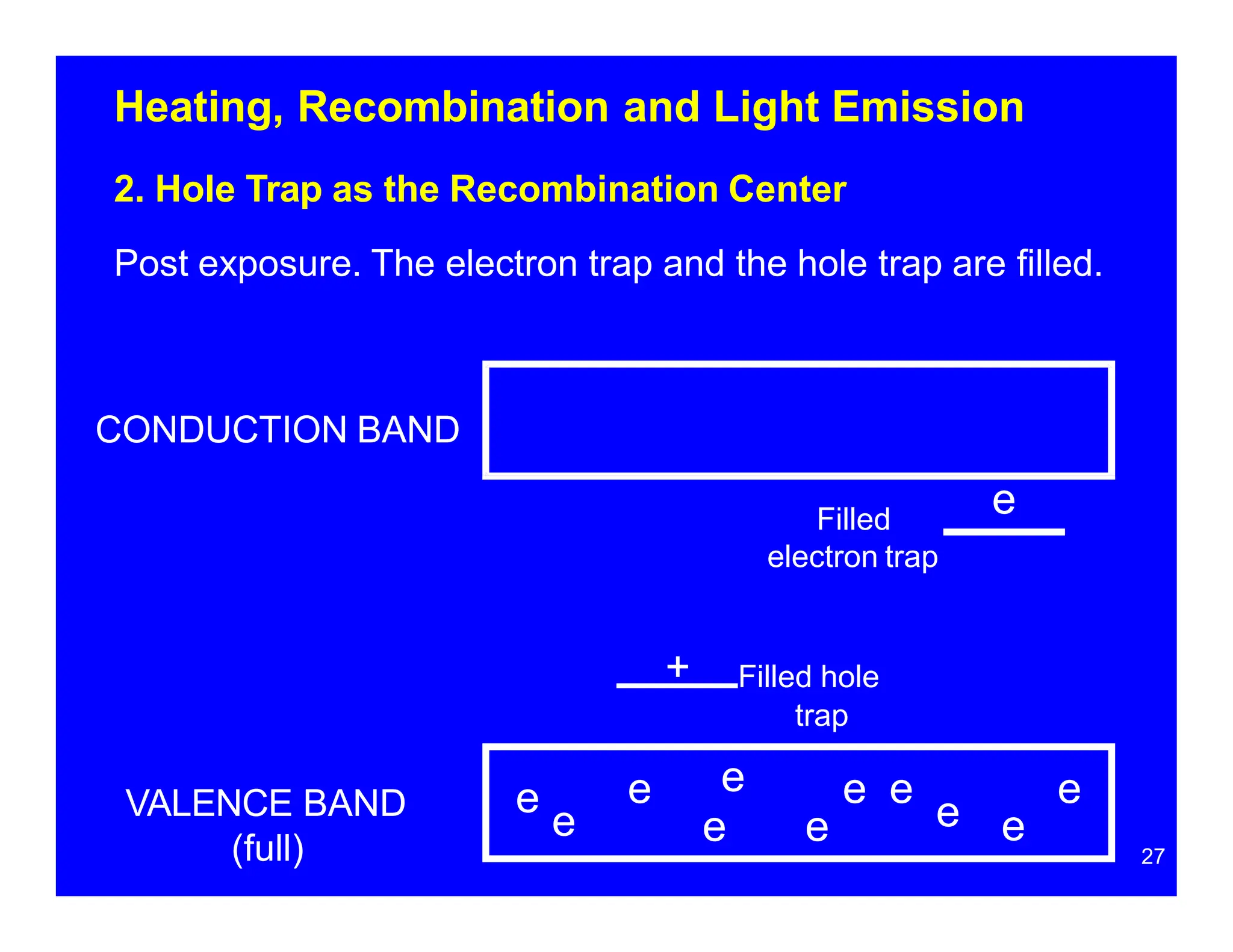
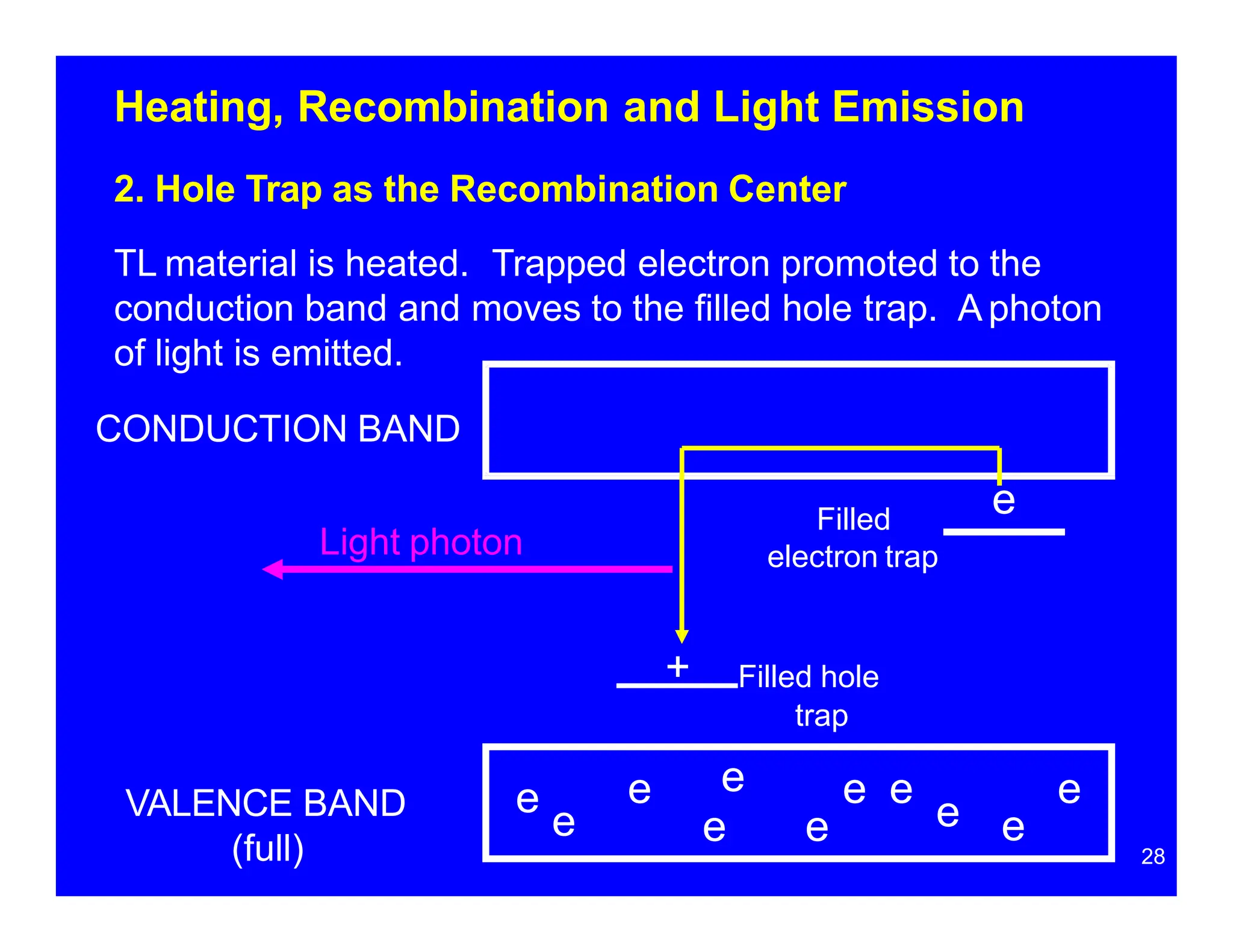
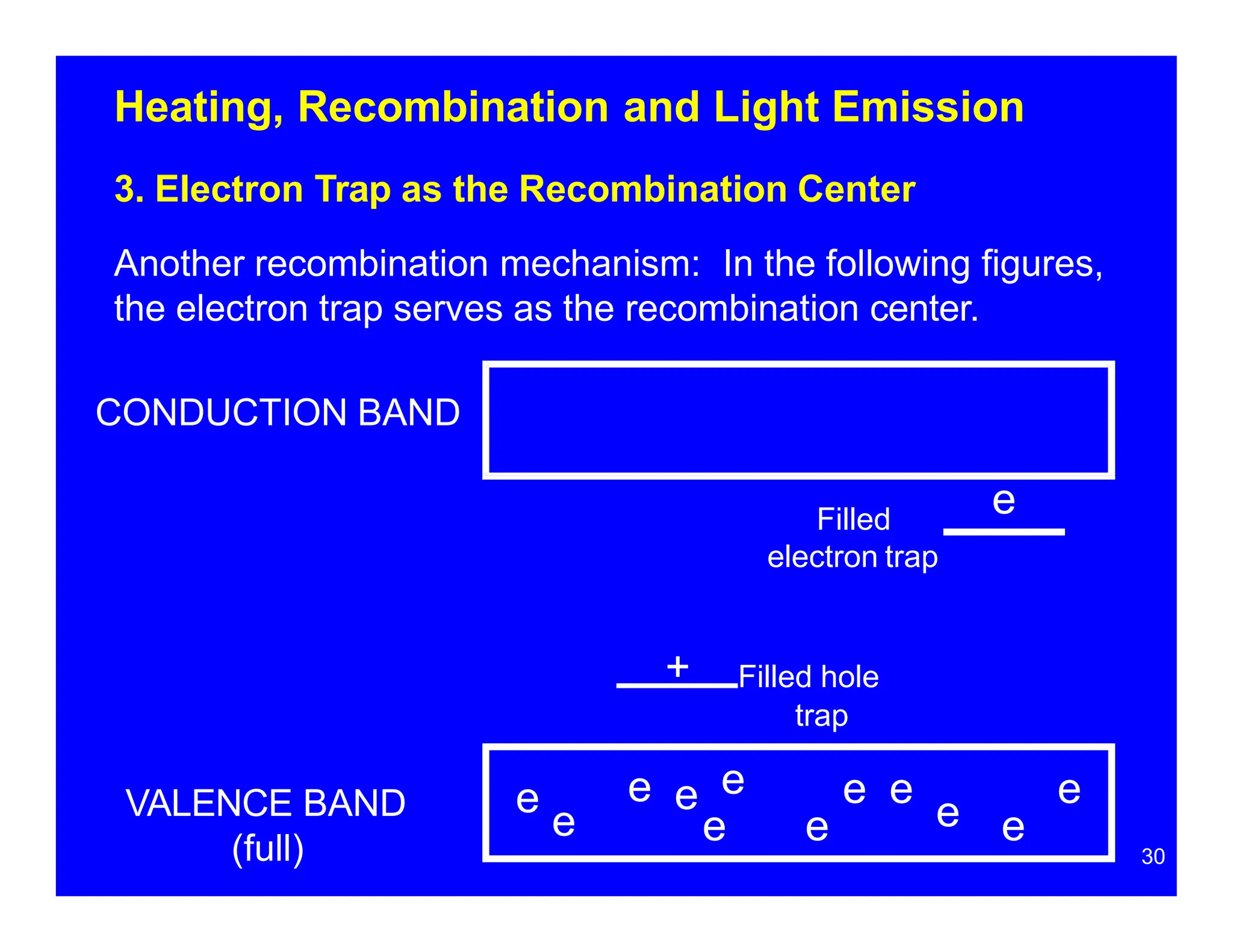
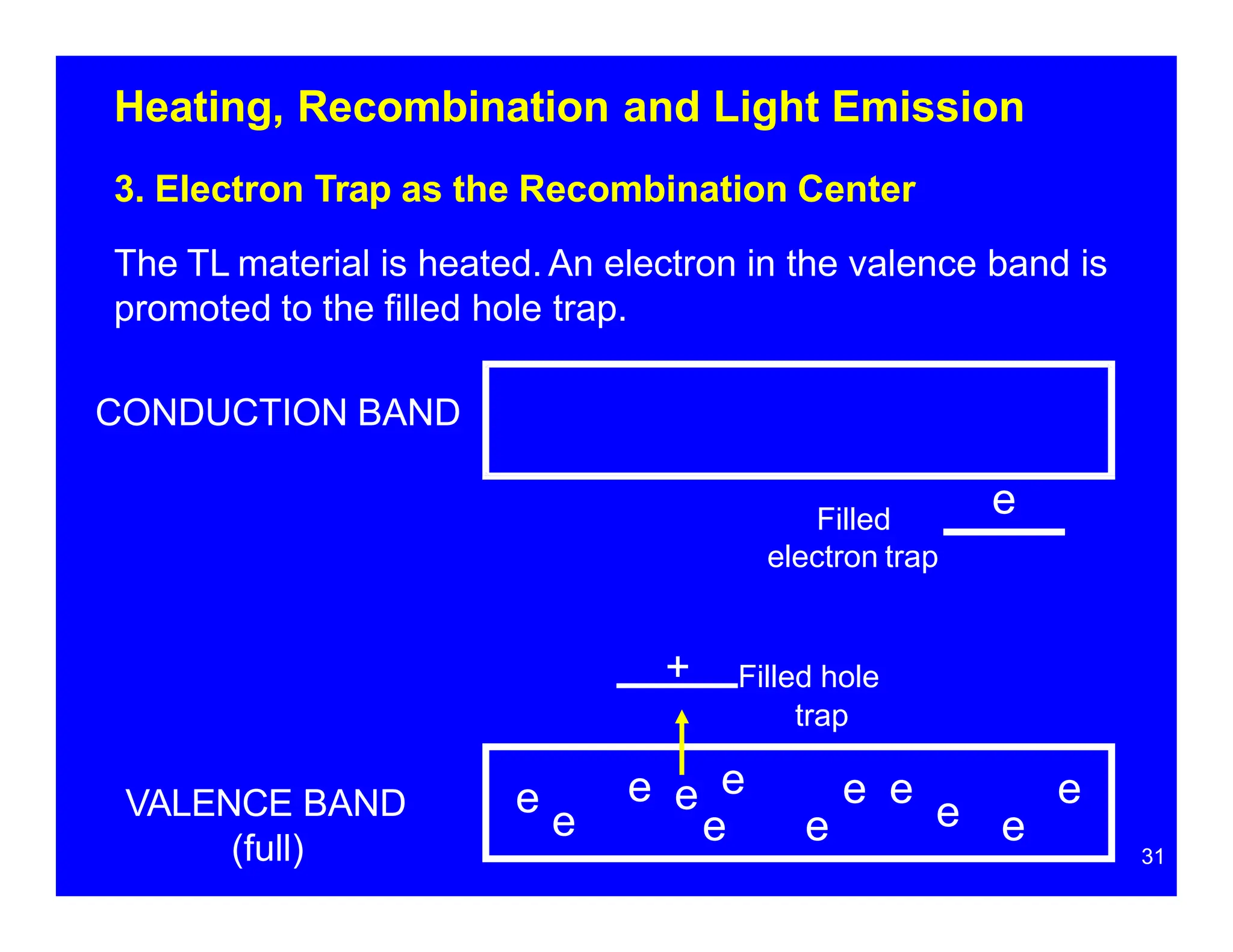
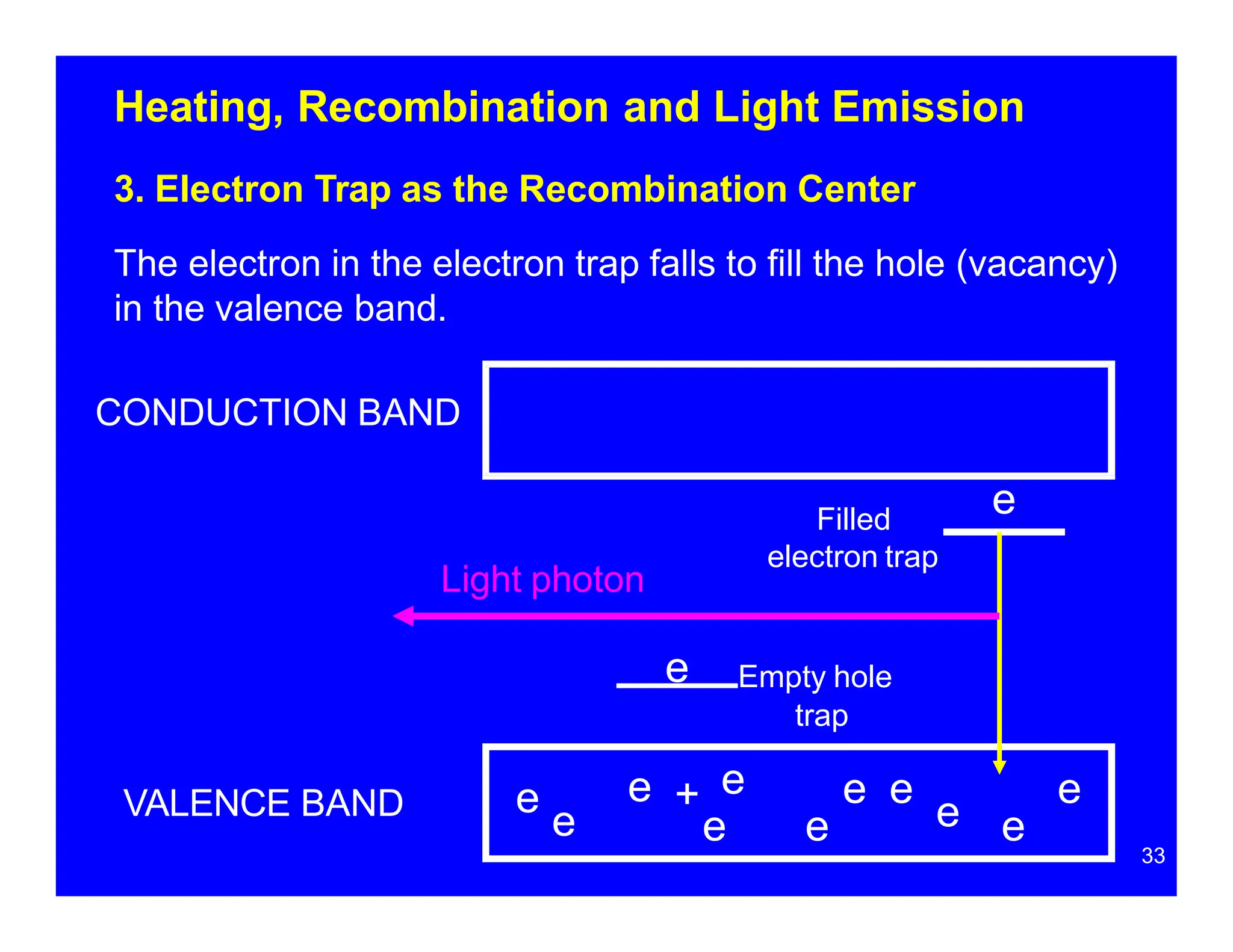
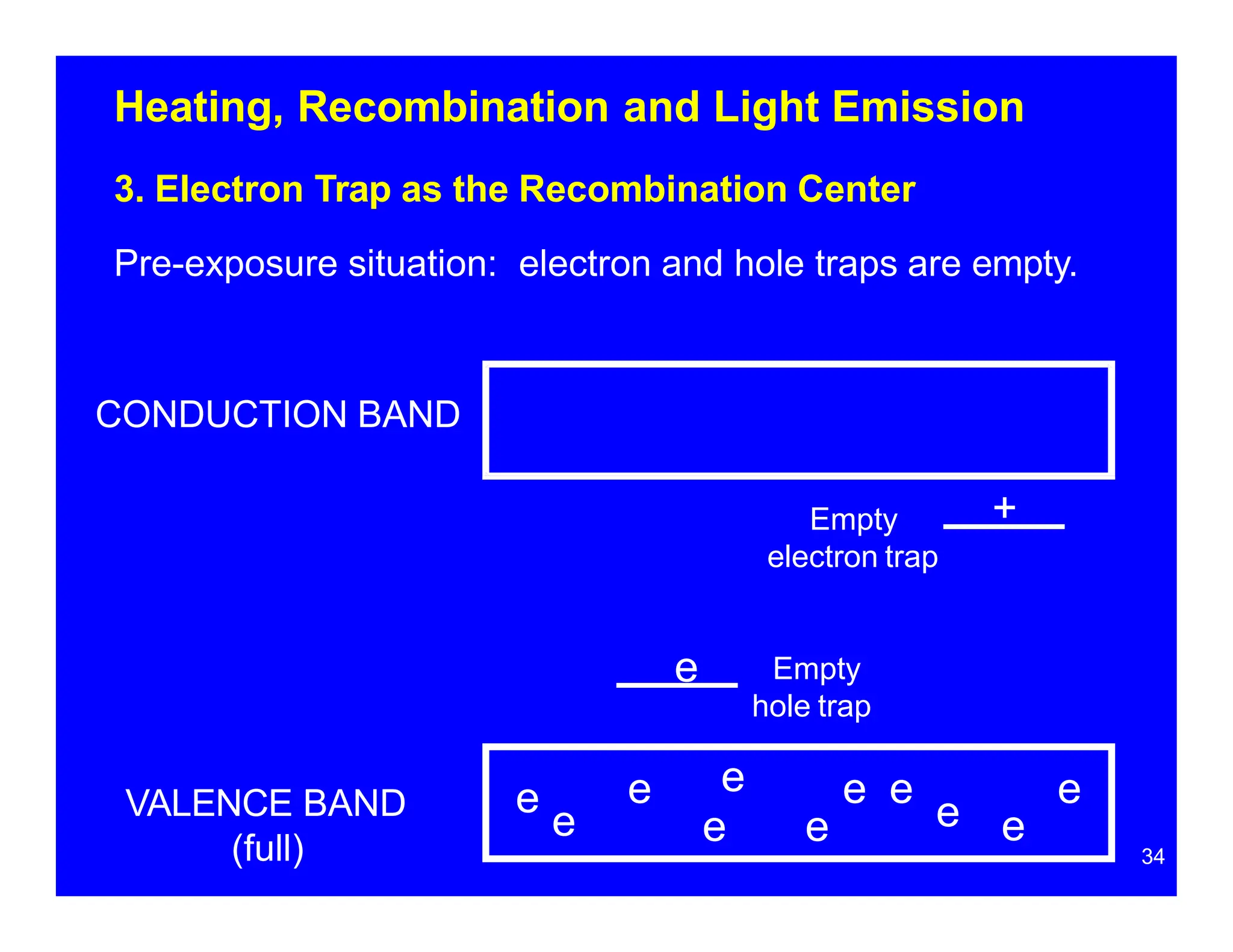
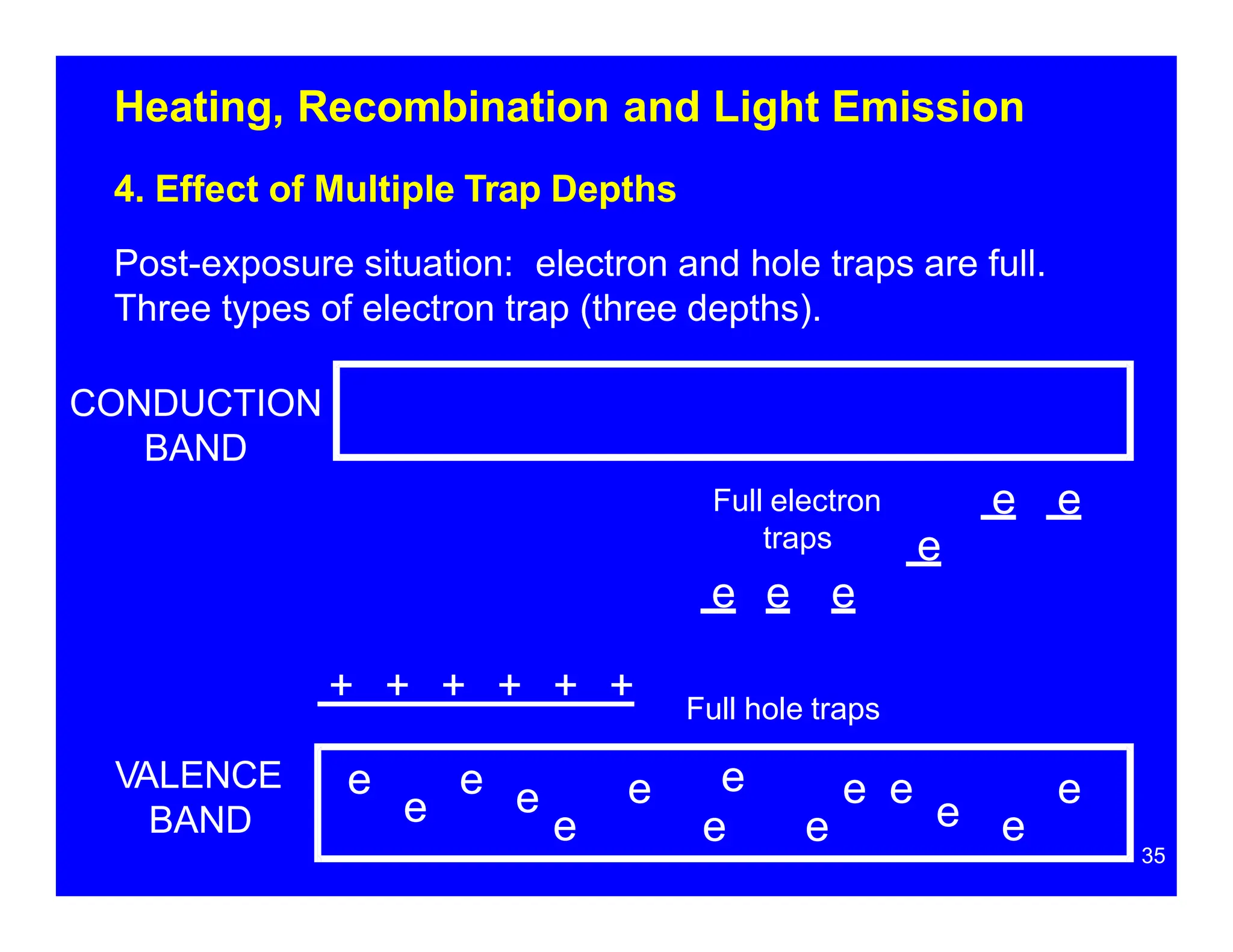
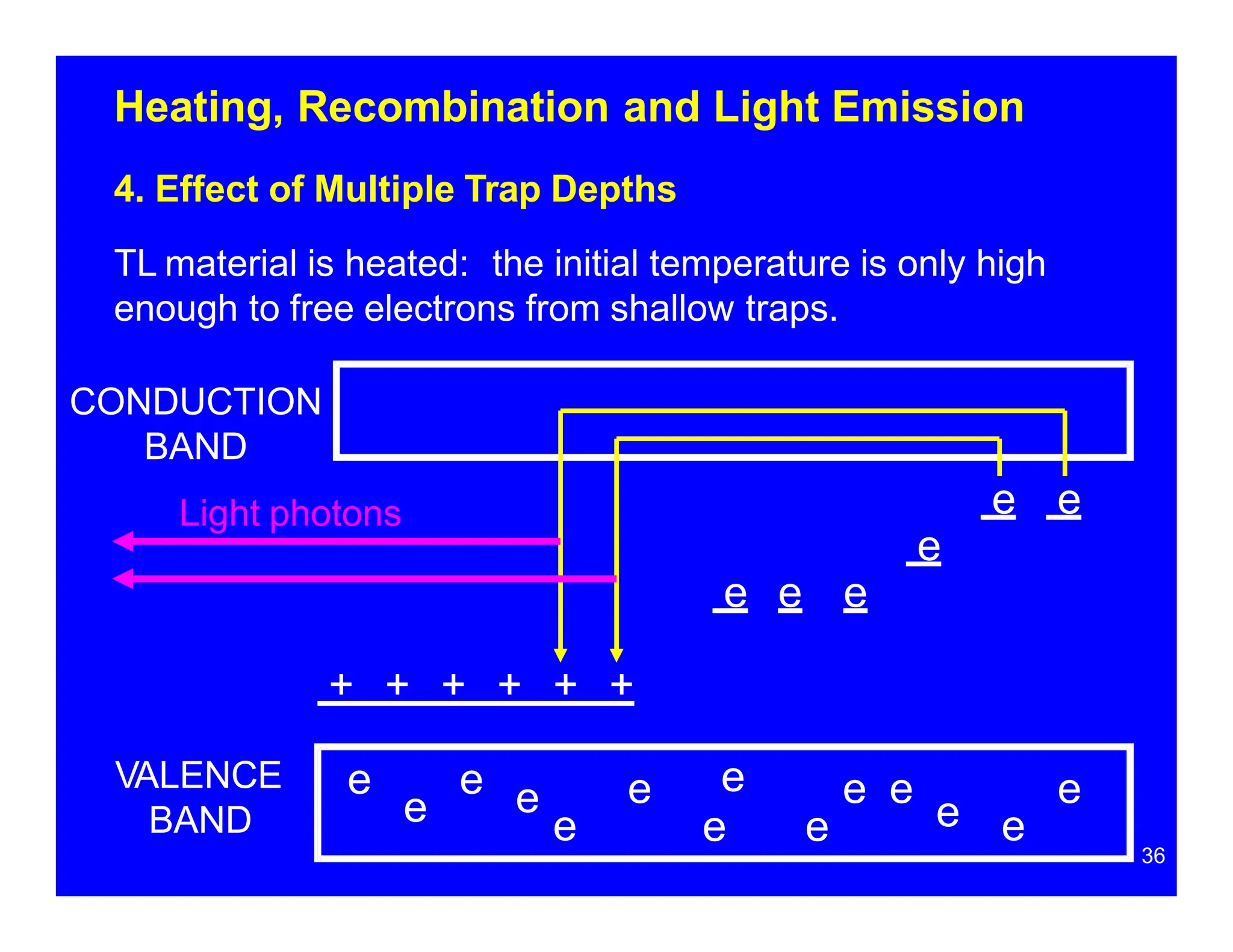
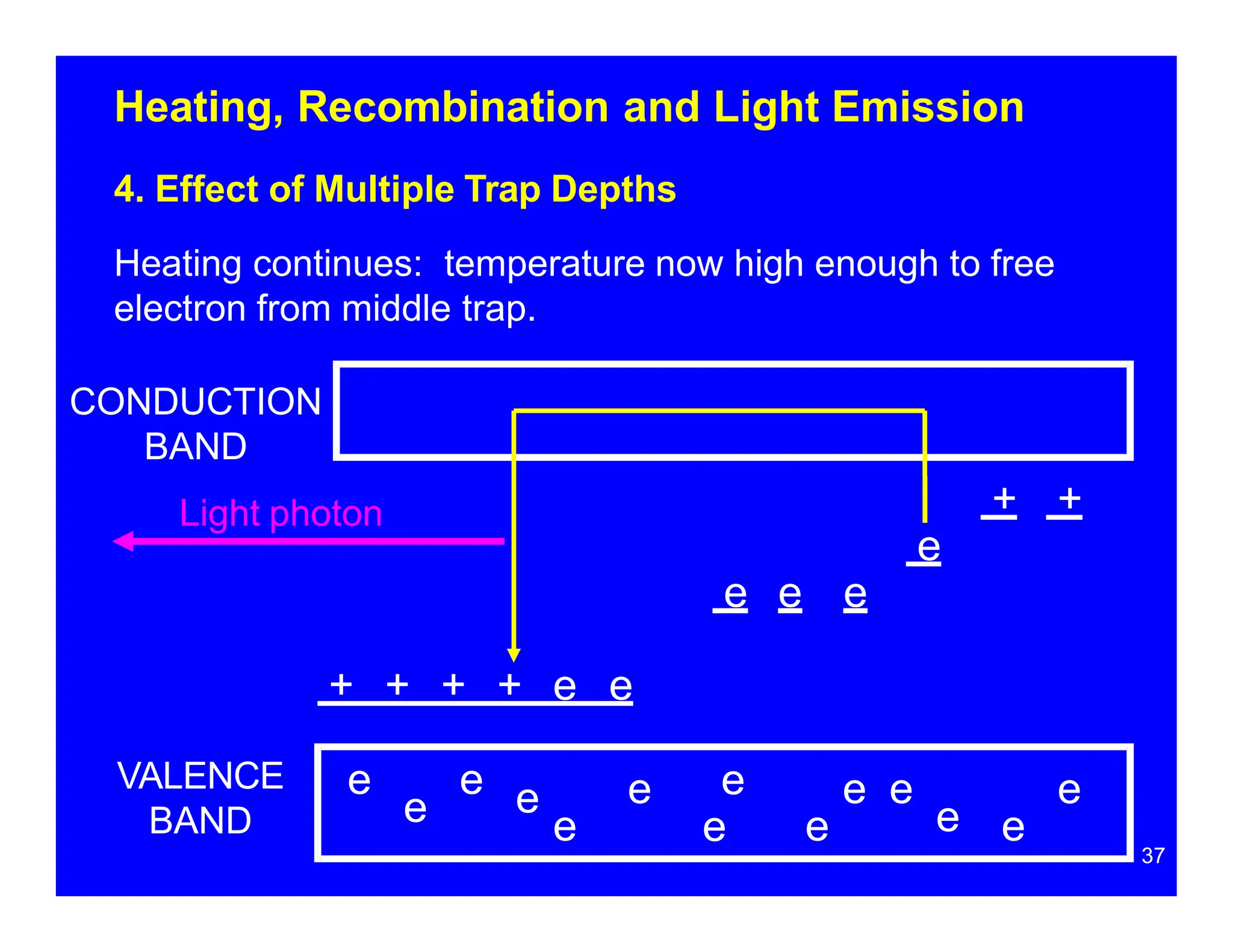
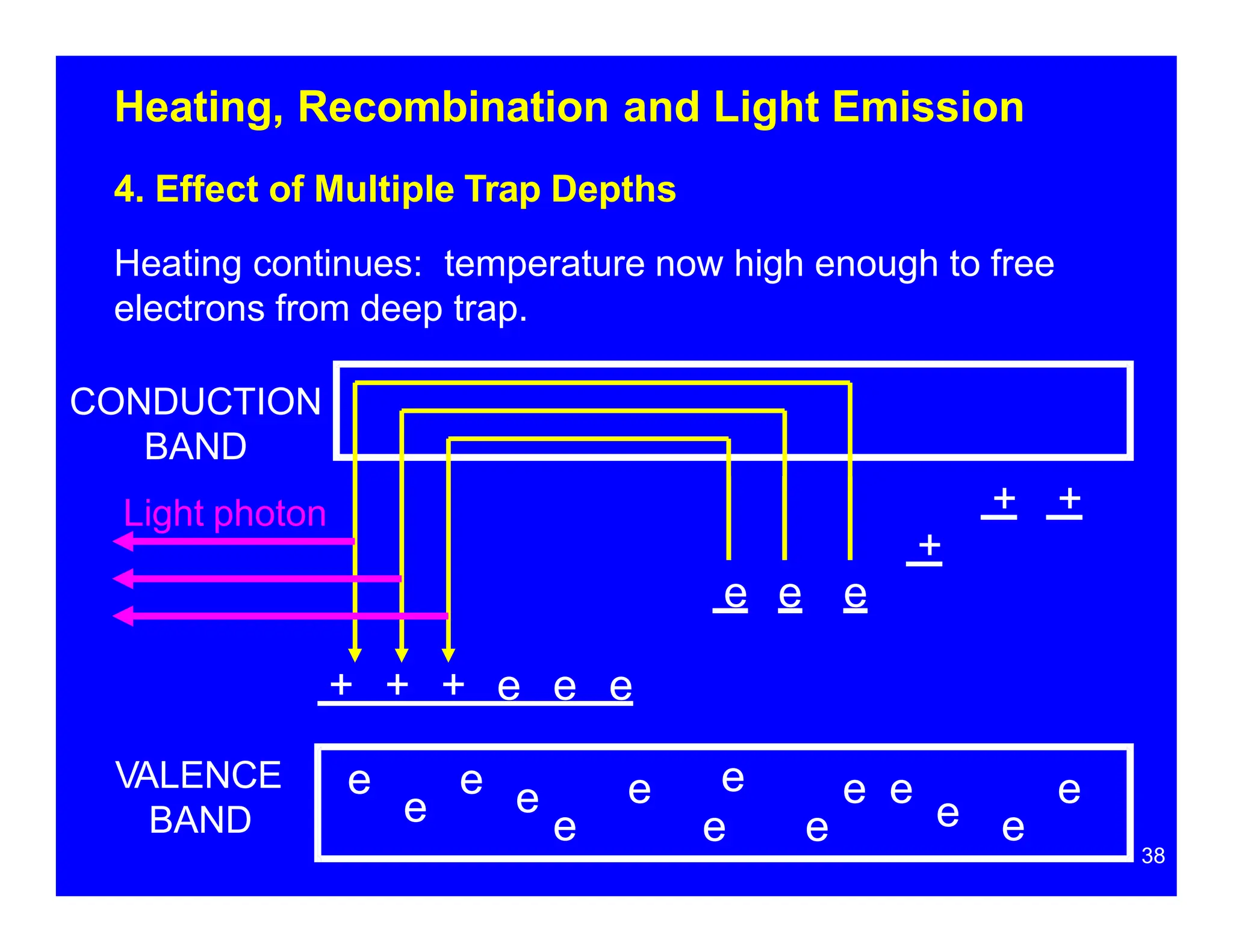
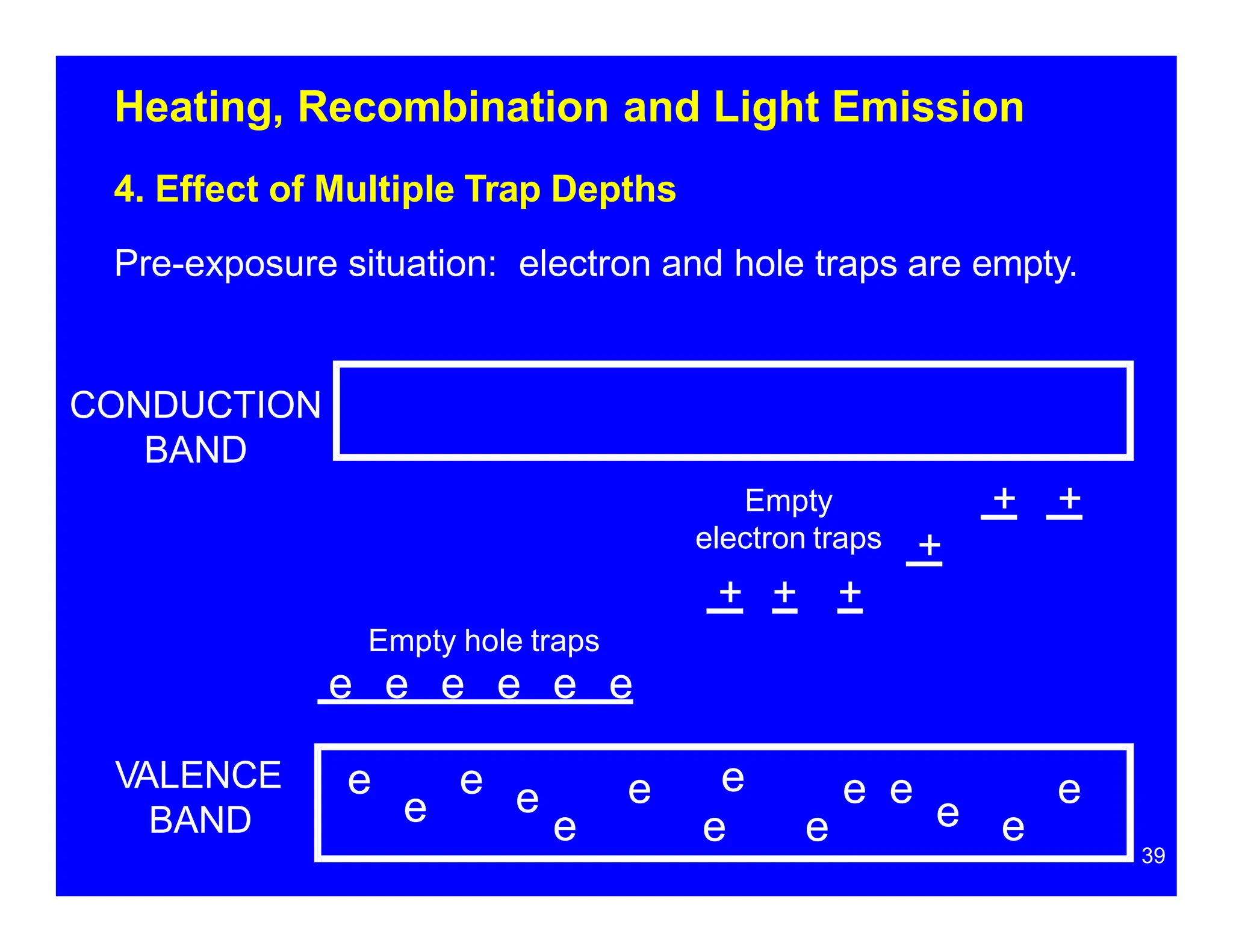
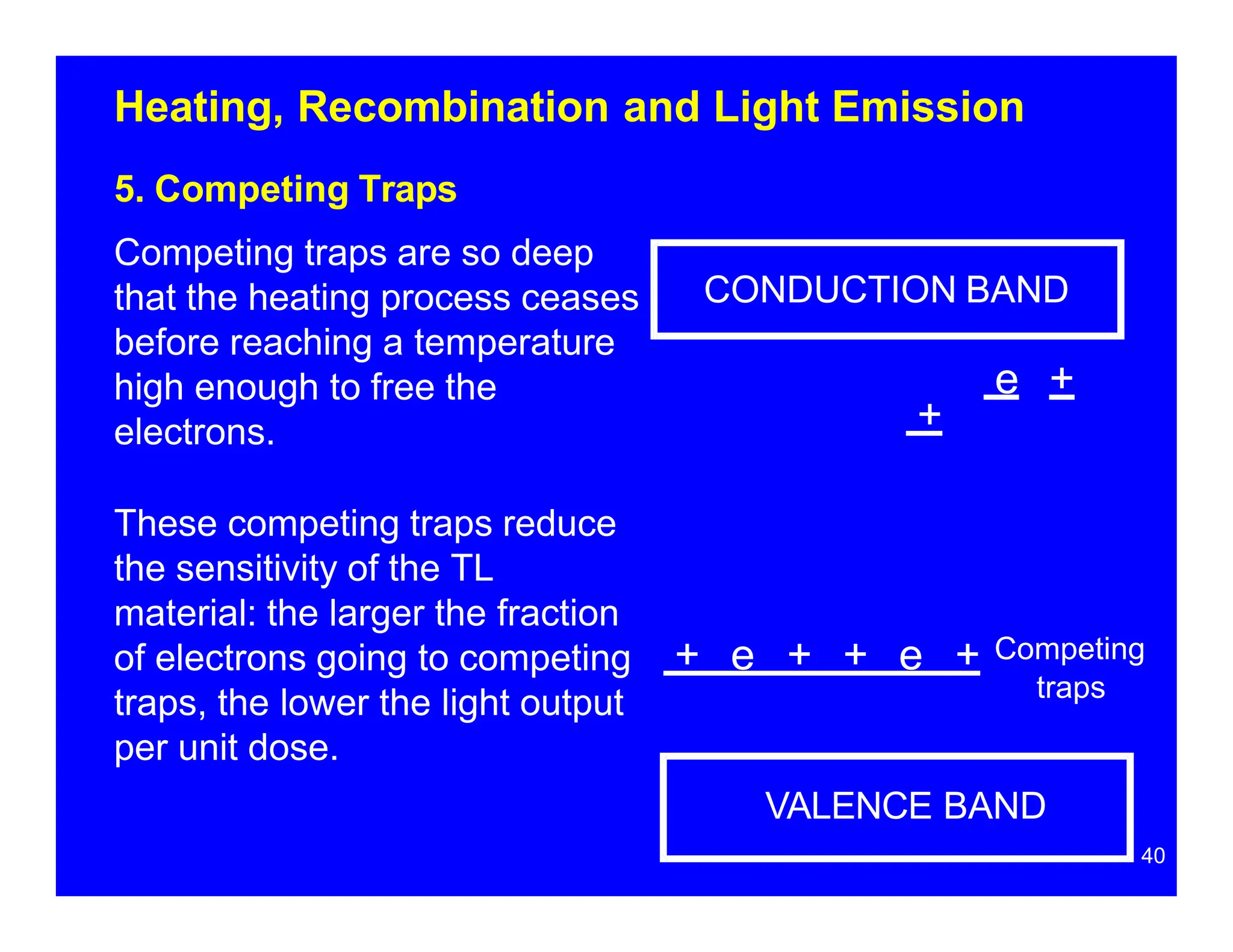
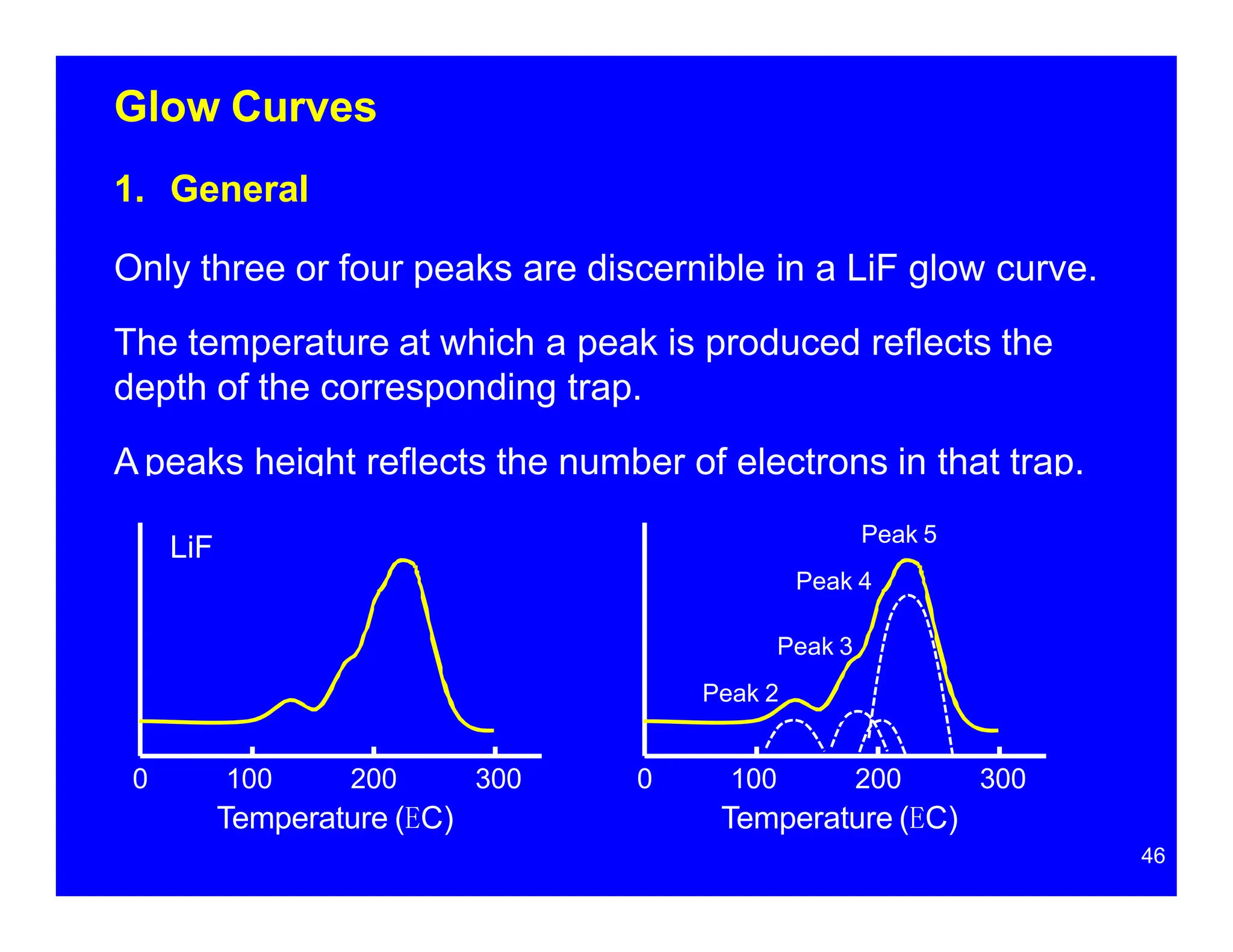
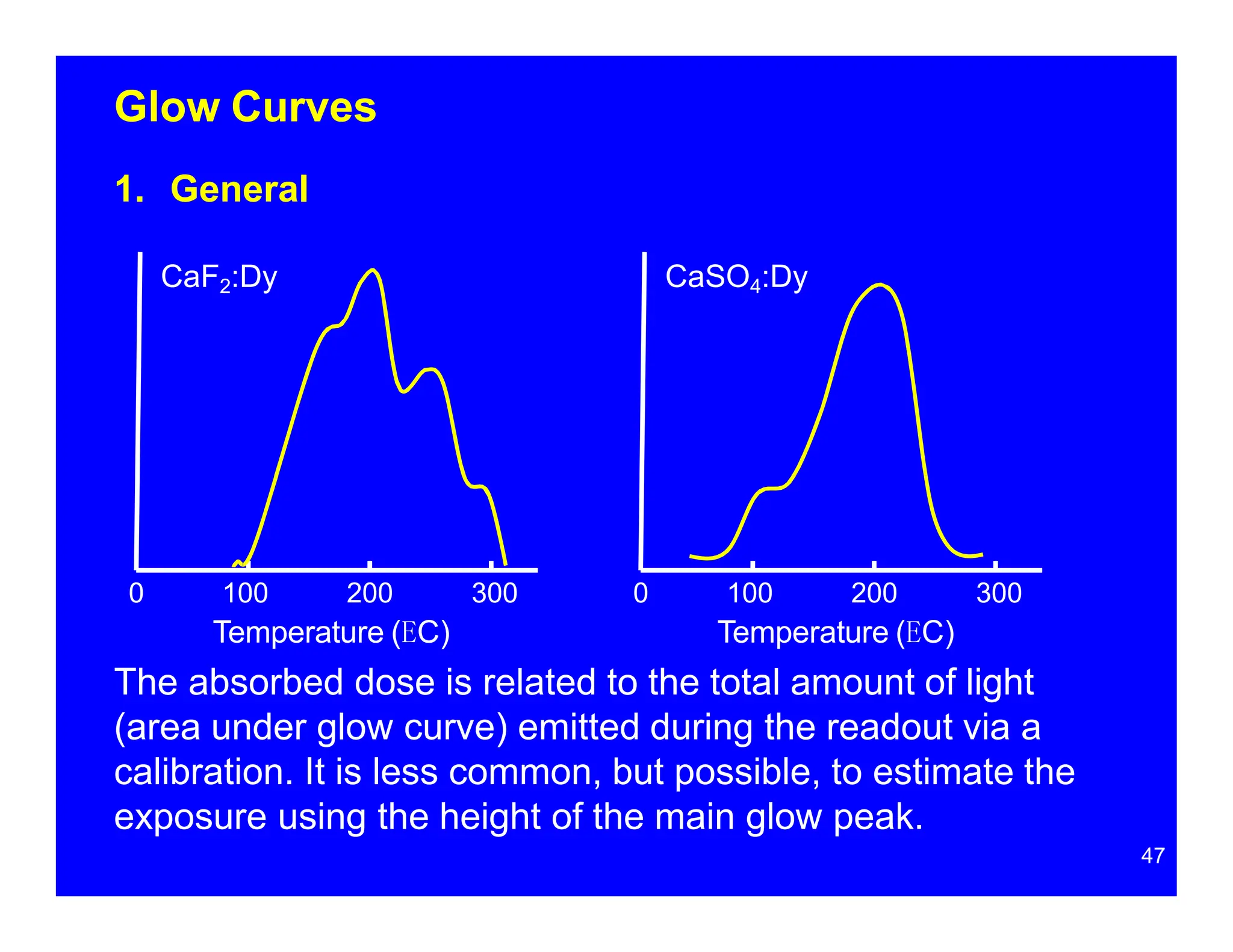
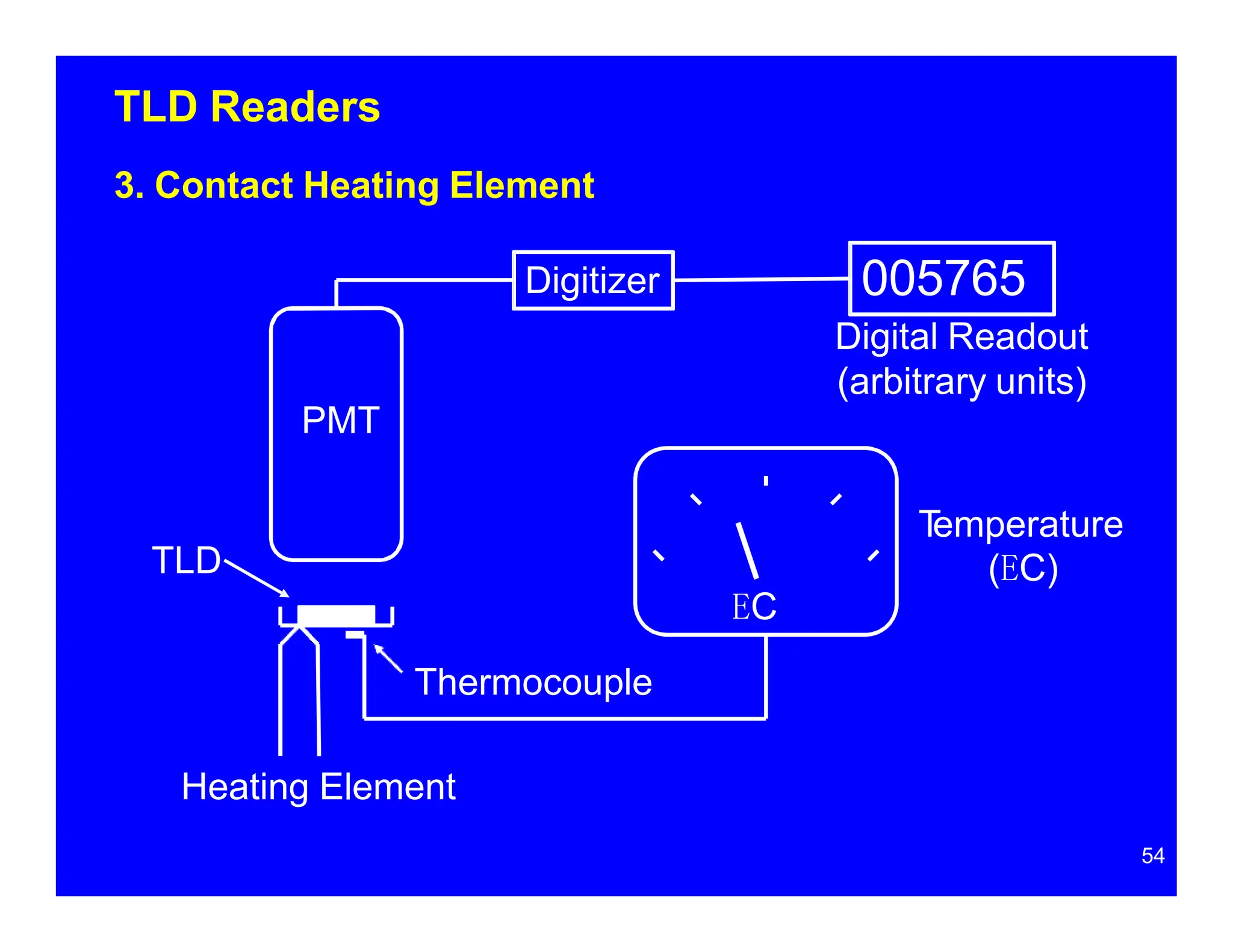
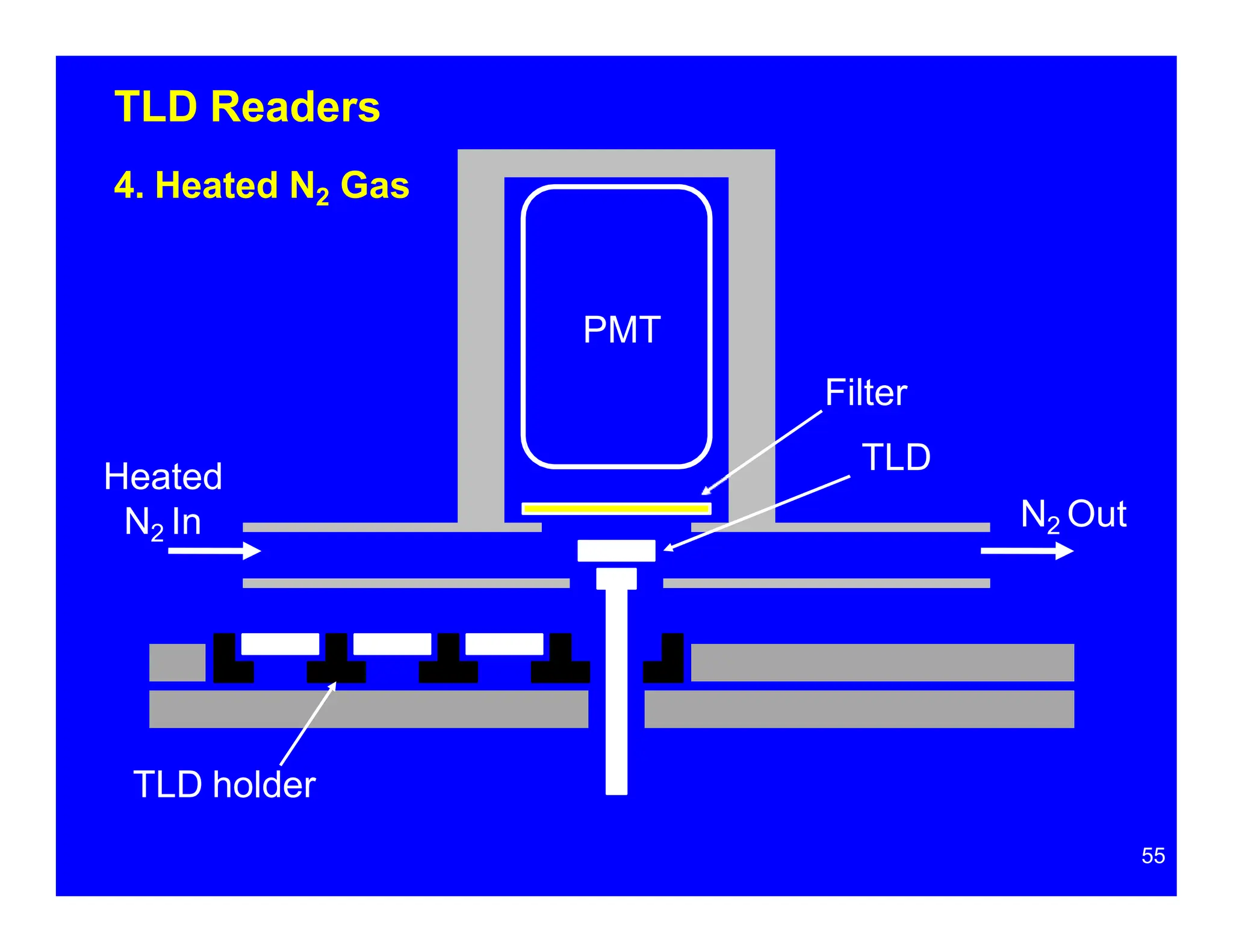
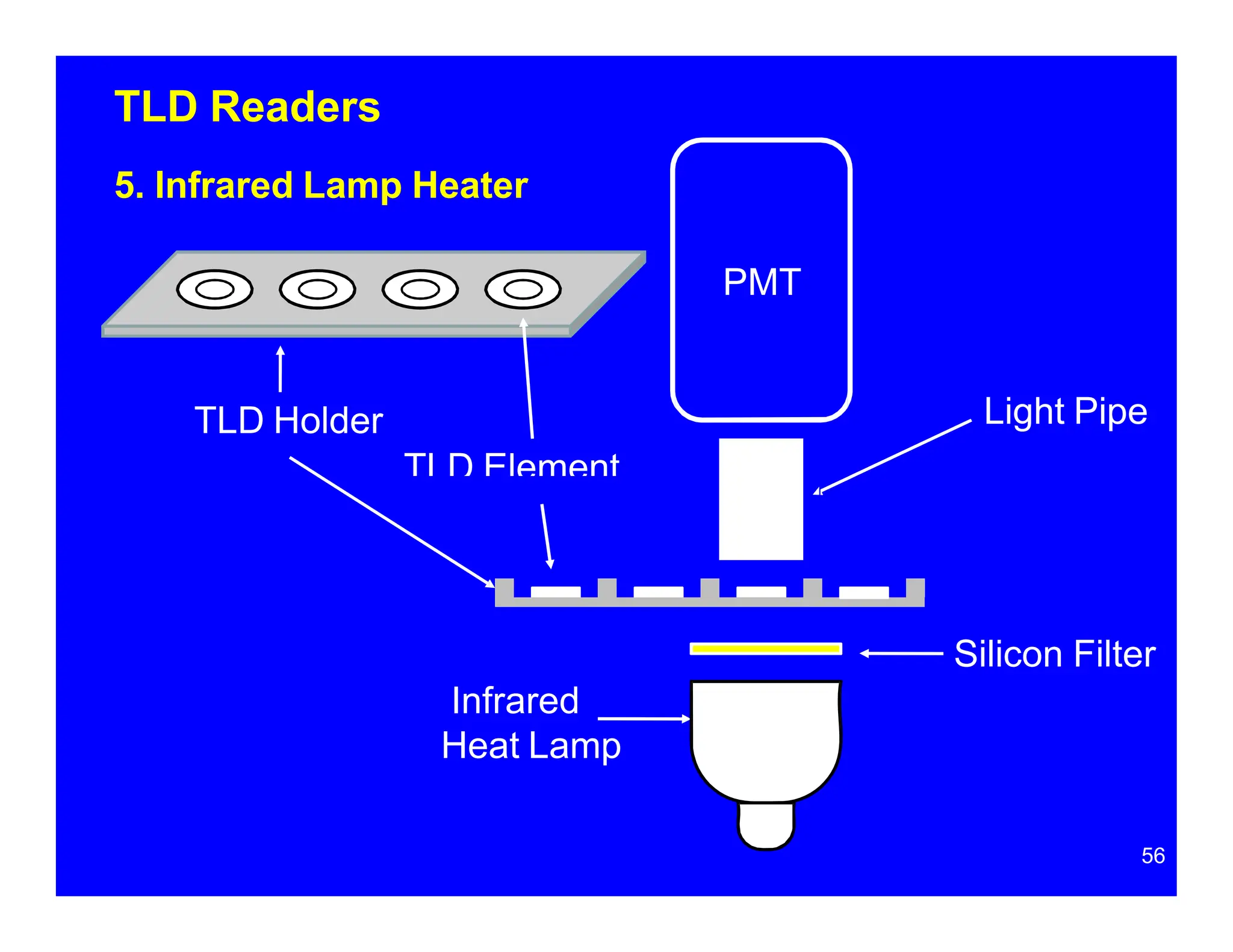
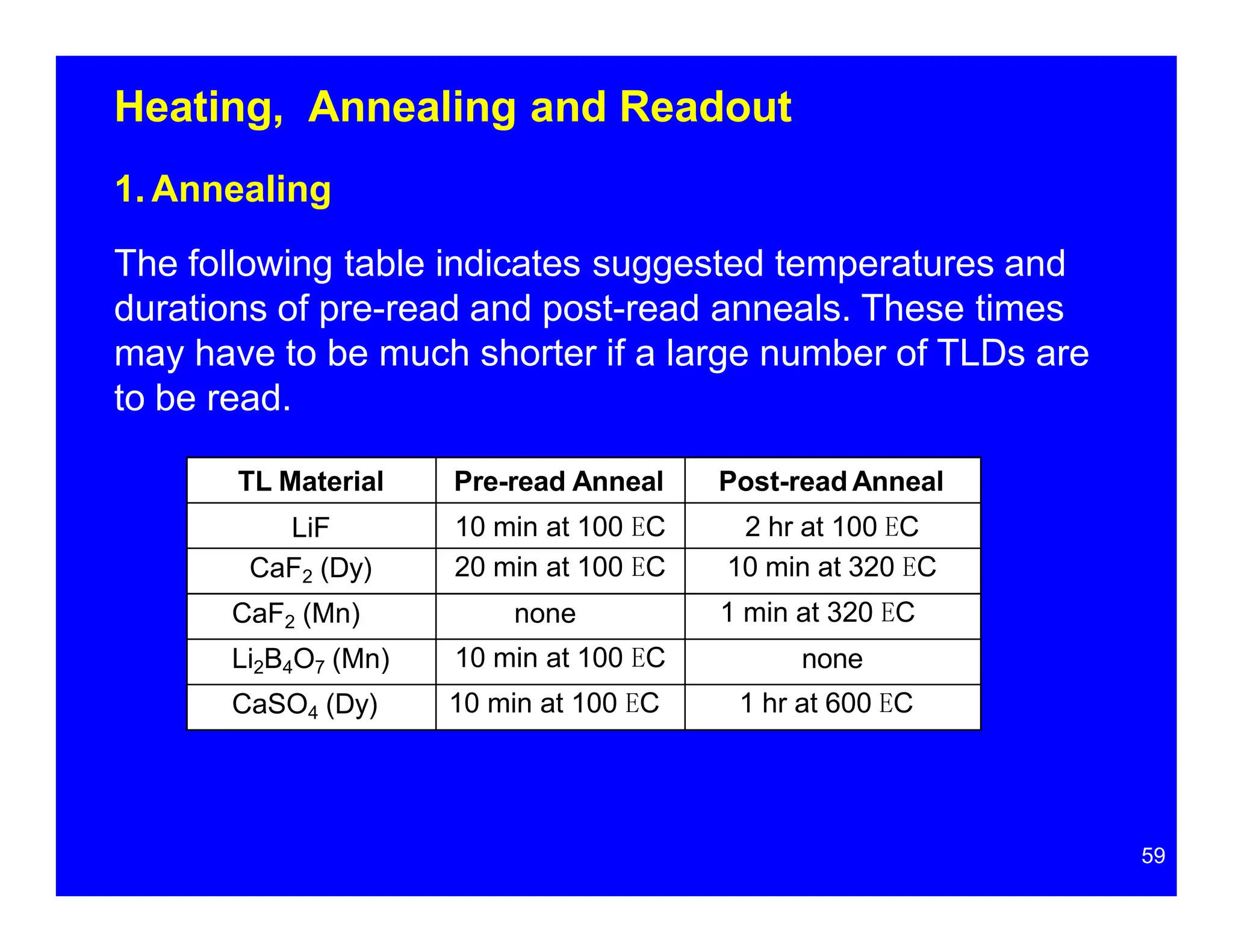
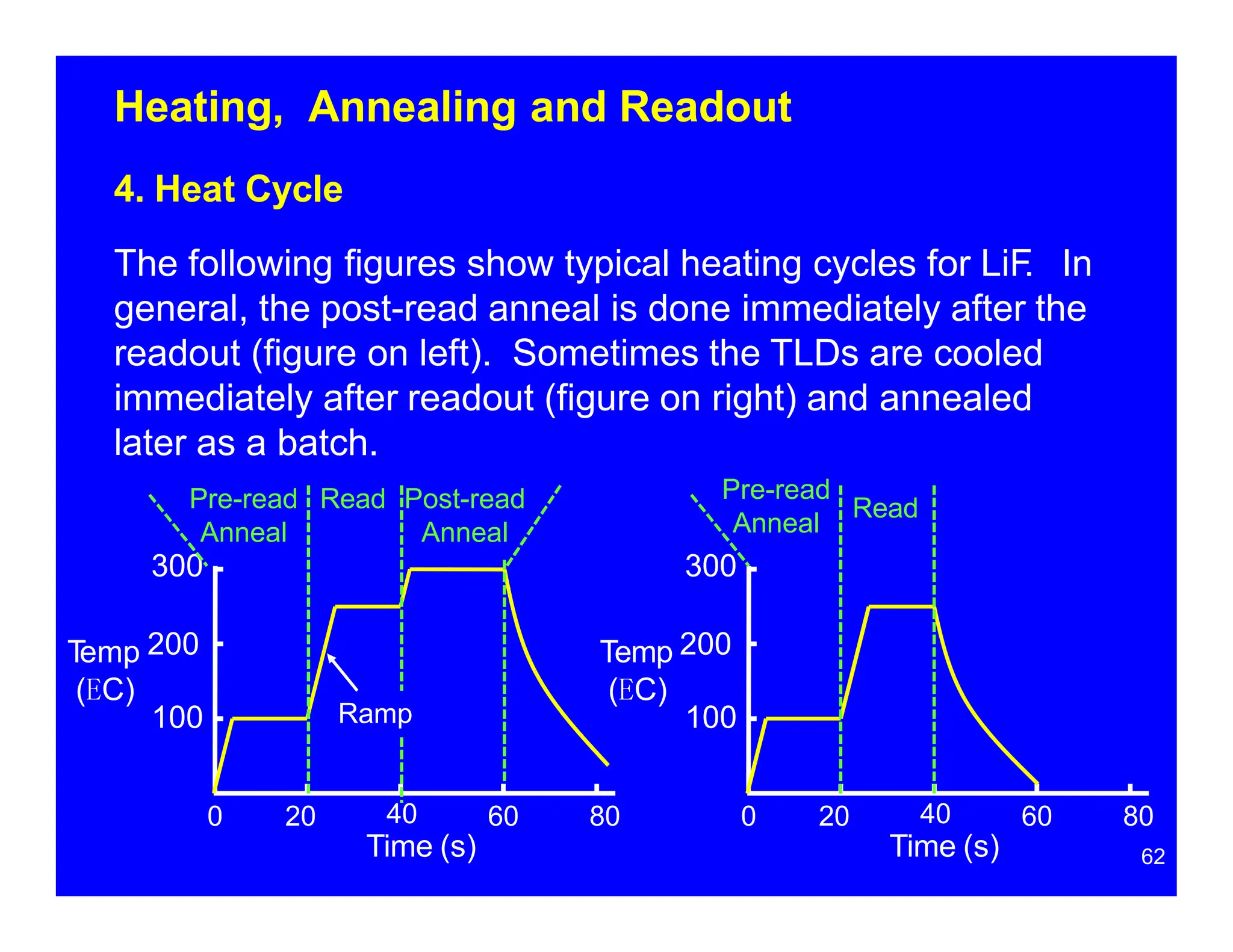
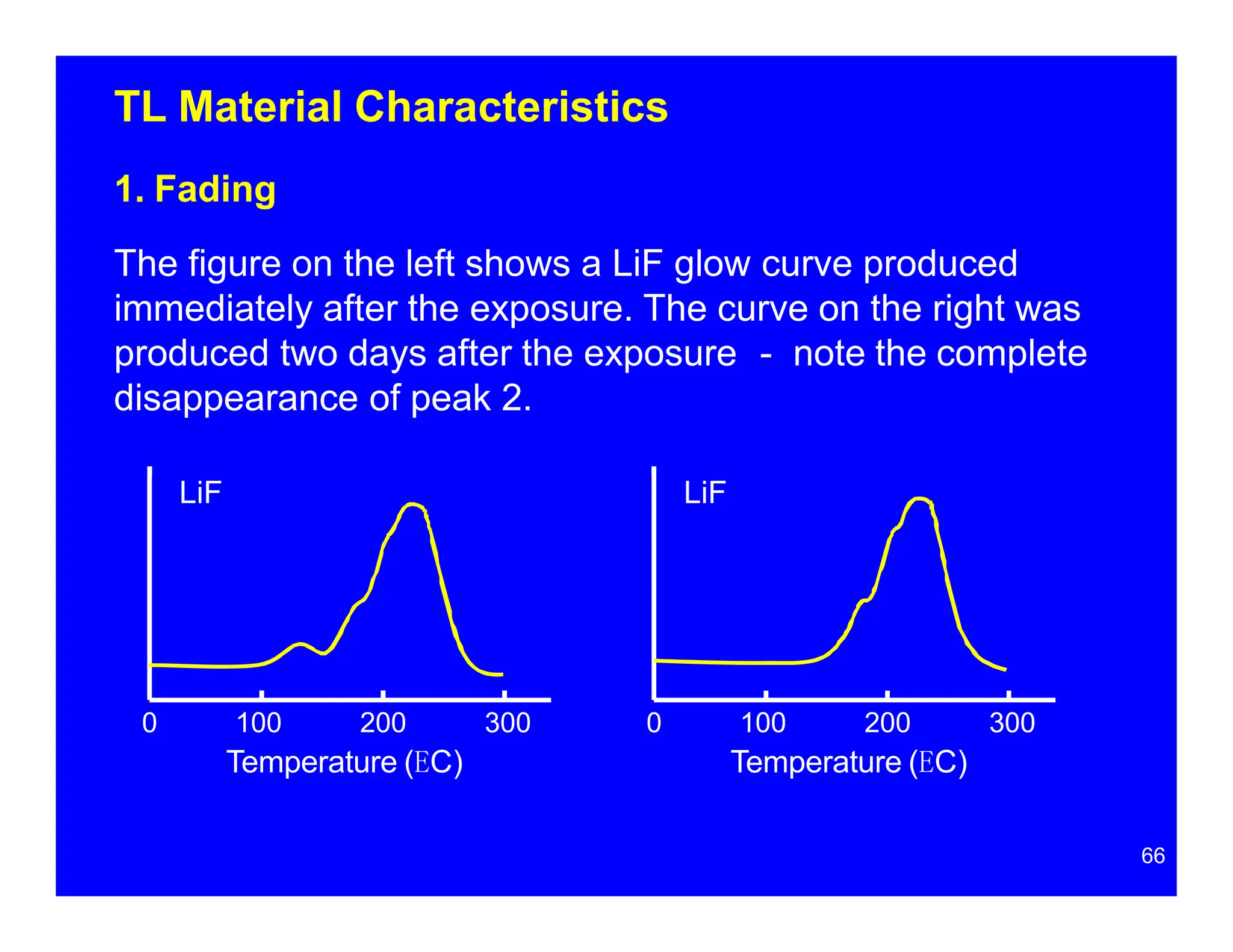
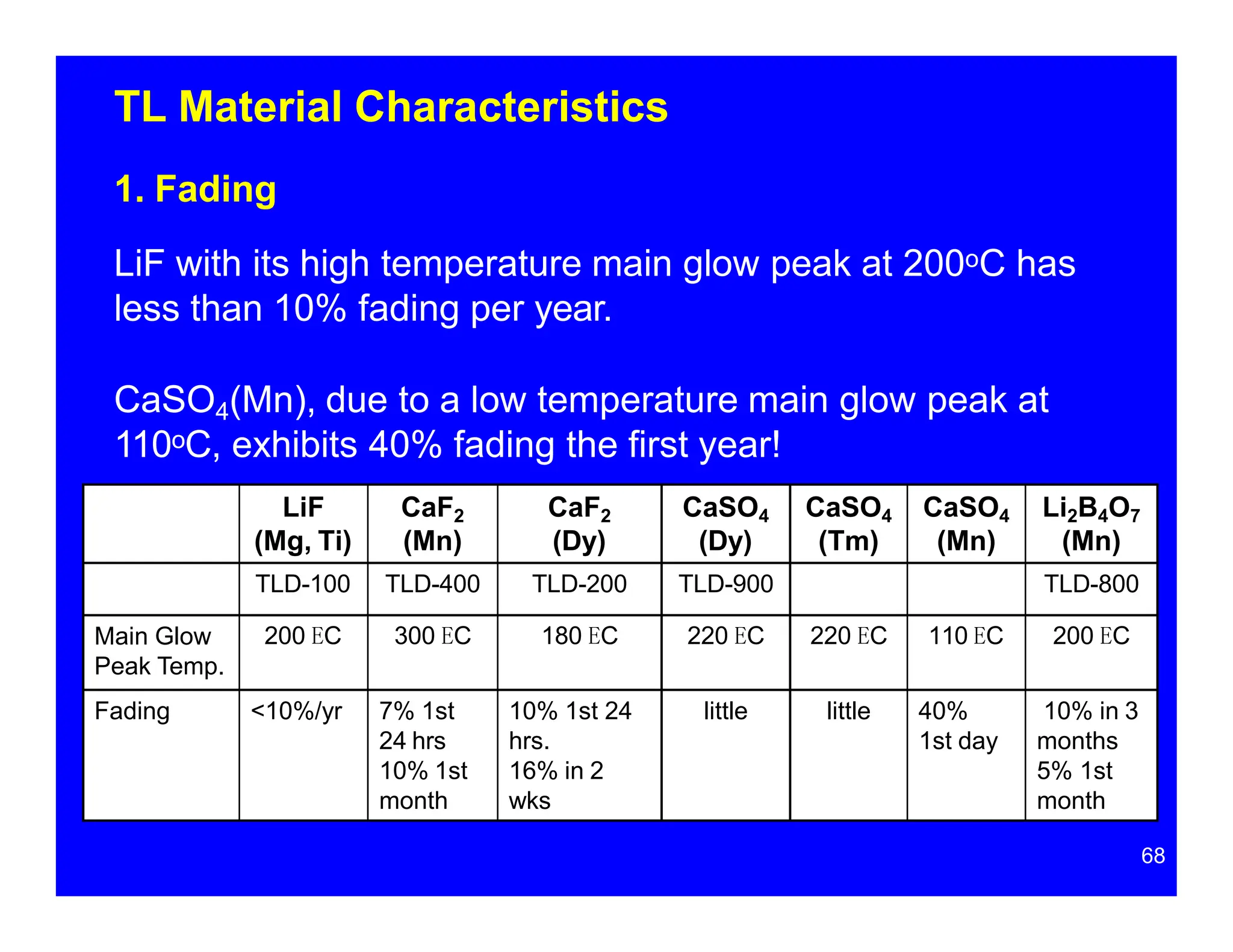
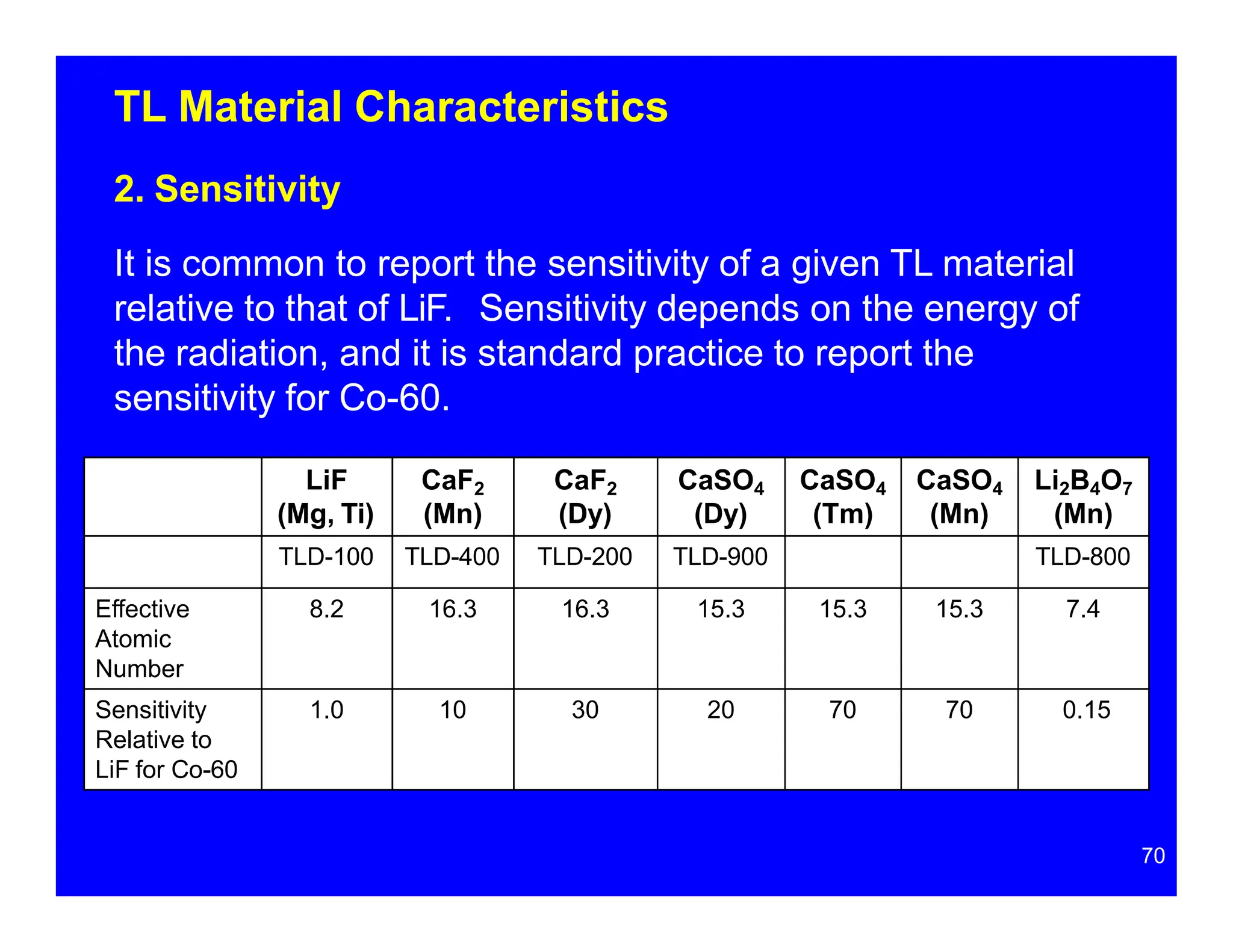
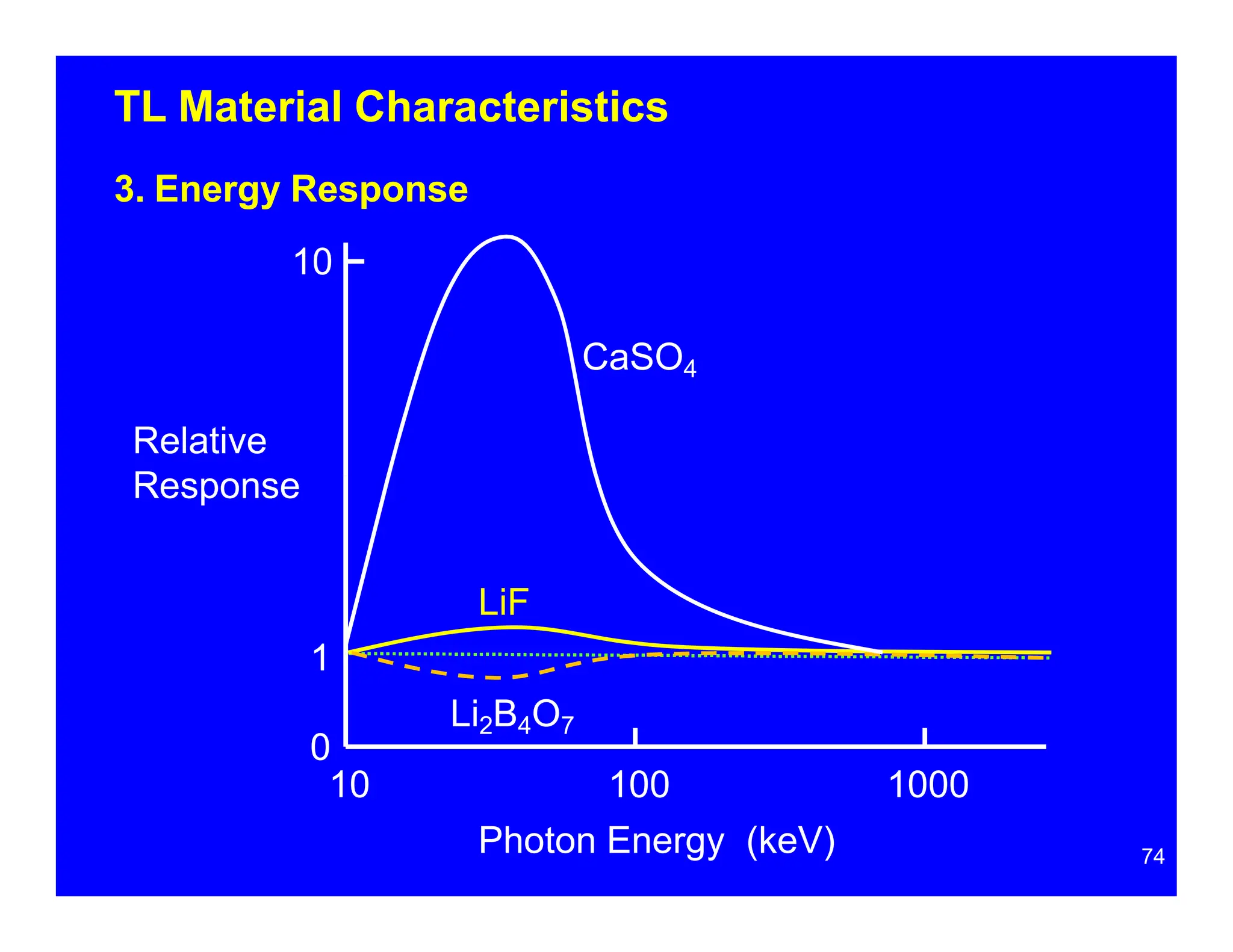
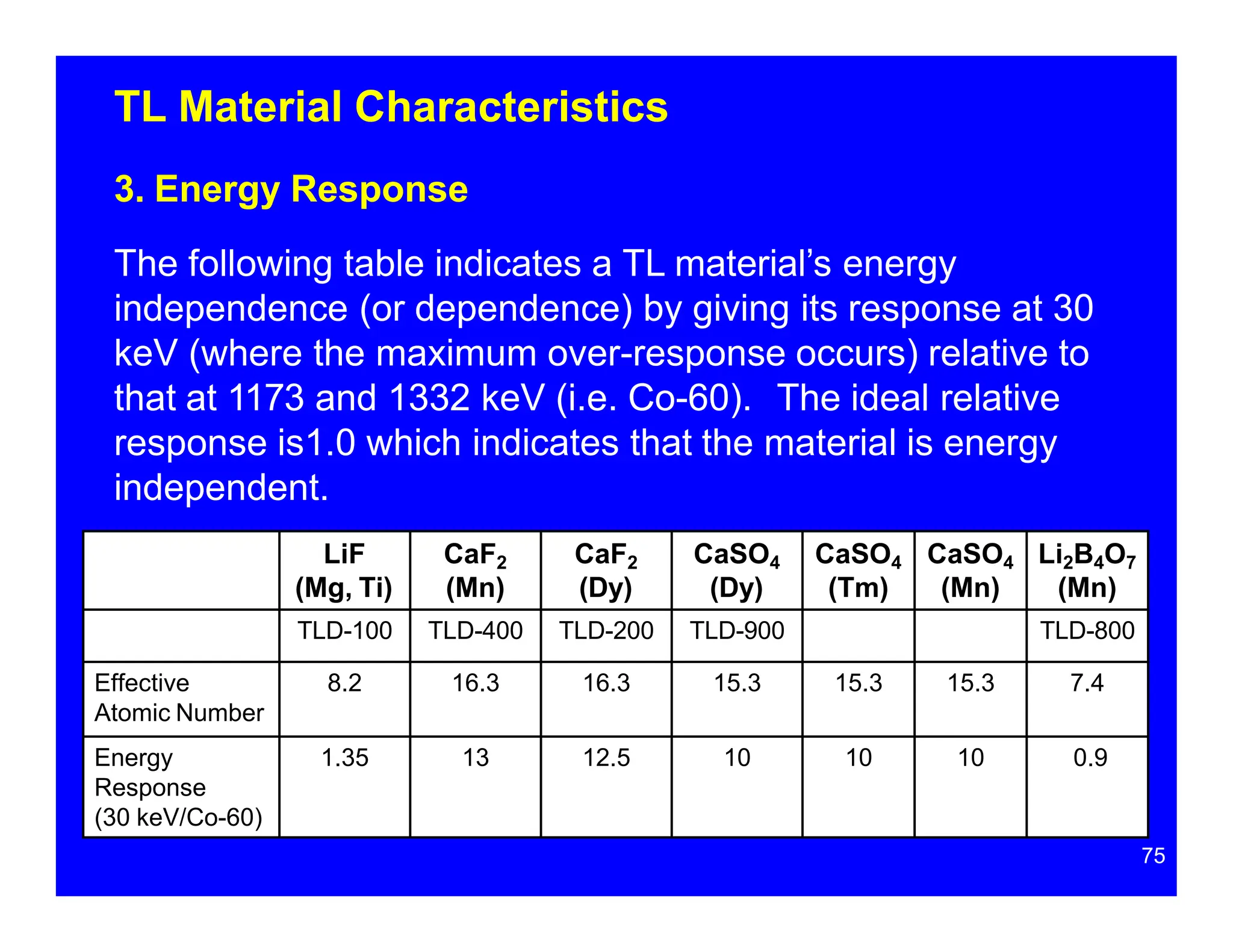
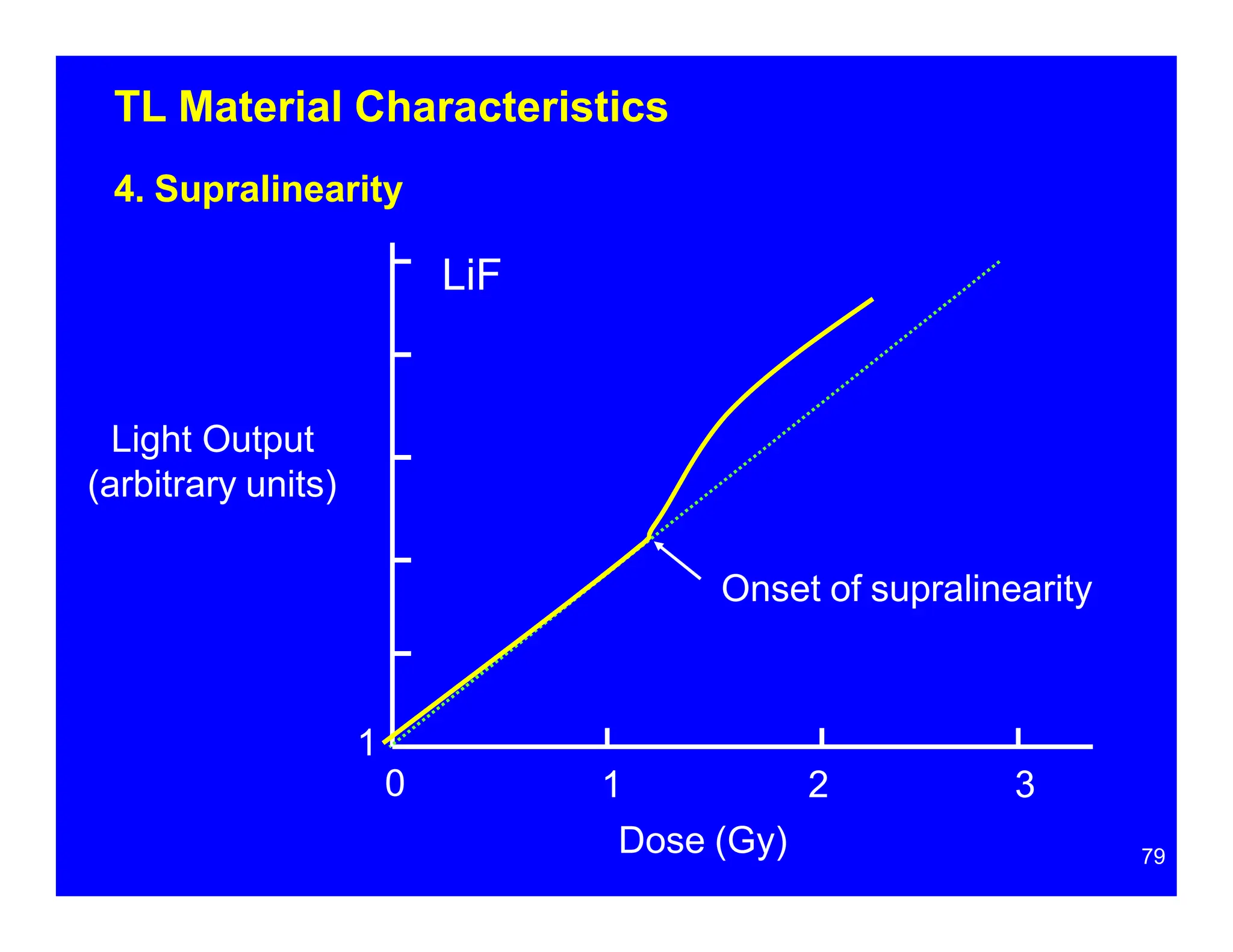
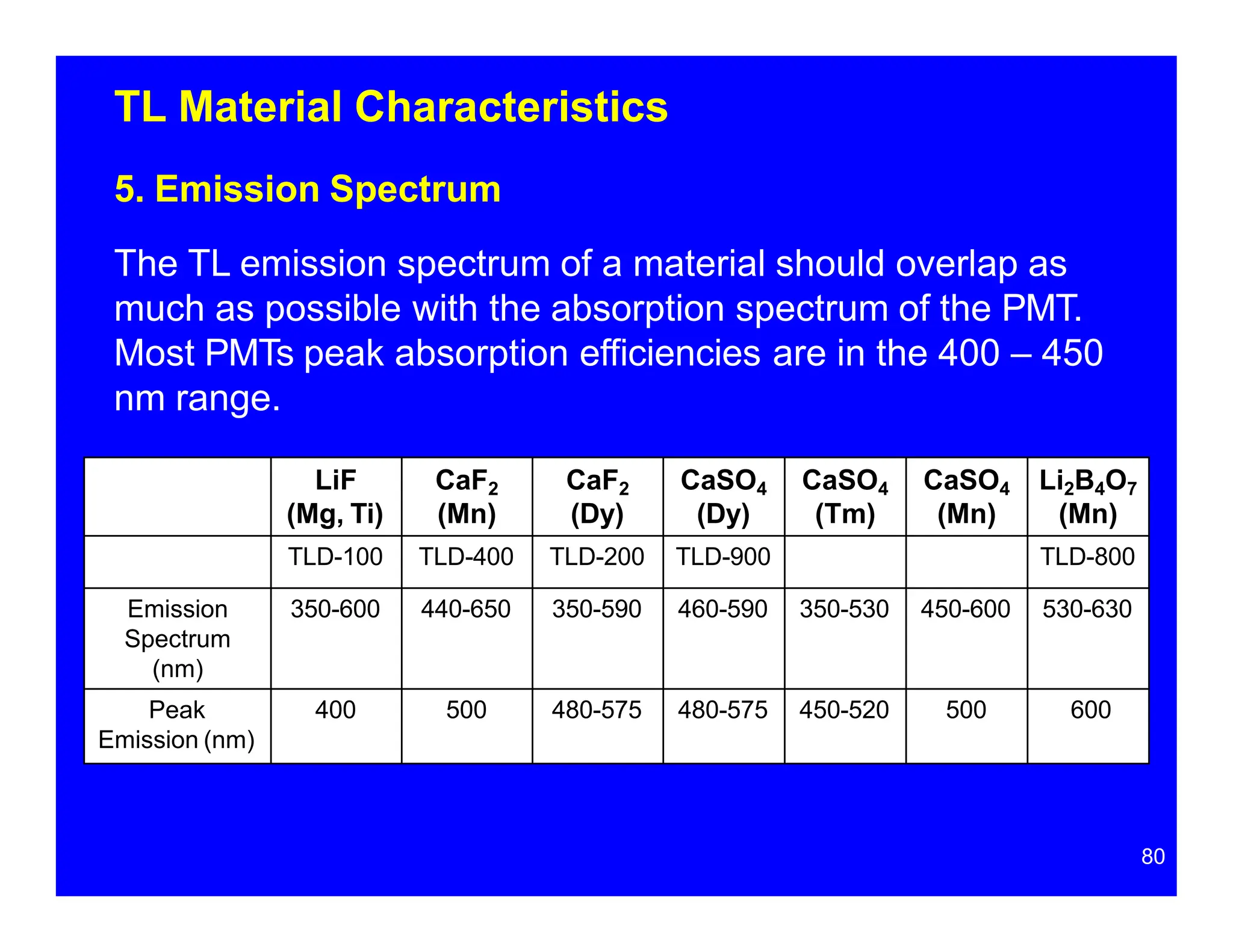
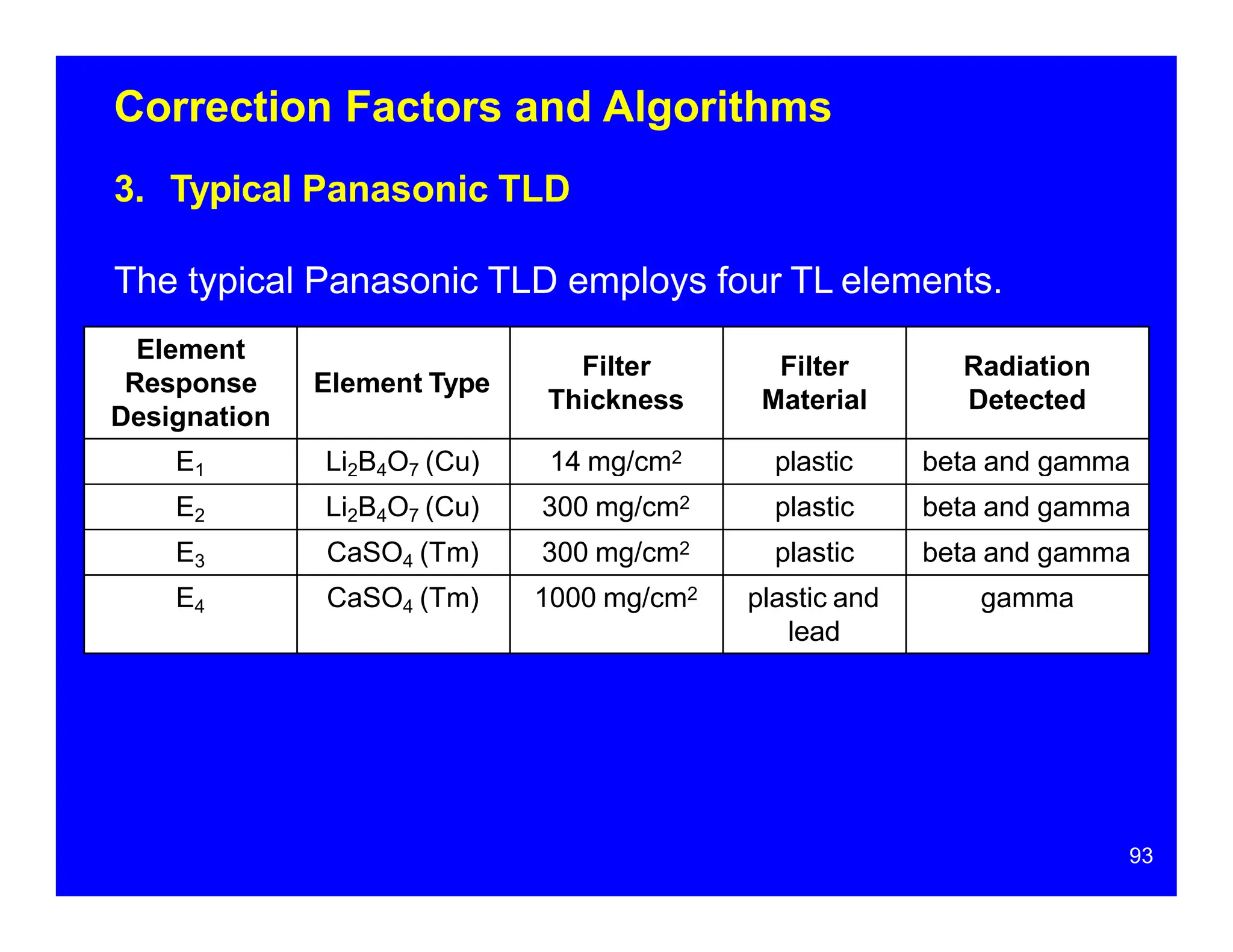
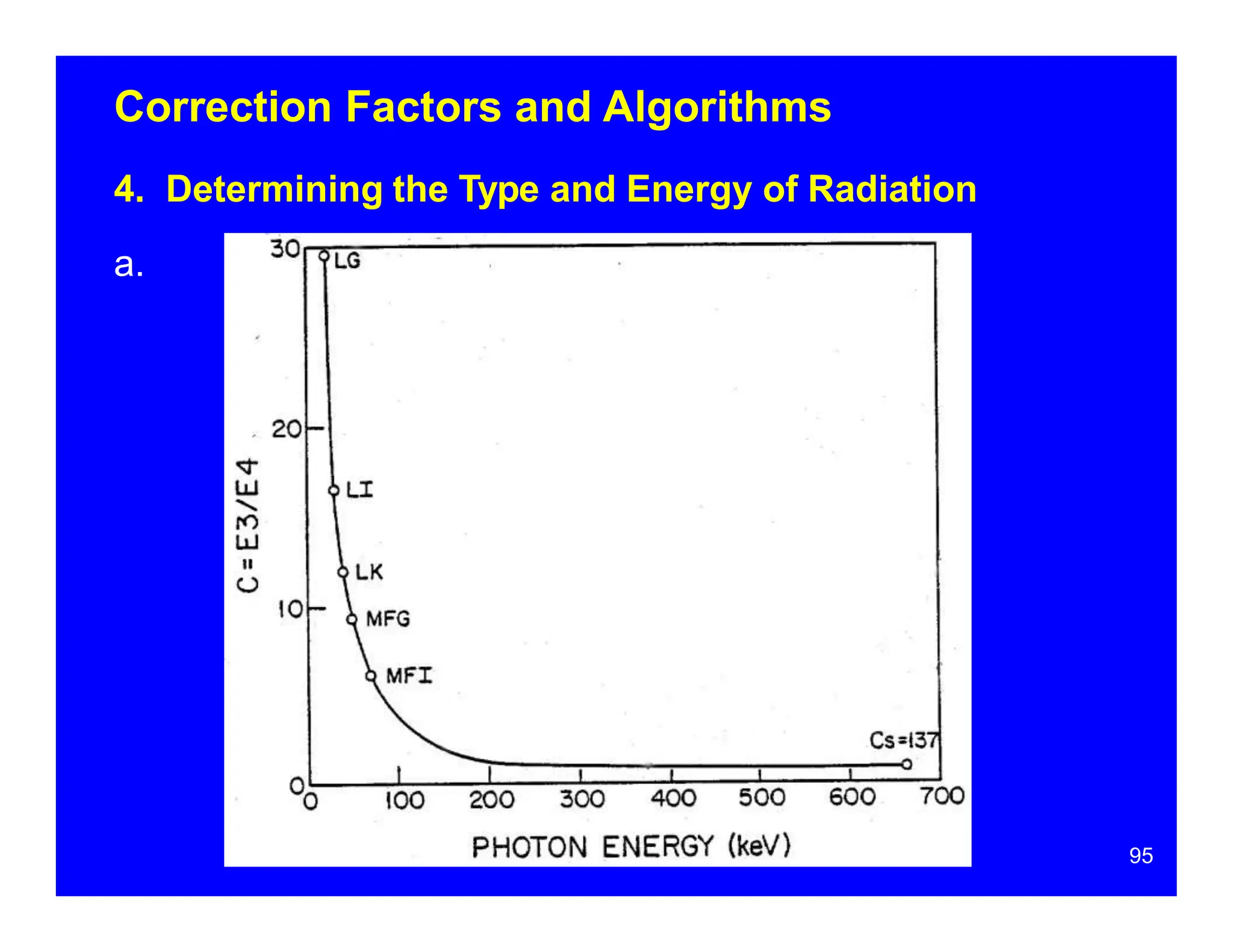
Thermoluminescent dosimeters (TLDs) contain materials that trap energy when exposed to ionizing radiation. Upon heating, the trapped energy is released as light emission. TLD readers heat the materials and measure the emitted light, producing a glow curve that reflects the absorbed radiation dose. The glow curve peaks correspond to electron traps of different depths within the material's band structure. Multiple trap depths and competing traps can affect the shape of the glow curve and the material's sensitivity.