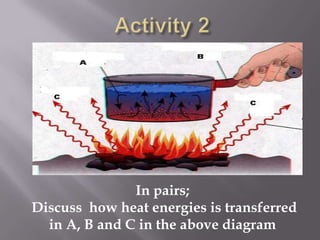
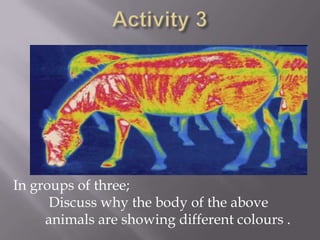
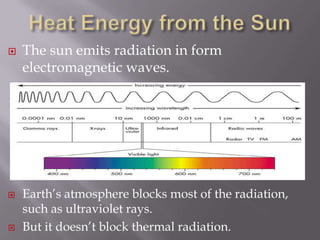
Thermal radiation and surface radiation are discussed. Every object emits thermal radiation depending on its temperature, with hotter objects emitting more radiation. Surfaces can emit and absorb radiation. Dull black surfaces are good absorbers and emitters of radiation, while shiny surfaces reduce absorption and emission, explaining why car radiators are black and thermal blankets have shiny exteriors. The greenhouse effect occurs when gases like carbon dioxide and methane in the atmosphere trap the Earth's outgoing infrared radiation, warming the planet's surface.