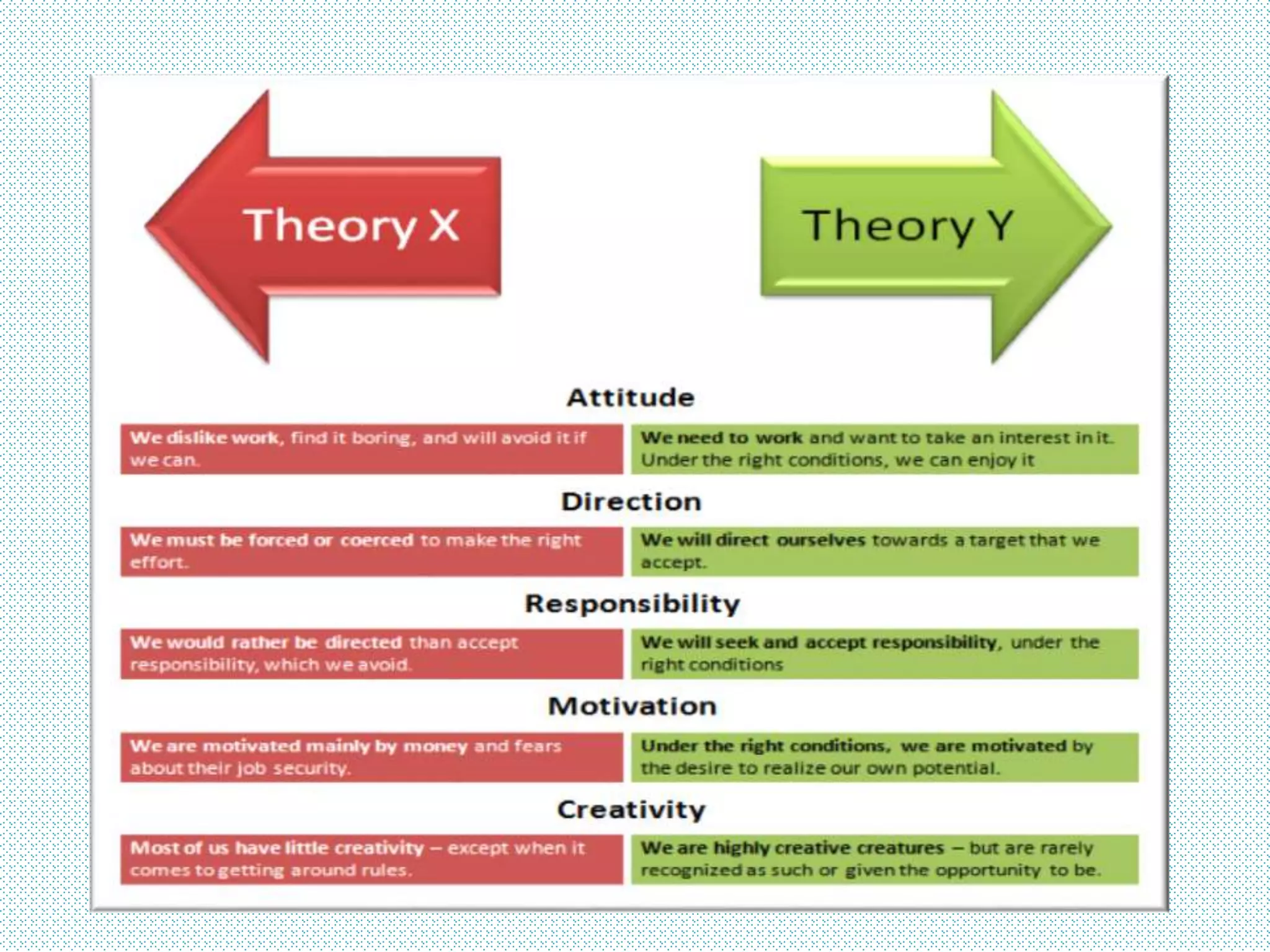
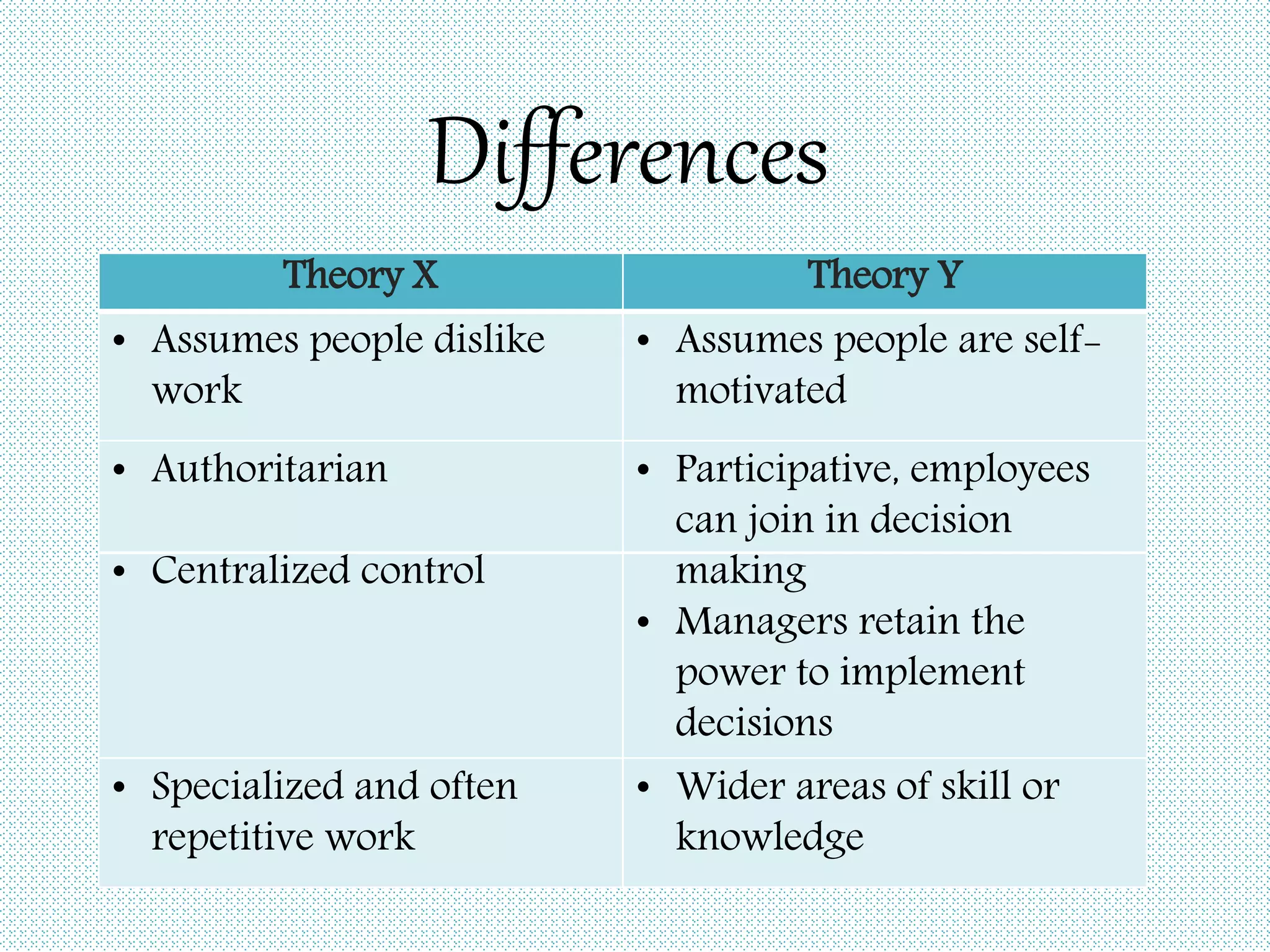
Douglas McGregor proposed two contrasting theories of human motivation and management in the 1960s: Theory X and Theory Y. Theory X assumes employees are unmotivated and dislike work, encouraging an authoritarian management style. Theory Y assumes employees are self-motivated and happy to work, promoting a participative and decentralized style of management that involves employees in decision making. While Theory X may be more applicable to large-scale production environments, Theory Y is considered superior and more widely adopted, especially for knowledge work and professional services.